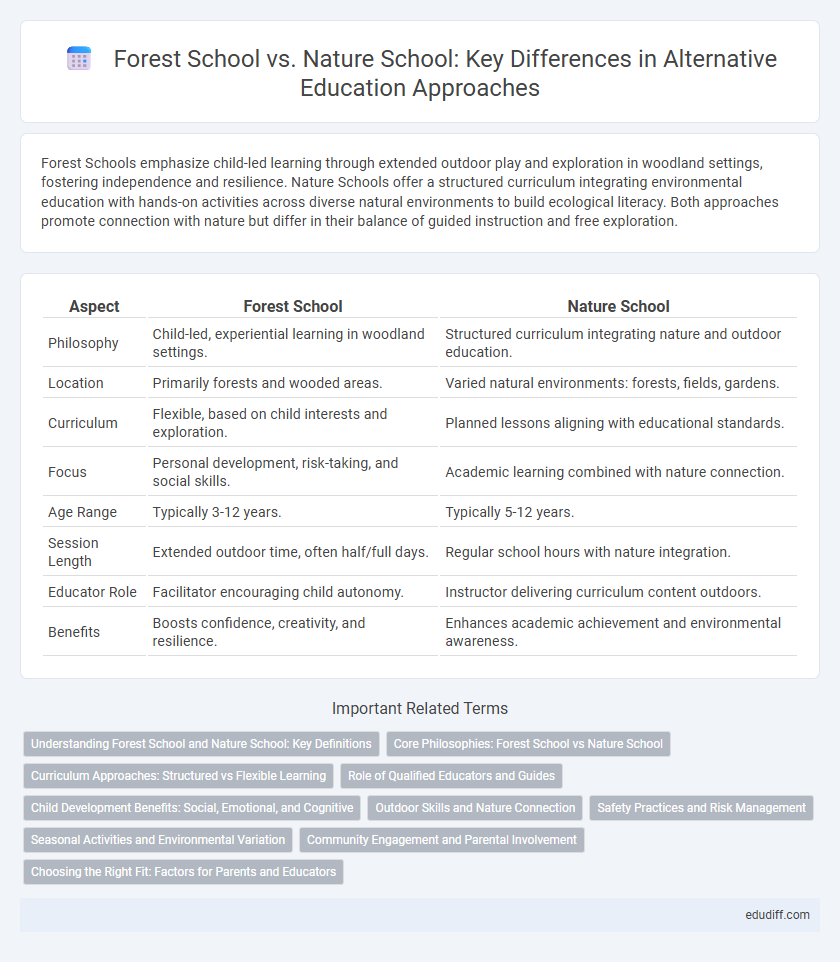
Forest Schools emphasize child-led learning through extended outdoor play and exploration in woodland settings, fostering independence and resilience. Nature Schools offer a structured curriculum integrating environmental education with hands-on activities across diverse natural environments to build ecological literacy. Both approaches promote connection with nature but differ in their balance of guided instruction and free exploration.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Forest School | Nature School |
|---|---|---|
| Philosophy | Child-led, experiential learning in woodland settings. | Structured curriculum integrating nature and outdoor education. |
| Location | Primarily forests and wooded areas. | Varied natural environments: forests, fields, gardens. |
| Curriculum | Flexible, based on child interests and exploration. | Planned lessons aligning with educational standards. |
| Focus | Personal development, risk-taking, and social skills. | Academic learning combined with nature connection. |
| Age Range | Typically 3-12 years. | Typically 5-12 years. |
| Session Length | Extended outdoor time, often half/full days. | Regular school hours with nature integration. |
| Educator Role | Facilitator encouraging child autonomy. | Instructor delivering curriculum content outdoors. |
| Benefits | Boosts confidence, creativity, and resilience. | Enhances academic achievement and environmental awareness. |
Understanding Forest School and Nature School: Key Definitions
Forest School emphasizes child-led learning in woodland environments, fostering independence and resilience through hands-on outdoor activities. Nature School integrates broader ecosystems, combining structured curriculum with outdoor exploration to enhance environmental awareness and cognitive development. Both approaches prioritize experiential learning but differ in setting and educational framework, with Forest School rooted deeply in forest habitats and Nature School embracing diverse natural landscapes.
