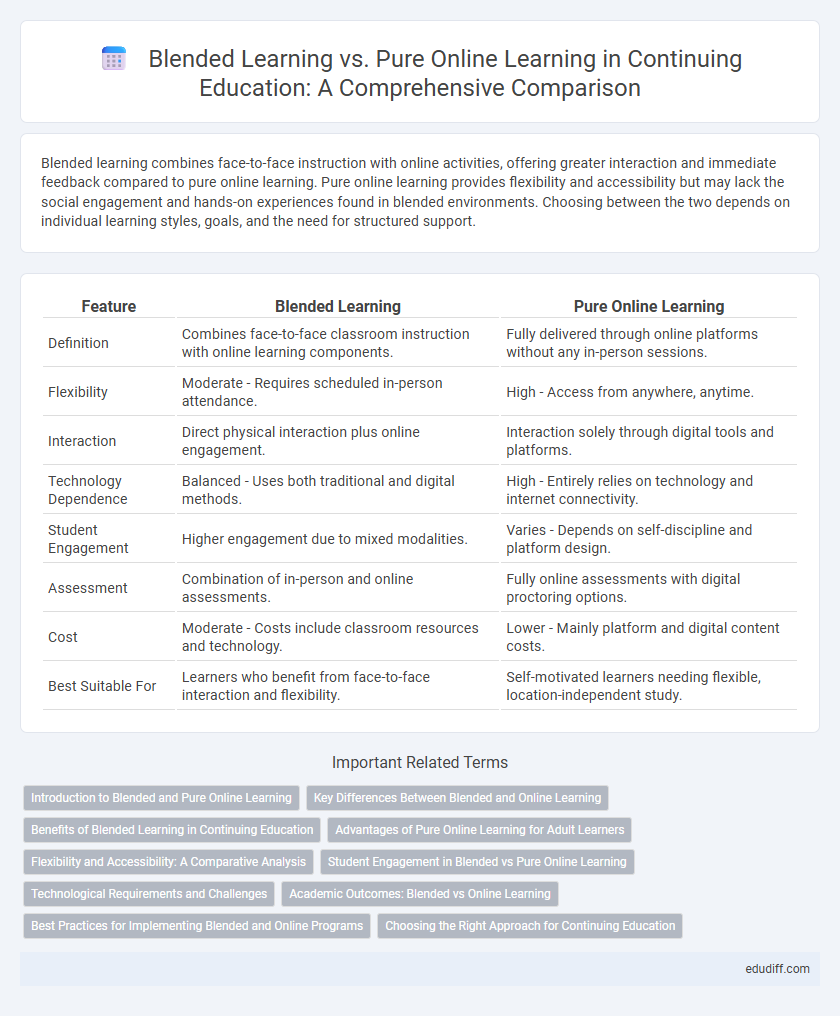
Blended learning combines face-to-face instruction with online activities, offering greater interaction and immediate feedback compared to pure online learning. Pure online learning provides flexibility and accessibility but may lack the social engagement and hands-on experiences found in blended environments. Choosing between the two depends on individual learning styles, goals, and the need for structured support.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Blended Learning | Pure Online Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines face-to-face classroom instruction with online learning components. | Fully delivered through online platforms without any in-person sessions. |
| Flexibility | Moderate - Requires scheduled in-person attendance. | High - Access from anywhere, anytime. |
| Interaction | Direct physical interaction plus online engagement. | Interaction solely through digital tools and platforms. |
| Technology Dependence | Balanced - Uses both traditional and digital methods. | High - Entirely relies on technology and internet connectivity. |
| Student Engagement | Higher engagement due to mixed modalities. | Varies - Depends on self-discipline and platform design. |
| Assessment | Combination of in-person and online assessments. | Fully online assessments with digital proctoring options. |
| Cost | Moderate - Costs include classroom resources and technology. | Lower - Mainly platform and digital content costs. |
| Best Suitable For | Learners who benefit from face-to-face interaction and flexibility. | Self-motivated learners needing flexible, location-independent study. |
Introduction to Blended and Pure Online Learning
Blended learning combines traditional face-to-face classroom instruction with online digital media, allowing for flexibility and a more personalized learning experience. Pure online learning occurs entirely in a virtual environment, utilizing Learning Management Systems (LMS) to deliver content, assess progress, and facilitate communication. Both methods leverage technology but differ in the level of physical interaction and structure provided to students.
