Competency-based progression in alternative education allows students to advance upon demonstrating mastery of skills and concepts, promoting personalized learning and adaptability. This approach contrasts with age-based progression, where students move forward based on their age or time spent in class, often overlooking individual learning paces and abilities. Emphasizing competency ensures that learners build a solid foundation before progressing, enhancing retention and real-world application.
Table of Comparison
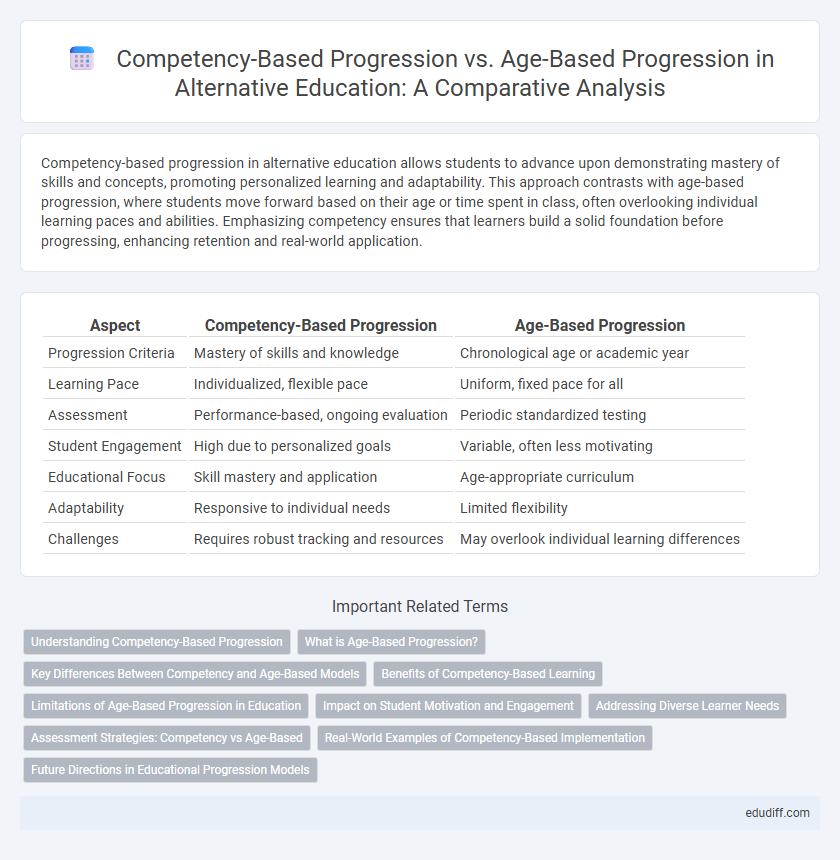
| Aspect | Competency-Based Progression | Age-Based Progression |
|---|---|---|
| Progression Criteria | Mastery of skills and knowledge | Chronological age or academic year |
| Learning Pace | Individualized, flexible pace | Uniform, fixed pace for all |
| Assessment | Performance-based, ongoing evaluation | Periodic standardized testing |
| Student Engagement | High due to personalized goals | Variable, often less motivating |
| Educational Focus | Skill mastery and application | Age-appropriate curriculum |
| Adaptability | Responsive to individual needs | Limited flexibility |
| Challenges | Requires robust tracking and resources | May overlook individual learning differences |
Understanding Competency-Based Progression
Competency-Based Progression prioritizes mastering specific skills and knowledge at an individual pace rather than adhering to traditional age or grade levels. This approach enables personalized learning pathways, ensuring students demonstrate proficiency before advancing to more complex topics. Data shows that competency-based models improve student engagement and mastery, supporting long-term academic success.
What is Age-Based Progression?
Age-Based Progression refers to the traditional education model where students advance through grade levels based on their chronological age rather than mastery of specific skills or competencies. This system groups learners into age cohorts, promoting uniform pacing regardless of individual learning differences or readiness. The approach often leads to varying levels of knowledge within a single grade and may overlook personalized learning needs.
Key Differences Between Competency and Age-Based Models
Competency-based progression advances students upon mastering specific skills and knowledge, ensuring personalized learning paths tailored to individual capabilities rather than chronological age. Age-based progression groups students by their birth year, often resulting in uniform pacing regardless of mastery or readiness. This key difference emphasizes skill acquisition and readiness in competency models versus time spent in grade levels in age-based systems.
Benefits of Competency-Based Learning
Competency-based learning accelerates educational outcomes by allowing students to progress upon mastery of specific skills, ensuring personalized pacing that aligns with individual capabilities rather than chronological age. This approach enhances student engagement and motivation by emphasizing real-world application and mastery, leading to improved retention and deeper understanding. Institutions adopting competency-based progression report higher graduation rates, better workforce preparedness, and more efficient resource utilization compared to traditional age-based models.
Limitations of Age-Based Progression in Education
Age-based progression in education often neglects individual learning speeds, causing some students to advance without mastering essential skills while others lag behind. This system can undermine student motivation and engagement by failing to accommodate diverse abilities and learning needs. Competency-based progression addresses these limitations by allowing learners to advance upon demonstrating mastery, promoting personalized and effective education.
Impact on Student Motivation and Engagement
Competency-Based Progression boosts student motivation and engagement by allowing learners to advance upon mastering skills, fostering a sense of achievement and personalized growth. Age-Based Progression often leads to disengagement as students are grouped by age rather than ability, which can cause boredom or frustration if the curriculum is too easy or too difficult. Schools implementing competency-based models report higher student retention rates and increased intrinsic motivation compared to traditional age-based systems.
Addressing Diverse Learner Needs
Competency-Based Progression tailors education to individual student mastery, allowing learners to advance upon demonstrating skills regardless of age, which effectively addresses diverse learning paces and styles. Age-Based Progression imposes uniform advancement, often failing to accommodate variability in student readiness and comprehension, potentially hindering personalized growth. Emphasizing competency ensures targeted support and maximizes learner potential by aligning educational outcomes with demonstrated ability rather than chronological benchmarks.
Assessment Strategies: Competency vs Age-Based
Competency-based progression relies on formative and summative assessments that measure mastery of specific skills and knowledge, allowing learners to advance upon demonstrating competence regardless of time spent. Age-based progression typically uses standardized tests and grade-level benchmarks tied to chronological age, often emphasizing seat time over mastery. This shift to competency assessments fosters personalized learning paths, ensuring students meet clearly defined objectives before moving forward.
Real-World Examples of Competency-Based Implementation
Competency-based progression is exemplified by institutions like Western Governors University, where students advance upon demonstrating mastery of specific skills rather than age or seat time. Companies such as Google utilize competency frameworks to tailor employee development, emphasizing skill acquisition over tenure. Charter schools like Lindsay Unified School District implement personalized learning plans, enabling students to progress at their own pace based on competencies demonstrated through project-based assessments.
Future Directions in Educational Progression Models
Competency-Based Progression prioritizes mastery of skills and knowledge over time spent in grade levels, enabling personalized learning pathways that adapt to individual student needs. Future educational progression models are increasingly integrating technology-driven assessments and real-time data analytics to refine competency evaluations and support seamless transitions between learning stages. This shift promises to enhance equity and efficiency, promoting lifelong learning and better alignment with workforce demands.
Competency-Based Progression vs Age-Based Progression Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com