Lifelong learning emphasizes continuous personal and professional growth throughout an individual's entire life, adapting to changing interests and career demands. Adult education typically focuses on structured programs designed for mature learners aiming to acquire specific skills or qualifications. Both approaches support ongoing development, but lifelong learning encourages a broader, self-directed pursuit of knowledge beyond formal settings.
Table of Comparison
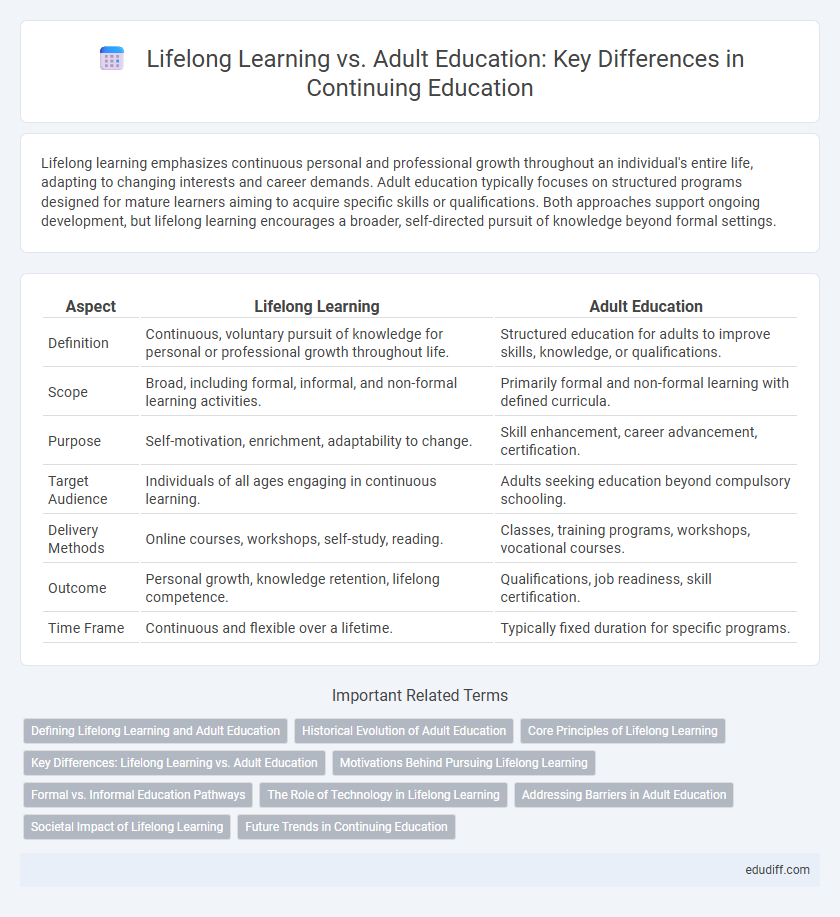
| Aspect | Lifelong Learning | Adult Education |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Continuous, voluntary pursuit of knowledge for personal or professional growth throughout life. | Structured education for adults to improve skills, knowledge, or qualifications. |
| Scope | Broad, including formal, informal, and non-formal learning activities. | Primarily formal and non-formal learning with defined curricula. |
| Purpose | Self-motivation, enrichment, adaptability to change. | Skill enhancement, career advancement, certification. |
| Target Audience | Individuals of all ages engaging in continuous learning. | Adults seeking education beyond compulsory schooling. |
| Delivery Methods | Online courses, workshops, self-study, reading. | Classes, training programs, workshops, vocational courses. |
| Outcome | Personal growth, knowledge retention, lifelong competence. | Qualifications, job readiness, skill certification. |
| Time Frame | Continuous and flexible over a lifetime. | Typically fixed duration for specific programs. |
Defining Lifelong Learning and Adult Education
Lifelong learning emphasizes continuous, self-motivated acquisition of knowledge and skills throughout an individual's life, promoting personal and professional growth beyond formal education. Adult education specifically targets adults through structured programs designed to enhance literacy, vocational skills, and civic participation. Distinguishing these concepts highlights lifelong learning as an ongoing, informal process, while adult education involves organized, institutionalized learning opportunities.
