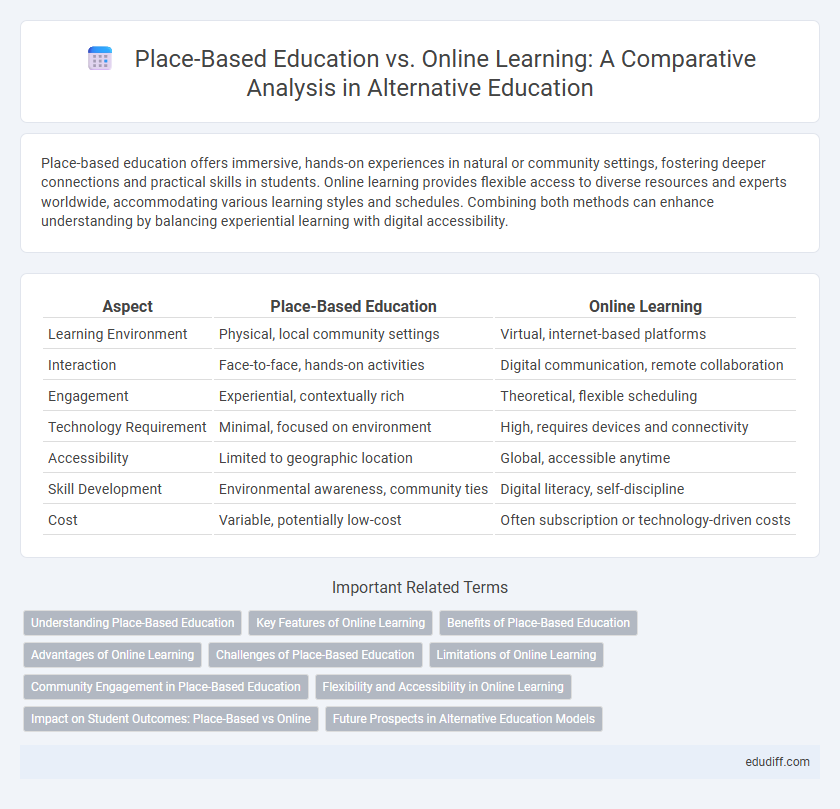
Place-based education offers immersive, hands-on experiences in natural or community settings, fostering deeper connections and practical skills in students. Online learning provides flexible access to diverse resources and experts worldwide, accommodating various learning styles and schedules. Combining both methods can enhance understanding by balancing experiential learning with digital accessibility.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Place-Based Education | Online Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Environment | Physical, local community settings | Virtual, internet-based platforms |
| Interaction | Face-to-face, hands-on activities | Digital communication, remote collaboration |
| Engagement | Experiential, contextually rich | Theoretical, flexible scheduling |
| Technology Requirement | Minimal, focused on environment | High, requires devices and connectivity |
| Accessibility | Limited to geographic location | Global, accessible anytime |
| Skill Development | Environmental awareness, community ties | Digital literacy, self-discipline |
| Cost | Variable, potentially low-cost | Often subscription or technology-driven costs |
Understanding Place-Based Education
Place-Based Education immerses students in local environments, fostering experiential learning through direct interaction with community ecosystems, history, and culture. This approach enhances critical thinking and regional awareness by connecting curriculum to tangible, real-world contexts. It contrasts with online learning's virtual settings by emphasizing sensory engagement and community involvement.
Key Features of Online Learning
Online learning offers flexible scheduling and access to diverse digital resources, enabling personalized and self-paced education. It supports multimedia content integration, interactive simulations, and real-time feedback through learning management systems. This approach facilitates global connectivity, breaking geographical barriers and promoting collaborative learning across various locations.
Benefits of Place-Based Education
Place-Based Education enhances student engagement by connecting learning to local environments, fostering a deeper understanding of community and cultural heritage. It promotes hands-on experiences that improve critical thinking and problem-solving skills through real-world applications. Research shows students involved in Place-Based Education exhibit higher retention rates and increased motivation compared to traditional online learning methods.
Advantages of Online Learning
Online learning offers unparalleled flexibility, allowing students to access coursework anytime and anywhere, which is ideal for diverse schedules and remote locations. It provides a vast array of digital resources and interactive tools that enhance engagement and personalized learning experiences. Cost-effectiveness and scalability make online learning accessible to a broader audience, reducing expenses related to transportation, housing, and physical materials.
Challenges of Place-Based Education
Place-based education faces challenges such as limited access to diverse resources and dependency on geographic location, which can restrict experiential learning opportunities for students. Weather conditions and safety concerns may disrupt outdoor activities, leading to inconsistent learning schedules. Additionally, schools in urban or resource-poor areas struggle to implement place-based methodologies effectively due to limited natural environments and community partnerships.
Limitations of Online Learning
Online learning often struggles with limited hands-on experiences and reduced opportunities for community engagement, which are fundamental in place-based education. The lack of physical presence can hinder the development of social skills and practical knowledge tied to local environments. Connectivity issues and screen fatigue further restrict students' ability to fully immerse and interact with learning materials.
Community Engagement in Place-Based Education
Place-Based Education fosters deep community engagement by involving students directly in local environments, cultural sites, and civic projects, enhancing experiential learning and social responsibility. This approach leverages local resources and stakeholders, creating meaningful connections between education and community needs that online learning often lacks. Immersive participation in local settings cultivates a stronger sense of place, collaboration, and real-world problem-solving skills among students.
Flexibility and Accessibility in Online Learning
Online learning offers unmatched flexibility, allowing students to access course materials anytime and anywhere, which accommodates diverse schedules and learning paces. Digital platforms eliminate geographical barriers, providing accessibility to quality education for learners in remote or underserved areas. This mode of education supports personalized learning experiences through adaptive technologies and a wide range of multimedia resources.
Impact on Student Outcomes: Place-Based vs Online
Place-Based Education fosters deeper student engagement and higher retention rates by connecting learning to local environments and communities. Online Learning offers flexible access and diverse resources but may result in lower social interaction and practical skill application. Comparative studies reveal that Place-Based Education often leads to improved critical thinking and collaboration skills, enhancing overall student outcomes.
Future Prospects in Alternative Education Models
Place-based education cultivates deep community connections and experiential learning, fostering environmental stewardship and local engagement. Online learning offers scalable access, personalized pacing, and integration of innovative digital tools that support diverse learning styles. Future prospects in alternative education models likely involve hybrid approaches combining place-based immersion with online flexibility to maximize student engagement and global competencies.
Place-Based Education vs Online Learning Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com