Micro-schooling offers a personalized educational experience with small student groups led by a dedicated educator, fostering deep connections and tailored instruction. Learning pods bring together families or caregivers to collaboratively support children's learning, often supplementing traditional schooling with shared resources. Both alternatives emphasize flexibility and community involvement, enhancing social interaction and individualized attention in education.
Table of Comparison
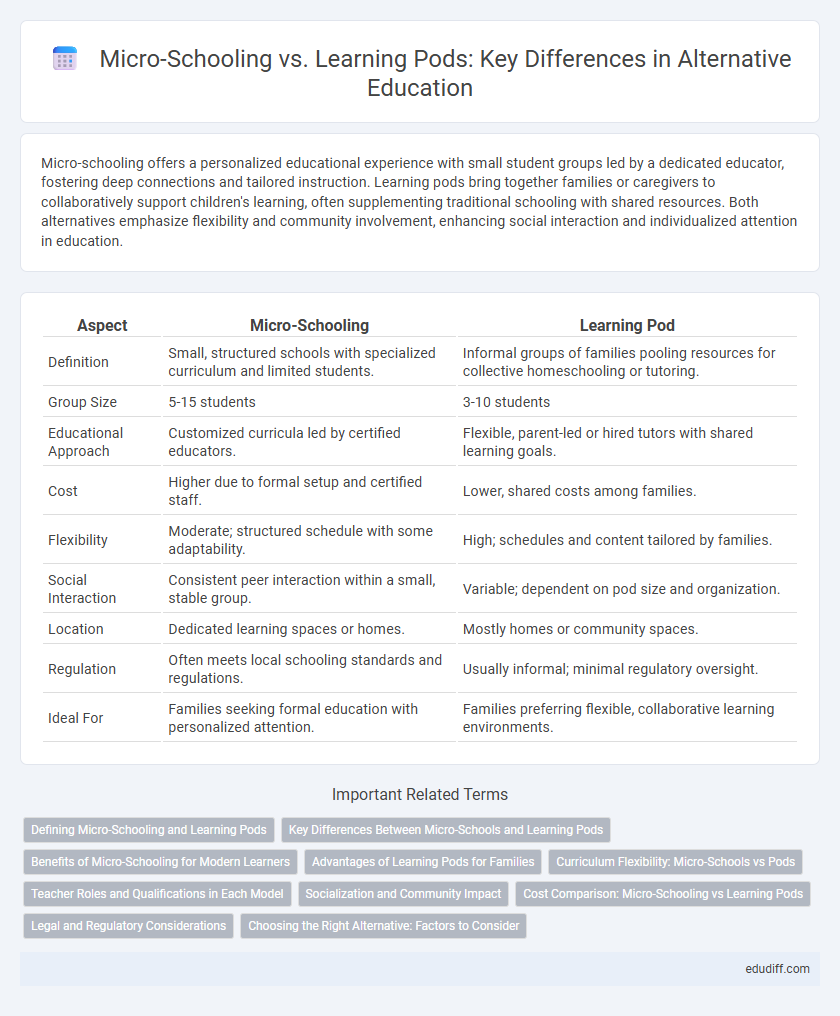
| Aspect | Micro-Schooling | Learning Pod |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Small, structured schools with specialized curriculum and limited students. | Informal groups of families pooling resources for collective homeschooling or tutoring. |
| Group Size | 5-15 students | 3-10 students |
| Educational Approach | Customized curricula led by certified educators. | Flexible, parent-led or hired tutors with shared learning goals. |
| Cost | Higher due to formal setup and certified staff. | Lower, shared costs among families. |
| Flexibility | Moderate; structured schedule with some adaptability. | High; schedules and content tailored by families. |
| Social Interaction | Consistent peer interaction within a small, stable group. | Variable; dependent on pod size and organization. |
| Location | Dedicated learning spaces or homes. | Mostly homes or community spaces. |
| Regulation | Often meets local schooling standards and regulations. | Usually informal; minimal regulatory oversight. |
| Ideal For | Families seeking formal education with personalized attention. | Families preferring flexible, collaborative learning environments. |
Defining Micro-Schooling and Learning Pods
Micro-schooling is a small-scale educational model with typically 5 to 15 students, offering personalized instruction often led by a certified teacher or experienced educator. Learning pods, also known as pandemic pods or micropods, consist of small groups of students who learn together in informal settings, guided primarily by parents or hired tutors. Both approaches emphasize close-knit community learning but differ in structure, staffing, and educational oversight.