Historical Evolution of Adult Education
Adult education has evolved significantly since the 19th century, initially focusing on vocational training and literacy for industrial workers during the Industrial Revolution. The mid-20th century expanded adult education into broader domains such as civic participation, personal development, and social integration. This historical progression laid the foundation for lifelong learning, emphasizing continuous skill development and adaptability in a rapidly changing socio-economic environment.
Core Principles of Lifelong Learning
Core principles of lifelong learning include continuous personal and professional development, adaptability to changing knowledge and skills, and the integration of learning within everyday life. Emphasis on learner autonomy encourages individuals to take responsibility for their own educational journeys, fostering motivation and self-directed learning. These principles distinguish lifelong learning from adult education by promoting a seamless, ongoing process beyond formal or structured settings.
Key Differences: Lifelong Learning vs. Adult Education
Lifelong learning encompasses continuous, self-motivated acquisition of knowledge and skills throughout an individual's entire life, often driven by personal or professional interests without formal curricula. Adult education typically refers to structured learning programs specifically designed for adults, emphasizing formal instruction, certification, or vocational training. Key differences lie in scope and motivation: lifelong learning is an ongoing, voluntary pursuit beyond traditional settings, whereas adult education targets explicit educational goals within organized frameworks.
Motivations Behind Pursuing Lifelong Learning
Motivations behind pursuing lifelong learning often stem from a desire to stay relevant in rapidly evolving job markets and to foster personal growth through continuous skill acquisition. Unlike adult education, which is frequently goal-oriented towards specific qualifications or employment outcomes, lifelong learning is driven by intrinsic curiosity and the commitment to adapt to new technologies and knowledge domains. This proactive approach enhances cognitive flexibility and promotes sustained intellectual engagement across the lifespan.
Formal vs. Informal Education Pathways
Lifelong learning encompasses both formal and informal education pathways, where formal education involves structured programs like degrees and certificates typically offered by institutions. Informal education pathways include self-directed learning, workshops, and experiential activities that promote continuous skill development outside traditional classrooms. Adult education often prioritizes formal credentials but increasingly integrates informal methods to address diverse learner needs and evolving skill demands.
The Role of Technology in Lifelong Learning
Technology plays a pivotal role in lifelong learning by providing flexible, accessible platforms such as MOOCs, mobile apps, and virtual classrooms that cater to diverse learning needs. Digital tools enable personalized learning experiences through adaptive algorithms and real-time feedback, enhancing skill acquisition and knowledge retention. The integration of AI-driven content, interactive simulations, and collaborative online communities fosters continuous skill development beyond traditional adult education frameworks.
Addressing Barriers in Adult Education
Addressing barriers in adult education requires tailored strategies that consider diverse learning needs, socioeconomic challenges, and time constraints faced by adult learners. Integrating flexible scheduling, accessible learning technologies, and supportive community resources enhances engagement and retention in continuing education programs. Overcoming psychological barriers such as fear of failure and lack of confidence also plays a critical role in fostering lifelong learning habits.
Societal Impact of Lifelong Learning
Lifelong learning fosters continuous skill development, enhancing workforce adaptability and driving economic growth in rapidly changing industries. It promotes social inclusion by providing diverse populations with ongoing access to knowledge, reducing inequalities and supporting community resilience. This inclusive educational approach strengthens civic engagement and cultural awareness, contributing to more cohesive and informed societies.
Future Trends in Continuing Education
Future trends in continuing education emphasize personalized learning pathways driven by artificial intelligence and adaptive technologies, enabling learners to acquire skills tailored to rapidly evolving job markets. Integration of micro-credentials and stackable certificates offers flexible, modular options that support continuous upskilling and reskilling throughout life. Emphasis on digital platforms and virtual reality enhances accessibility and engagement, bridging gaps between lifelong learning and formal adult education frameworks.
Lifelong Learning vs Adult Education Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com