Unschooling empowers children to follow their natural interests and learn through life experiences without a formal curriculum, fostering intrinsic motivation and creativity. Deschooling serves as a transitional phase, helping children and families disengage from traditional schooling mindsets to adapt to more flexible, child-centered learning methods. Both approaches challenge conventional education by prioritizing autonomy and personalized growth over standardized instruction.
Table of Comparison
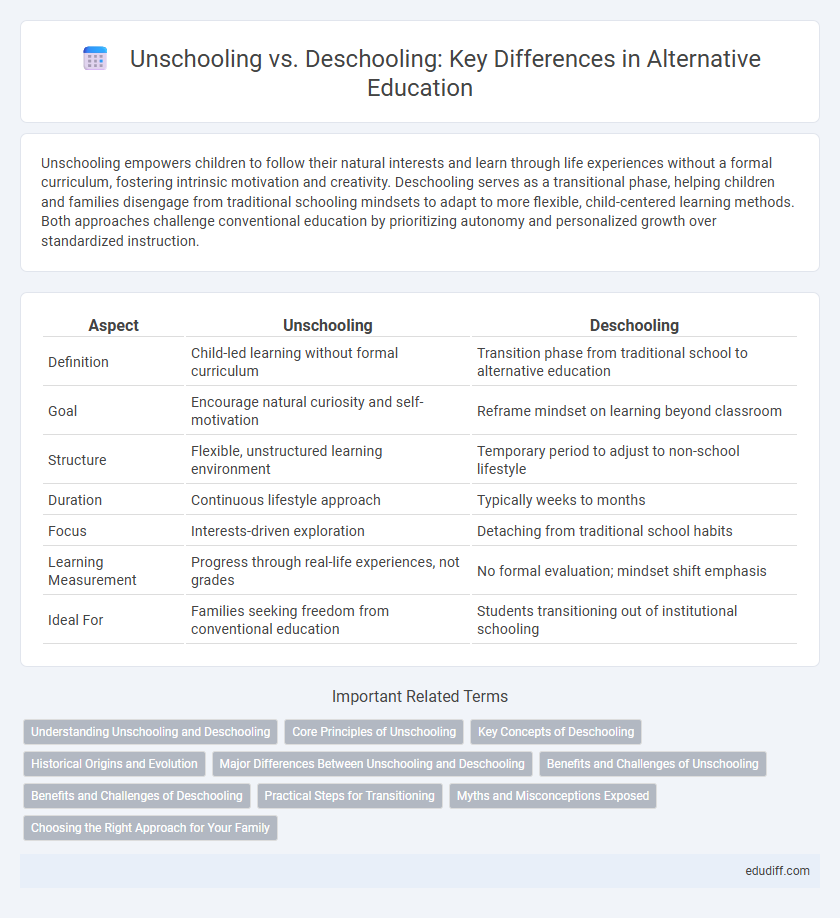
| Aspect | Unschooling | Deschooling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Child-led learning without formal curriculum | Transition phase from traditional school to alternative education |
| Goal | Encourage natural curiosity and self-motivation | Reframe mindset on learning beyond classroom |
| Structure | Flexible, unstructured learning environment | Temporary period to adjust to non-school lifestyle |
| Duration | Continuous lifestyle approach | Typically weeks to months |
| Focus | Interests-driven exploration | Detaching from traditional school habits |
| Learning Measurement | Progress through real-life experiences, not grades | No formal evaluation; mindset shift emphasis |
| Ideal For | Families seeking freedom from conventional education | Students transitioning out of institutional schooling |
Understanding Unschooling and Deschooling
Unschooling emphasizes learner-led education, allowing children to pursue their interests without a fixed curriculum, fostering intrinsic motivation and autonomy. Deschooling is a transitional phase designed to dismantle traditional schooling habits, enabling families to shift mindset away from conventional education systems and prepare for alternative learning approaches. Both practices prioritize personalized, flexible learning environments that challenge standard educational models and support self-directed growth.