Key Differences Between Micro-Schools and Learning Pods
Micro-schools typically operate with a structured curriculum led by one or more certified educators in a dedicated space, facilitating personalized education for a small group of students. Learning pods, by contrast, are informal, parent-organized groups that may use a mix of virtual and in-person instruction with varied educational approaches tailored to student needs. The key differences lie in micro-schools' formal educational framework and staff qualifications versus learning pods' flexibility and reliance on communal parental involvement for coordination and teaching.
Benefits of Micro-Schooling for Modern Learners
Micro-schooling offers personalized instruction with low student-to-teacher ratios, catering to individual learning styles and paces, which enhances academic achievement for modern learners. The flexible curriculum in micro-schools integrates real-world skills and interdisciplinary approaches, promoting critical thinking and creativity. Small, community-based settings foster strong social connections and emotional support, improving student motivation and engagement.
Advantages of Learning Pods for Families
Learning pods offer families personalized education by grouping students with similar learning needs, promoting tailored instruction and social interaction within a manageable cohort size. This model enhances flexibility in scheduling and curriculum choices, allowing parents to maintain greater control over their child's educational experience while benefiting from shared resources and expertise. Learning pods also provide a community-driven approach, fostering collaboration among families and enabling cost-effective access to diverse educational opportunities.
Curriculum Flexibility: Micro-Schools vs Pods
Micro-schools offer greater curriculum flexibility by allowing personalized lesson plans tailored to each student's learning style and pace, often blending traditional subjects with experiential and project-based learning. Learning pods typically follow a more structured curriculum set by parents or external educators, focusing on group cohesion but with less customization for individual academic needs. This difference makes micro-schools a preferred choice for families seeking adaptive, student-centered education in alternative learning environments.
Teacher Roles and Qualifications in Each Model
Micro-schooling typically involves certified teachers who possess formal qualifications and utilize personalized curricula to address individual student needs. Learning pods often rely on parent facilitators or educators with varied teaching backgrounds, focusing on collaborative learning environments rather than standardized instruction. The teacher's role in micro-schools centers on direct academic instruction, while in learning pods, they act more as guides supporting peer interaction and flexible learning activities.
Socialization and Community Impact
Micro-schooling fosters individualized socialization through small, consistent peer groups, promoting deeper relationships and tailored social skills development. Learning pods facilitate flexible community engagement by connecting families with shared educational goals, enhancing collaboration and resource sharing. Both models impact community cohesion by creating localized support networks that strengthen social bonds and collective involvement in children's education.
Cost Comparison: Micro-Schooling vs Learning Pods
Micro-schooling often involves higher upfront costs due to professional educators, structured curricula, and dedicated learning spaces, averaging $10,000 to $15,000 annually depending on location and program. Learning pods typically offer more affordable alternatives, with shared expenses among a small group of families, reducing costs to approximately $2,000 to $5,000 per child annually by leveraging parent-led instruction or mixed tutoring options. Cost efficiency varies by pod size, educational goals, and resource allocation, making micro-schools a more substantial investment for comprehensive academic support compared to the flexible, budget-conscious model of learning pods.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Micro-schooling typically operates under more flexible legal frameworks as small private learning environments, often requiring minimal state oversight depending on jurisdiction. Learning pods, however, may face complex regulatory scrutiny related to zoning, liability, and curriculum standards since they function as informal groupings within existing school frameworks or community settings. Both models must navigate state-specific education laws and health regulations to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal challenges.
Choosing the Right Alternative: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right alternative between micro-schooling and learning pods depends on factors such as group size, curriculum flexibility, and social interaction opportunities. Micro-schooling often offers personalized instruction and a structured environment, while learning pods provide a more informal setting with peer collaboration. Parents should evaluate educational goals, budget, and the child's learning style to make an informed decision.
Micro-Schooling vs Learning Pod Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com