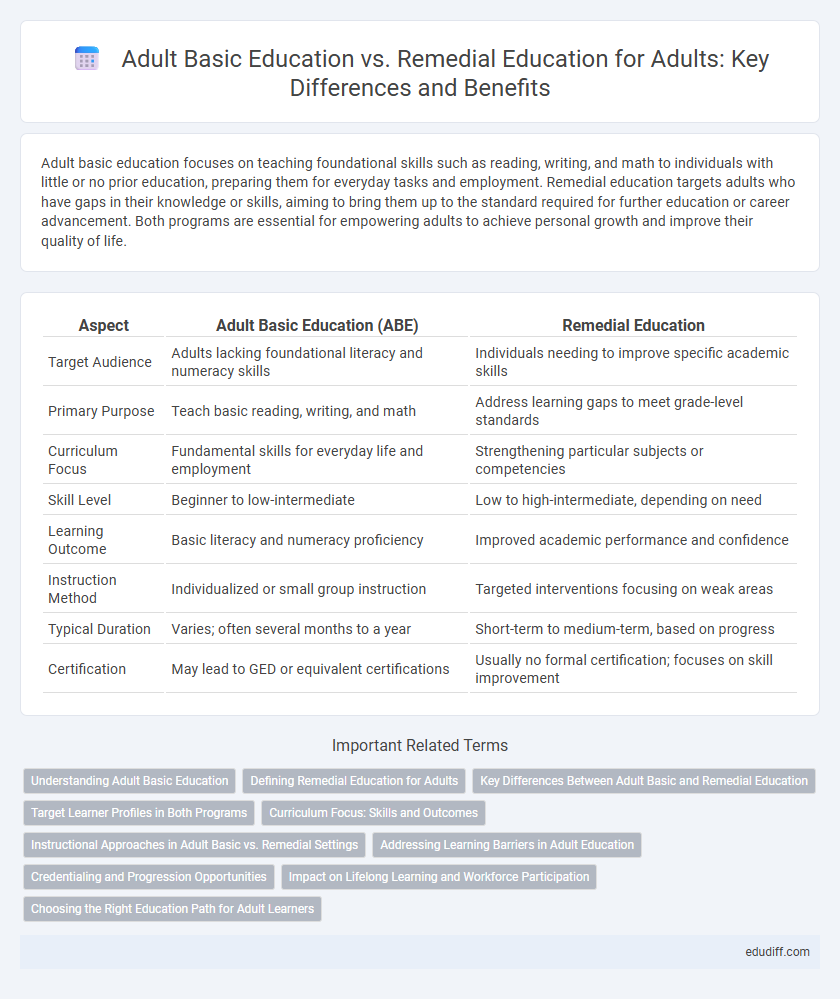
Adult basic education focuses on teaching foundational skills such as reading, writing, and math to individuals with little or no prior education, preparing them for everyday tasks and employment. Remedial education targets adults who have gaps in their knowledge or skills, aiming to bring them up to the standard required for further education or career advancement. Both programs are essential for empowering adults to achieve personal growth and improve their quality of life.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Adult Basic Education (ABE) | Remedial Education |
|---|---|---|
| Target Audience | Adults lacking foundational literacy and numeracy skills | Individuals needing to improve specific academic skills |
| Primary Purpose | Teach basic reading, writing, and math | Address learning gaps to meet grade-level standards |
| Curriculum Focus | Fundamental skills for everyday life and employment | Strengthening particular subjects or competencies |
| Skill Level | Beginner to low-intermediate | Low to high-intermediate, depending on need |
| Learning Outcome | Basic literacy and numeracy proficiency | Improved academic performance and confidence |
| Instruction Method | Individualized or small group instruction | Targeted interventions focusing on weak areas |
| Typical Duration | Varies; often several months to a year | Short-term to medium-term, based on progress |
| Certification | May lead to GED or equivalent certifications | Usually no formal certification; focuses on skill improvement |
Understanding Adult Basic Education
Adult Basic Education (ABE) focuses on foundational skills in reading, writing, and mathematics tailored for adults who have limited formal education, aiming to enhance their ability to function effectively in everyday life and the workplace. Unlike Remedial Education, which addresses specific academic deficiencies to bring learners up to grade level, ABE provides a broader curriculum designed to build essential literacy and numeracy skills from the ground up. Understanding the scope of ABE is crucial for developing programs that support adult learners in achieving independence, employment readiness, and further educational opportunities.
