Adult learning emphasizes acquiring specific skills or knowledge at particular stages, often driven by career or personal development goals. Lifelong learning, however, is a continuous, self-motivated process aimed at evolving personal and professional abilities throughout an entire life span. Both approaches foster growth, but lifelong learning integrates ongoing adaptability and curiosity beyond formal education settings.
Table of Comparison
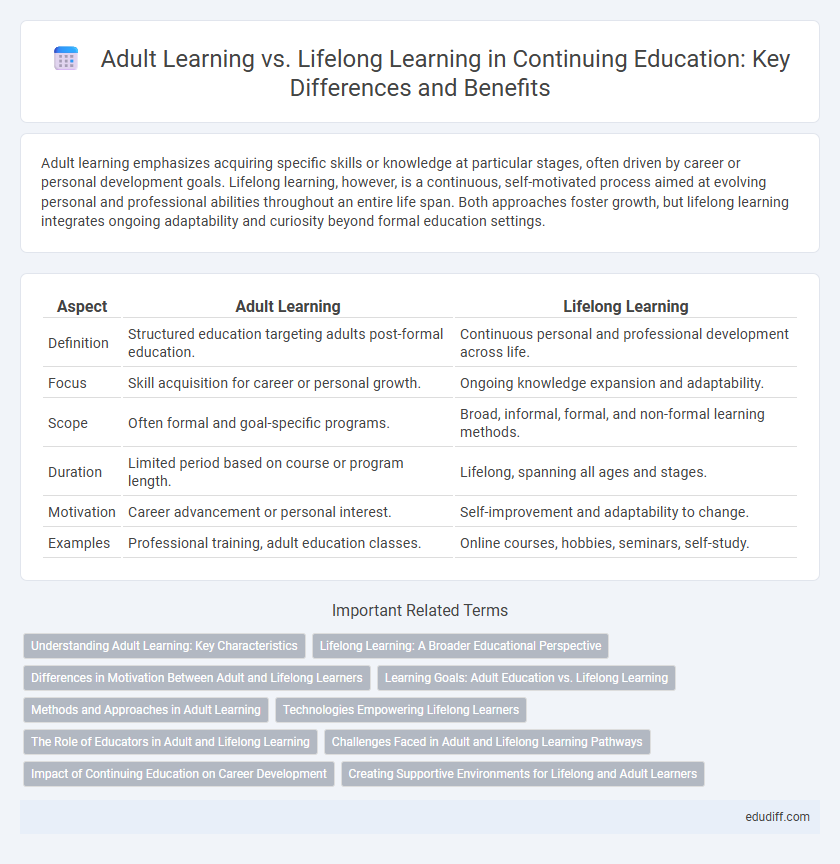
| Aspect | Adult Learning | Lifelong Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured education targeting adults post-formal education. | Continuous personal and professional development across life. |
| Focus | Skill acquisition for career or personal growth. | Ongoing knowledge expansion and adaptability. |
| Scope | Often formal and goal-specific programs. | Broad, informal, formal, and non-formal learning methods. |
| Duration | Limited period based on course or program length. | Lifelong, spanning all ages and stages. |
| Motivation | Career advancement or personal interest. | Self-improvement and adaptability to change. |
| Examples | Professional training, adult education classes. | Online courses, hobbies, seminars, self-study. |
Understanding Adult Learning: Key Characteristics
Adult learning is characterized by self-direction, practical application, and a wealth of prior experience that shapes the learning process. Adults prefer learning that is relevant, problem-centered, and allows immediate implementation in personal or professional contexts. Understanding these key characteristics helps educators design effective programs tailored to adult learners' unique motivations and challenges.
Lifelong Learning: A Broader Educational Perspective
Lifelong learning encompasses continuous, self-motivated education pursued throughout an individual's entire life, beyond formal schooling and professional development. It integrates diverse learning experiences, including informal, non-formal, and formal education, adapting to evolving personal and societal needs. This broader educational perspective promotes adaptability, critical thinking, and the ability to acquire new skills essential in a rapidly changing world.
Differences in Motivation Between Adult and Lifelong Learners
Adult learners often pursue education driven by immediate goals such as career advancement or skill acquisition, whereas lifelong learners are motivated by a continuous desire for personal growth and curiosity. Adult learning typically centers on practical application relevant to current life circumstances, while lifelong learning embraces a broader, intrinsic motivation to explore diverse knowledge areas over time. Understanding these motivational differences helps tailor educational approaches for each group effectively.
Learning Goals: Adult Education vs. Lifelong Learning
Adult education primarily targets specific learning goals tied to career advancement or skill acquisition, emphasizing structured programs like vocational training or certification courses. Lifelong learning encompasses broader personal and professional development objectives, encouraging continuous, self-directed exploration beyond formal education. Both approaches enhance knowledge retention and adaptability but differ in scope and learner motivation.
Methods and Approaches in Adult Learning
Adult learning methods emphasize experiential techniques such as problem-based learning, reflective practice, and collaborative activities that leverage learners' prior knowledge and real-world experiences. Facilitators often adopt a learner-centered approach, incorporating flexible, personalized instruction and self-directed learning to enhance engagement and retention. Techniques like case studies, simulations, and peer discussions support critical thinking and practical skill development within adult education frameworks.
Technologies Empowering Lifelong Learners
Technologies empowering lifelong learners include adaptive learning platforms, mobile apps, and virtual reality tools that create personalized and immersive educational experiences. Artificial intelligence-driven analytics help identify skill gaps and recommend targeted resources, enhancing continuous skill development. Cloud-based collaboration tools enable seamless access to learning materials and peer interactions anytime, supporting ongoing knowledge acquisition beyond traditional adult learning settings.
The Role of Educators in Adult and Lifelong Learning
Educators in adult and lifelong learning environments tailor instructional approaches to accommodate diverse learner experiences and goals, employing flexible methods that foster critical thinking and practical application. They emphasize creating inclusive and supportive learning spaces that encourage continuous skill development and self-directed learning. Effective educators also serve as facilitators and mentors, guiding adults in navigating evolving knowledge landscapes and adapting to changing personal and professional contexts.
Challenges Faced in Adult and Lifelong Learning Pathways
Challenges in adult learning often stem from balancing educational commitments with work and family responsibilities, creating time constraints and stress. Lifelong learners face difficulties adapting to evolving technologies and maintaining motivation across diverse learning stages. Both pathways require overcoming financial barriers and limited access to tailored resources that support individual learning needs.
Impact of Continuing Education on Career Development
Continuing education enhances career development by equipping adults with updated skills and knowledge essential for adapting to evolving industry demands. Lifelong learning fosters continuous personal and professional growth, enabling individuals to seize new opportunities and maintain long-term employability. Both approaches contribute significantly to increased job performance, career advancement, and earning potential in a competitive workforce.
Creating Supportive Environments for Lifelong and Adult Learners
Creating supportive environments for lifelong and adult learners involves designing flexible learning spaces that accommodate diverse schedules and learning styles. Utilizing technology-enhanced tools and personalized feedback fosters engagement and motivation, while providing access to resources such as mentorship programs and peer networks promotes continuous development. Emphasizing emotional support and inclusivity helps adult learners overcome barriers and sustain long-term educational commitments.
Adult Learning vs Lifelong Learning Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com