Key Differences Between Blended and Online Learning
Blended learning combines face-to-face classroom instruction with online educational materials and activities, fostering interactive, personalized experiences, while pure online learning relies entirely on digital platforms for content delivery and student engagement. Key differences include the level of instructor interaction, where blended learning offers direct teacher support and peer collaboration, whereas online learning emphasizes self-paced study and virtual communication. The flexibility of online learning contrasts with the structured schedule of blended courses, impacting student motivation and learning outcomes.
Benefits of Blended Learning in Continuing Education
Blended learning in continuing education combines face-to-face instruction with online resources, enhancing learner engagement and retention through varied interaction methods. This approach supports flexible scheduling and personalized learning paths while maintaining direct access to instructors for immediate feedback and support. By integrating traditional classroom benefits with digital convenience, blended learning fosters deeper comprehension and practical skill application in professional development.
Advantages of Pure Online Learning for Adult Learners
Pure online learning offers adult learners unparalleled flexibility, allowing them to balance education with work and family responsibilities. This mode provides access to a wide range of courses and expert instructors from anywhere in the world, eliminating geographic barriers. Cost-effectiveness and self-paced learning enhance the appeal, making it easier for adults to acquire new skills and advance their careers efficiently.
Flexibility and Accessibility: A Comparative Analysis
Blended learning combines in-person and online instruction, offering greater flexibility by allowing students to manage their schedules more effectively compared to pure online learning, which relies entirely on digital platforms. Accessibility in blended learning benefits from physical resources and face-to-face interactions, making it more inclusive for students with limited internet access or digital literacy challenges. Pure online learning excels in providing access to educational content anywhere and anytime but may pose difficulties for learners needing hands-on support or real-time engagement.
Student Engagement in Blended vs Pure Online Learning
Student engagement in blended learning significantly surpasses that of pure online learning due to the integration of face-to-face interaction, hands-on activities, and real-time feedback. Blended learning environments promote active participation and collaborative problem-solving, which enhance motivation and retention compared to the isolated nature of pure online courses. Data from educational studies show higher completion rates and deeper cognitive engagement in blended formats than purely virtual ones.
Technological Requirements and Challenges
Blended learning demands robust technological infrastructure including reliable high-speed internet, compatible devices, and sophisticated Learning Management Systems (LMS) to seamlessly integrate face-to-face and digital components. Pure online learning relies heavily on advanced software platforms enabling synchronous and asynchronous interactions, often encountering challenges related to digital accessibility and varying user tech proficiency. Both models face cybersecurity risks and require continuous technical support and user training to ensure smooth educational delivery.
Academic Outcomes: Blended vs Online Learning
Blended learning, combining online and face-to-face instruction, consistently demonstrates higher academic outcomes compared to pure online learning, with studies showing improved student engagement, retention, and understanding. Research indicates that students in blended environments often achieve better grades and demonstrate deeper conceptual mastery due to the integration of interactive, personalized support alongside digital resources. Pure online learning, while flexible, may lack the immediate feedback and social interaction necessary for optimal academic performance in some disciplines.
Best Practices for Implementing Blended and Online Programs
Effective implementation of blended learning involves integrating interactive digital tools with face-to-face instruction to enhance student engagement and retention. Pure online learning programs benefit from structured course design, clear communication channels, and consistent assessment methods to maintain learner motivation and track progress. Leveraging learning analytics and regular feedback loops supports continuous improvement and personalized learning experiences in both modalities.
Choosing the Right Approach for Continuing Education
Blended learning combines online digital media with traditional face-to-face instruction, offering greater flexibility and personalized support compared to pure online learning, which relies solely on virtual platforms. For continuing education, selecting the right approach depends on factors like learner engagement, accessibility, and the need for hands-on practice or direct interaction. Organizations should evaluate course objectives, technological resources, and learner preferences to maximize educational outcomes.
Blended Learning vs Pure Online Learning Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com