Noncredit courses offer flexible learning opportunities without the pressure of grades, making them ideal for skill development or personal enrichment. Credit courses provide a structured curriculum with assessments that contribute toward degree or certificate requirements, enhancing academic progress and career prospects. Choosing between noncredit and credit courses depends on your goals, whether seeking knowledge for personal growth or credits for formal education.
Table of Comparison
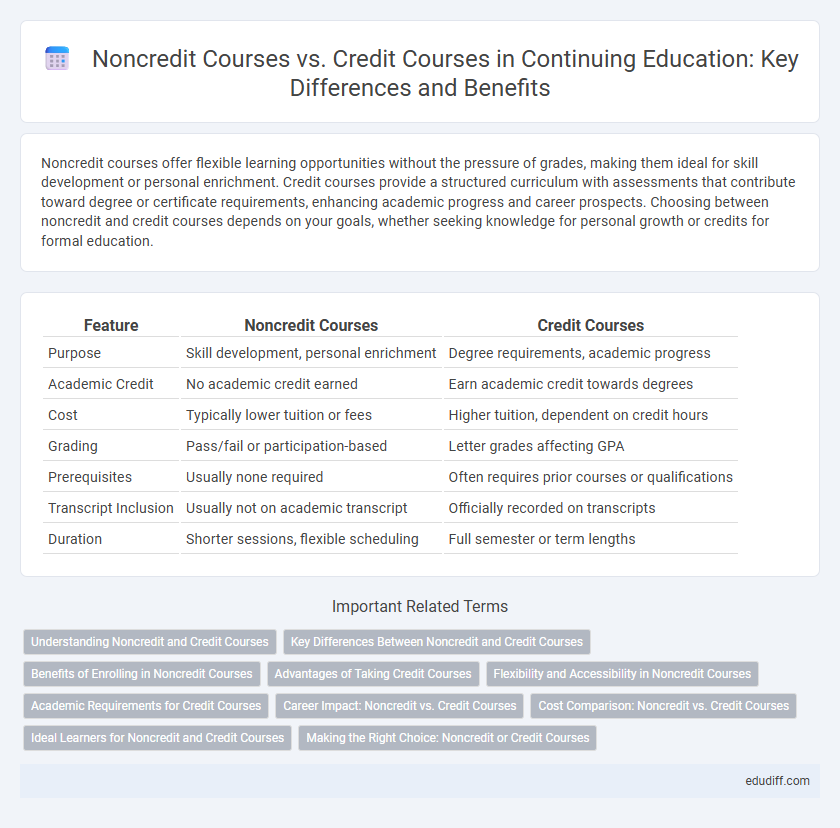
| Feature | Noncredit Courses | Credit Courses |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Skill development, personal enrichment | Degree requirements, academic progress |
| Academic Credit | No academic credit earned | Earn academic credit towards degrees |
| Cost | Typically lower tuition or fees | Higher tuition, dependent on credit hours |
| Grading | Pass/fail or participation-based | Letter grades affecting GPA |
| Prerequisites | Usually none required | Often requires prior courses or qualifications |
| Transcript Inclusion | Usually not on academic transcript | Officially recorded on transcripts |
| Duration | Shorter sessions, flexible scheduling | Full semester or term lengths |
Understanding Noncredit and Credit Courses
Credit courses offer students the opportunity to earn academic credits that count towards a degree or certification, typically involving graded assessments and a structured curriculum. Noncredit courses prioritize skill development or personal enrichment without providing credits applicable to formal academic programs, often featuring flexible scheduling and diverse topics. Understanding the distinction helps learners select courses aligned with their educational goals, whether for career advancement, personal growth, or degree completion.
Key Differences Between Noncredit and Credit Courses
Noncredit courses typically provide skill development or personal enrichment without contributing to a degree, whereas credit courses are part of a formal academic program that counts toward graduation requirements. Noncredit classes often have open enrollment and flexible schedules, while credit courses usually require prerequisites and maintain academic standards like graded assessments. Cost and transferability of credits also differ, with credit courses generally having higher tuition and recognized credit transfer across accredited institutions.
Benefits of Enrolling in Noncredit Courses
Enrolling in noncredit courses offers flexible learning opportunities without the pressure of grades or GPA impact, appealing to adult learners and professionals seeking skill enhancement. These courses often provide practical, career-focused training that can be completed more quickly than traditional credit courses, facilitating immediate application in the workplace. Access to noncredit courses supports lifelong learning, personal enrichment, and can serve as a stepping stone toward formal education credentials.
Advantages of Taking Credit Courses
Credit courses provide academic recognition and contribute directly to degree completion, offering official transcripts that can enhance employment prospects and graduate school applications. They often include structured learning outcomes and assessment methods that ensure a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter. Moreover, credit courses may qualify for financial aid, making higher education more accessible to students.
Flexibility and Accessibility in Noncredit Courses
Noncredit courses offer greater flexibility by allowing learners to enroll without strict prerequisites or rigid scheduling, making education more accessible to a wider audience. These courses often provide online, evening, and weekend options tailored to accommodate working adults or busy individuals. The accessibility of noncredit programs supports lifelong learning and skill development without the pressure of grades or formal assessments.
Academic Requirements for Credit Courses
Credit courses require students to meet specific academic prerequisites such as minimum GPA, prerequisite coursework, and departmental approval, ensuring preparedness for advanced material. These courses align with degree requirements, contributing credits towards graduation and maintaining academic standards set by educational institutions. Noncredit courses, in contrast, do not impact academic standing or credit accumulation and often have more flexible enrollment criteria.
Career Impact: Noncredit vs. Credit Courses
Noncredit courses provide practical skills and flexibility, ideal for career changers or professionals seeking immediate job-related knowledge without the commitment of degree requirements. Credit courses contribute to academic credentials, enhancing professional qualifications and increasing opportunities for advancement or higher-paying roles within structured career paths. Employers often value credit courses for their rigor and standardized evaluation, while noncredit courses offer targeted expertise that can quickly boost job performance.
Cost Comparison: Noncredit vs. Credit Courses
Noncredit courses typically have lower tuition fees compared to credit courses, making them an affordable option for skill development and personal enrichment. Credit courses often include additional fees such as lab, technology, and student activity fees, increasing the overall cost significantly. Financial aid and scholarships usually apply only to credit courses, which can offset their higher price for eligible students.
Ideal Learners for Noncredit and Credit Courses
Ideal learners for noncredit courses are individuals seeking skill enhancement, professional development, or personal enrichment without the pressure of grades or degrees, often including working professionals, hobbyists, and adult learners. Credit courses attract students pursuing formal education credentials, such as degrees or certificates, typically including traditional college students and those aiming for academic or career advancement. Both course types cater to specific learner goals, with noncredit focusing on flexible, accessible learning and credit courses emphasizing accredited, structured academic progress.
Making the Right Choice: Noncredit or Credit Courses
Choosing between noncredit and credit courses depends on your academic and career goals, as credit courses contribute toward degree completion and often transfer between institutions. Noncredit courses offer flexible learning opportunities for skill development, professional advancement, or personal enrichment without affecting GPA or degree requirements. Evaluating your long-term objectives, time commitment, and financial resources will help determine whether credit-bearing coursework or noncredit programs align better with your educational pathway.
Noncredit Courses vs Credit Courses Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com