Extension programs offer specialized learning opportunities that complement the mainstream curriculum by targeting specific skills or interests, enhancing student engagement and knowledge retention. These programs provide flexible, personalized education paths that address diverse learning needs often unmet by standardized curricula. Integrating extension programs alongside the mainstream curriculum can foster deeper understanding and practical application of core concepts.
Table of Comparison
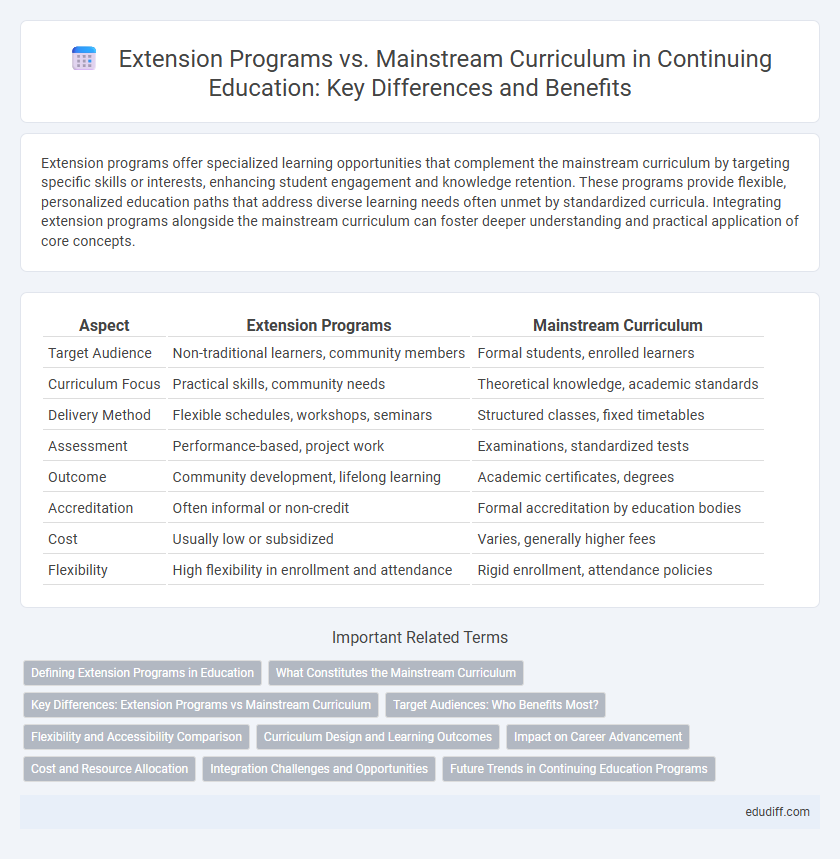
| Aspect | Extension Programs | Mainstream Curriculum |
|---|---|---|
| Target Audience | Non-traditional learners, community members | Formal students, enrolled learners |
| Curriculum Focus | Practical skills, community needs | Theoretical knowledge, academic standards |
| Delivery Method | Flexible schedules, workshops, seminars | Structured classes, fixed timetables |
| Assessment | Performance-based, project work | Examinations, standardized tests |
| Outcome | Community development, lifelong learning | Academic certificates, degrees |
| Accreditation | Often informal or non-credit | Formal accreditation by education bodies |
| Cost | Usually low or subsidized | Varies, generally higher fees |
| Flexibility | High flexibility in enrollment and attendance | Rigid enrollment, attendance policies |
Defining Extension Programs in Education
Extension programs in education offer supplementary learning opportunities beyond the mainstream curriculum, targeting diverse audiences such as adult learners, community members, and professionals seeking skill enhancement. These programs emphasize practical, flexible, and often non-credit courses designed to meet specific community needs and promote lifelong learning. By complementing formal education, extension programs foster broader access to knowledge and support continuous personal and professional development.
What Constitutes the Mainstream Curriculum
The mainstream curriculum constitutes the structured educational framework mandated by educational authorities, encompassing core subjects such as mathematics, science, language arts, and social studies that aim to provide comprehensive foundational knowledge. It follows standardized guidelines and assessment criteria designed to ensure consistent learning outcomes for all students within a specific grade or educational level. This curriculum emphasizes skill development, critical thinking, and content mastery aligned with national or regional educational standards.
Key Differences: Extension Programs vs Mainstream Curriculum
Extension programs offer specialized or accelerated learning opportunities tailored to individual interests or advanced skill levels, differing significantly from the standardized structure of the mainstream curriculum. While mainstream curriculum covers a broad range of foundational subjects designed for overall academic development, extension programs emphasize depth in specific areas such as STEM, arts, or leadership. This targeted approach in extension programs enhances student engagement and mastery beyond the general academic requirements of the mainstream curriculum.
Target Audiences: Who Benefits Most?
Extension programs primarily benefit non-traditional learners such as working adults, lifelong learners, and community members seeking skill enhancement. Mainstream curriculum targets traditional students pursuing formal education pathways, typically full-time learners within academic institutions. Tailoring educational offerings to these distinct audiences maximizes engagement and learning outcomes.
Flexibility and Accessibility Comparison
Extension programs offer greater flexibility by allowing learners to access courses online or in varied timeframes, accommodating diverse schedules and learning paces. Mainstream curricula typically follow fixed academic calendars and structured classroom settings, which can limit accessibility for non-traditional students or working professionals. The adaptable nature of extension programs enhances educational reach, enabling wider participation across different demographics.
Curriculum Design and Learning Outcomes
Extension programs emphasize flexible curriculum design tailored to diverse learner needs, promoting practical skills and real-world applications. Mainstream curriculum follows a standardized framework targeting comprehensive subject mastery and academic rigor. Learning outcomes in extension programs prioritize adaptability and immediate employability, whereas mainstream curriculum aims for foundational knowledge and long-term cognitive development.
Impact on Career Advancement
Extension programs offer specialized skills and practical knowledge that enhance career advancement opportunities beyond the foundational understanding provided by the mainstream curriculum. Employers often value the targeted expertise and real-world application gained through extension courses, leading to faster promotions and salary growth. Integrating extension programs with mainstream education creates a competitive edge by bridging academic theory and industry-relevant competencies.
Cost and Resource Allocation
Extension programs often require separate funding streams and dedicated resources, which can lead to higher overall costs compared to mainstream curriculum that typically utilizes existing infrastructure and staff. Allocating resources to extension programs may divert funds from the core curriculum, impacting the quality and availability of standard education services. Cost-benefit analysis is essential to balance investment in extension initiatives while maintaining efficient resource management within the mainstream educational framework.
Integration Challenges and Opportunities
Extension programs face integration challenges including curriculum alignment, resource allocation, and varying student engagement levels, which can hinder seamless incorporation into the mainstream educational framework. Opportunities arise in leveraging extension programs to enrich the mainstream curriculum through specialized skills training, flexible learning modalities, and community-based projects. Effective collaboration between program developers and mainstream educators is crucial to maximize the complementary benefits and address the operational complexities of integration.
Future Trends in Continuing Education Programs
Future trends in continuing education programs emphasize the integration of technology-enhanced learning platforms and personalized curriculum paths, providing learners with flexible, skills-based education aligned with evolving job market demands. Extension programs increasingly adopt micro-credentialing and competency-based assessments to offer targeted knowledge applicable to emerging industries such as artificial intelligence, renewable energy, and healthcare innovation. These developments position extension programs as agile alternatives to mainstream curricula, addressing lifelong learning needs and fostering continuous professional development in dynamic economic environments.
Extension Programs vs Mainstream Curriculum Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com