Core Philosophies: Forest School vs Nature School
Forest School emphasizes child-led play and experiential learning within woodland environments, fostering confidence and independence through risk-taking and real-world challenges. Nature School centers on holistic environmental education, integrating structured scientific inquiry with creative exploration to deepen children's connection to nature. Both models prioritize outdoor immersion but differ in pedagogical approaches, with Forest School focusing on learner autonomy and Nature School blending curriculum-aligned nature study.
Curriculum Approaches: Structured vs Flexible Learning
Forest School curriculum emphasizes a flexible learning approach that adapts to children's interests and natural rhythms, promoting experiential and play-based education. Nature School adopts a more structured curriculum with specific learning objectives aligned to environmental literacy and ecological skills. Both models prioritize outdoor engagement but differ in their balance between open exploration and goal-oriented instruction.
Role of Qualified Educators and Guides
Qualified educators in Forest Schools are specifically trained in child development and outdoor pedagogy, ensuring a structured learning environment that supports social, emotional, and cognitive skills through immersive natural experiences. Nature Schools emphasize guides with expertise in local ecology and environmental stewardship, fostering a deep connection to nature and promoting sustainability through observational learning and hands-on activities. The differing qualifications shape each program's approach, with Forest Schools focusing on developmental milestones and Nature Schools prioritizing ecological literacy and conservation ethics.
Child Development Benefits: Social, Emotional, and Cognitive
Forest School and Nature School both enhance child development by fostering social skills through group collaboration and communication in natural settings. Emotional benefits include increased resilience, self-confidence, and stress reduction as children engage with organic environments. Cognitive development is supported by experiential learning, problem-solving activities, and sensory exploration, promoting critical thinking and creativity.
Outdoor Skills and Nature Connection
Forest School emphasizes hands-on outdoor skills such as shelter building, fire making, and tool use to foster independence and resilience in natural settings. Nature School prioritizes deep nature connection through immersive activities like wildlife observation, plant identification, and sensory exploration to cultivate environmental stewardship. Both approaches promote experiential learning but differ in skill emphasis--Forest School focuses on practical survival techniques while Nature School centers on ecological awareness and emotional bonding with nature.
Safety Practices and Risk Management
Forest Schools implement structured safety practices including thorough site assessments and trained leaders to mitigate environmental risks, fostering secure outdoor learning environments. Nature Schools emphasize child-led exploration with flexible risk management strategies that encourage natural hazard awareness and resilience building. Both models prioritize safety through tailored protocols that balance risk and experiential learning in diverse natural settings.
Seasonal Activities and Environmental Variation
Forest Schools emphasize seasonal activities that align with natural cycles, such as leaf identification in fall, snow shelter building in winter, and wildflower foraging in spring, promoting adaptive learning through environmental variation. Nature Schools incorporate a broader outdoor curriculum that adapts to diverse ecosystems, integrating local flora and fauna observations, weather pattern studies, and habitat restoration projects throughout the year. Seasonal variation in both settings enhances experiential learning, fostering resilience and ecological literacy by engaging children directly with the changing environment.
Community Engagement and Parental Involvement
Forest Schools emphasize immersive outdoor learning with strong community ties, encouraging local experts and families to actively participate in curriculum development and nature-based activities. Nature Schools prioritize parental involvement through collaborative workshops and regular family nature outings, fostering a shared commitment to environmental stewardship and child-centered education. Both models enhance community engagement by promoting collective responsibility for children's holistic growth in natural settings.
Choosing the Right Fit: Factors for Parents and Educators
Forest School emphasizes experiential learning through child-led exploration in woodland environments, fostering independence and resilience. Nature School integrates structured environmental education with focus on ecological literacy and guided activities to deepen understanding of natural sciences. Parents and educators should consider the child's learning style, desired level of structure, and educational goals when selecting between the immersive, play-based approach of Forest School and the curriculum-driven, nature-focused framework of Nature School.
Forest School vs Nature School Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com