Defining Remedial Education for Adults
Remedial education for adults targets individuals lacking foundational skills in literacy, numeracy, or other core competencies necessary for everyday functioning and employment. It is designed to bridge gaps in knowledge caused by interrupted or ineffective prior education, providing tailored instruction that meets each learner's specific needs. Unlike adult basic education, which offers general skill development, remedial education focuses intensely on overcoming particular academic deficiencies to ensure learners achieve a minimum standard of proficiency.
Key Differences Between Adult Basic and Remedial Education
Adult Basic Education (ABE) focuses on foundational skills such as reading, writing, and arithmetic for adults lacking basic literacy or numeracy, while Remedial Education targets learners who have encountered academic deficiencies and need targeted support to meet grade-level standards. ABE programs are designed to elevate learners to functional literacy and life skills competency, whereas Remedial Education emphasizes overcoming specific academic gaps to facilitate success in subsequent educational courses. Both serve adult learners but differ in scope, objectives, and instructional strategies tailored to distinct educational needs.
Target Learner Profiles in Both Programs
Adult basic education targets learners acquiring foundational skills such as literacy, numeracy, and everyday problem-solving, often catering to individuals with limited formal education or those reentering the educational system after a long gap. Remedial education, in contrast, focuses on adults who have gaps or deficiencies in specific subject areas, aiming to elevate their competencies to meet standard academic or occupational requirements. Both programs prioritize personalized learning plans but differ in learner profiles, with basic education serving beginners and remedial education addressing targeted skill deficits.
Curriculum Focus: Skills and Outcomes
Adult basic education emphasizes foundational literacy, numeracy, and everyday life skills to enable learners to function effectively in daily tasks and employment. Remedial education targets specific academic gaps by reinforcing previously learned concepts, focusing on skill mastery and improving performance to meet standard educational benchmarks. Both curricula prioritize measurable outcomes but differ in scope, with adult basic education providing broader life and work skills, while remedial education concentrates on correcting deficiencies in core academic areas.
Instructional Approaches in Adult Basic vs. Remedial Settings
Instructional approaches in adult basic education emphasize foundational skill-building using learner-centered methods, incorporating real-life contexts to enhance literacy and numeracy. In contrast, remedial education targets specific gaps in knowledge or skills through diagnostic assessments and tailored interventions that reinforce prior learning. Both settings prioritize scaffolding and differentiated instruction but differ in intensity and focus based on learners' proficiency levels.
Addressing Learning Barriers in Adult Education
Adult basic education targets foundational skills such as literacy, numeracy, and everyday problem-solving to enable learners to meet personal and workplace demands. Remedial education focuses specifically on overcoming gaps and deficiencies from prior education, addressing cognitive or skill-based barriers that impede progress. Both approaches are essential in adult education to dismantle learning obstacles and promote lifelong skill acquisition and empowerment.
Credentialing and Progression Opportunities
Adult basic education focuses on foundational skills such as literacy and numeracy, enabling learners to obtain high school equivalency credentials that open pathways to employment and further education. Remedial education targets specific academic gaps to improve competency in subjects like math and English, often serving as a prerequisite for enrolling in college-level courses. Credentialing through adult basic education typically leads to recognized certifications, while remedial education supports progression by preparing adults for successful completion of advanced programs.
Impact on Lifelong Learning and Workforce Participation
Adult basic education builds foundational skills in literacy, numeracy, and digital competencies, directly enhancing lifelong learning capabilities and increasing employability in a rapidly evolving job market. Remedial education targets specific gaps in knowledge, enabling adults to meet educational standards crucial for career advancement and adapting to new workforce demands. Both education types play pivotal roles in fostering continuous skill development and improving workforce participation rates among adult learners.
Choosing the Right Education Path for Adult Learners
Adult basic education provides foundational skills in literacy, numeracy, and essential knowledge for everyday functioning, while remedial education targets specific academic deficits to help learners meet standard educational benchmarks. Choosing the right education path depends on assessing individual skill gaps and learning goals, ensuring the program aligns with career aspirations or personal development needs. Tailored assessment tools and learner-centered approaches enhance the effectiveness of both educational tracks for adult learners.
Adult basic education vs Remedial education Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com