Core Principles of Unschooling
Unschooling centers on learner-led education, emphasizing autonomy, curiosity, and real-life experiences as the primary drivers of knowledge acquisition. It rejects traditional curriculum structures, allowing children to explore subjects at their own pace and according to their interests. This approach fosters intrinsic motivation and holistic development, contrasting with deschooling's focus on transitioning away from formal schooling habits.
Key Concepts of Deschooling
Deschooling is a transitional process that helps children and families adjust to learning outside traditional school structures by shedding ingrained educational norms and expectations. It emphasizes self-directed learning, autonomy, and the dismantling of institutionalized beliefs about education. Key concepts include redefining motivation, fostering intrinsic curiosity, and creating flexible, personalized learning environments.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Unschooling originated in the late 20th century as a learner-centered alternative to traditional education, emphasizing freedom and self-directed learning. Deschooling, a concept popularized by Ivan Illich in the 1970s, critiques institutional schooling and advocates for dismantling conventional education systems. Both philosophies evolved from earlier progressive education movements, emphasizing autonomy and the rejection of standardized curricula.
Major Differences Between Unschooling and Deschooling
Unschooling centers on learner-directed education with no formal curriculum, emphasizing natural learning through life experiences, while deschooling serves as a transitional process to help children adjust from traditional school environments to more flexible learning methods. Unschooling allows complete freedom in choosing learning topics and pace, whereas deschooling typically involves a temporary suspension of structured learning to alleviate the stress of conventional schooling. The major difference lies in unschooling being a long-term educational philosophy, whereas deschooling is a short-term adjustment period facilitating the shift away from institutional education.
Benefits and Challenges of Unschooling
Unschooling promotes personalized, interest-driven learning that fosters creativity, critical thinking, and intrinsic motivation by allowing children to explore subjects at their own pace. This alternative education approach supports autonomy and adaptability but can present challenges in meeting standardized academic benchmarks and requires significant parental involvement and resource access. Families often experience benefits such as stronger learner engagement and flexibility, while also facing difficulties in socialization opportunities and structure maintenance.
Benefits and Challenges of Deschooling
Deschooling allows children to transition gently from traditional schooling to personalized, interest-led learning, fostering intrinsic motivation and creativity while addressing emotional and social adjustment needs. The process benefits learners by reducing stress and burnout, helping them regain confidence and autonomy, yet it challenges families with potential uncertainty, lack of structure, and the need for patience during this adjustment period. Successful deschooling requires a supportive environment that respects the child's pace and encourages exploration beyond conventional education frameworks.
Practical Steps for Transitioning
Transitioning from traditional education to unschooling involves recognizing the value of deschooling as a foundational process that allows learners to shed conventional academic habits and develop intrinsic motivation. Practical steps include creating a flexible daily routine that embraces curiosity-driven activities, establishing a rich learning environment with diverse resources, and gradually reducing structured assignments to foster autonomy. Parents and educators should encourage reflective discussions to help students internalize their learning progress and adapt to the unschooling philosophy effectively.
Myths and Misconceptions Exposed
Unschooling and deschooling often face myths equating them with a lack of structure or discipline, but both prioritize learner autonomy and gradual adjustment away from traditional schooling constraints. Misconceptions include the belief that unschooling means no learning occurs, whereas it actually fosters intrinsic motivation and personalized education paths. Deschooling serves as a critical transitional process to deprogram conventional educational expectations, enabling families to embrace alternative learning philosophies effectively.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Family
Unschooling empowers families to follow a child-led, interest-driven learning approach, fostering creativity and intrinsic motivation. Deschooling serves as an essential transitional phase, helping children and parents adjust from traditional schooling mindsets to more flexible educational methods. Selecting between unschooling and deschooling depends on your family's readiness for self-directed learning and the need to gradually shift existing educational habits.
Unschooling vs Deschooling Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com