Problem-based learning engages adult pet owners by addressing real-life challenges in pet care, promoting critical thinking and practical solutions tailored to individual animals. Content-based learning provides structured information on pet health and behavior but may lack the interactive element necessary for applying knowledge effectively. Combining both approaches can enhance understanding and improve outcomes in managing adult pets' needs.
Table of Comparison
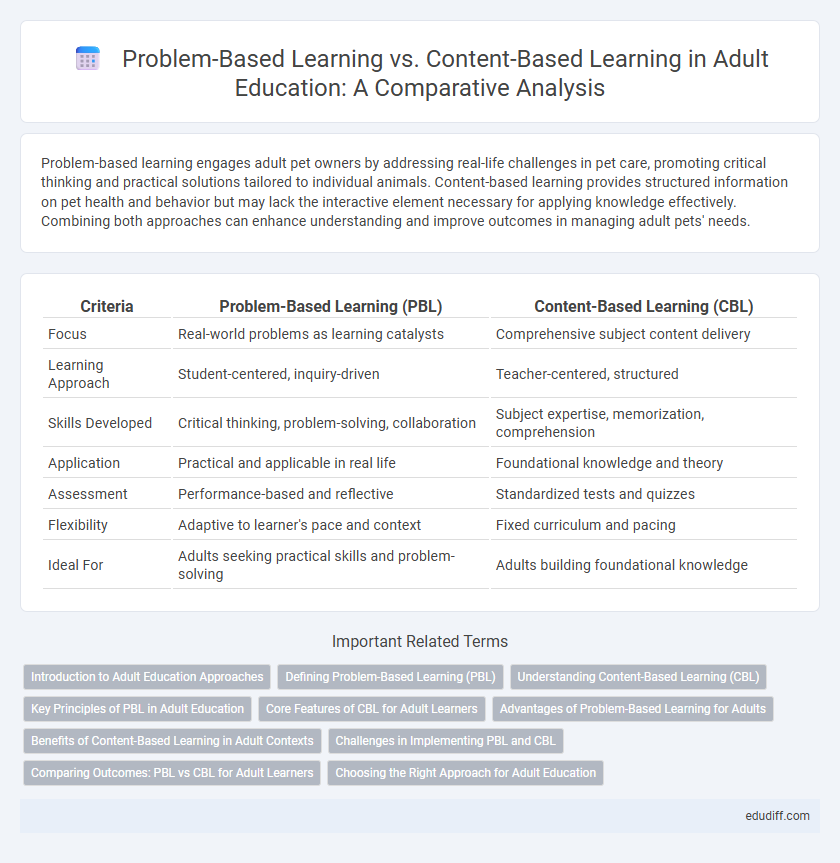
| Criteria | Problem-Based Learning (PBL) | Content-Based Learning (CBL) |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Real-world problems as learning catalysts | Comprehensive subject content delivery |
| Learning Approach | Student-centered, inquiry-driven | Teacher-centered, structured |
| Skills Developed | Critical thinking, problem-solving, collaboration | Subject expertise, memorization, comprehension |
| Application | Practical and applicable in real life | Foundational knowledge and theory |
| Assessment | Performance-based and reflective | Standardized tests and quizzes |
| Flexibility | Adaptive to learner's pace and context | Fixed curriculum and pacing |
| Ideal For | Adults seeking practical skills and problem-solving | Adults building foundational knowledge |
Introduction to Adult Education Approaches
Problem-based learning in adult education emphasizes real-world scenarios to develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills, fostering active engagement and self-directed learning. Content-based learning, however, focuses on the systematic delivery of subject-specific knowledge, often structured around curricula and cognitive mastery. Both approaches address different educational goals, but problem-based learning aligns closely with adult learners' needs for practical application and experiential learning.
Defining Problem-Based Learning (PBL)
Problem-Based Learning (PBL) centers on engaging adult learners with real-world problems to develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills. This learner-driven approach emphasizes collaboration, inquiry, and application of knowledge rather than passive absorption of content. PBL contrasts with content-based learning by prioritizing experiential learning processes tailored to adult cognitive and motivational frameworks.
Understanding Content-Based Learning (CBL)
Content-Based Learning (CBL) centers on acquiring specific knowledge and facts within a subject area, emphasizing the mastery of content over problem-solving skills. This approach facilitates structured information delivery, which enhances memory retention and systematic understanding of academic material. In adult education, CBL is effective for learners who require deep expertise in a particular domain, supporting clear benchmarks for knowledge assessment and progression.
Key Principles of PBL in Adult Education
Problem-based learning (PBL) in adult education centers on learner-driven inquiry, real-world problem solving, and collaborative knowledge construction. It emphasizes critical thinking, self-directed learning, and application of theoretical concepts to practical situations, fostering deeper understanding and retention. Core principles include learner autonomy, contextual relevance, and active engagement, which differentiate it from traditional content-based approaches focused primarily on information delivery.
Core Features of CBL for Adult Learners
Content-based learning (CBL) for adult learners emphasizes real-world application by integrating subject matter knowledge with skill development relevant to their professional and personal contexts. Core features include contextualized content that aligns with adults' prior experiences, fostering critical thinking and deeper comprehension through meaningful engagement. This approach supports self-directed learning, encouraging adults to connect new information with practical challenges and collaborative problem-solving.
Advantages of Problem-Based Learning for Adults
Problem-Based Learning (PBL) enhances critical thinking and real-world problem-solving skills for adult learners, promoting deeper understanding through active engagement and collaboration. Adults benefit from PBL's learner-centered approach that aligns with their prior experiences, fostering motivation and retention by applying knowledge in practical contexts. This method also encourages adaptability and lifelong learning, essential traits in dynamic professional environments.
Benefits of Content-Based Learning in Adult Contexts
Content-based learning in adult contexts enhances practical knowledge by integrating real-world subjects with language skills, fostering deeper comprehension and retention. This approach aligns learning materials with adults' professional and personal experiences, promoting immediate application of knowledge and meaningful communication. By focusing on relevant content, adults develop critical thinking and problem-solving abilities within familiar frameworks, improving motivation and engagement.
Challenges in Implementing PBL and CBL
Problem-based learning (PBL) faces challenges including the need for skilled facilitators, increased preparation time, and student resistance to self-directed learning. Content-based learning (CBL) often struggles with outdated or overly rigid curricula, limiting student engagement and flexibility. Both methods demand significant institutional support to overcome obstacles related to resource allocation and assessment strategies.
Comparing Outcomes: PBL vs CBL for Adult Learners
Problem-based learning (PBL) enhances critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and learner engagement more effectively for adults than content-based learning (CBL), which prioritizes knowledge acquisition and content mastery. Studies show PBL fosters deeper understanding and retention by situating learning in real-world contexts, increasing motivation and practical application in professional settings. Conversely, CBL remains valuable for foundational knowledge but often results in passive learning and limited transferability to complex workplace challenges.
Choosing the Right Approach for Adult Education
Problem-based learning (PBL) enhances critical thinking and real-world problem-solving skills, making it highly effective for adult learners seeking practical application of knowledge. Content-based learning (CBL) emphasizes structured information delivery and foundational knowledge, suitable for adults who need comprehensive understanding of a subject. Selecting the right approach depends on learners' goals, with PBL favoring experiential engagement and CBL providing depth and clarity in complex topics.
Problem-based learning vs Content-based learning Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com