Blended learning combines in-person and online instruction, offering pets interactive and hands-on experiences that enhance their training effectiveness. Fully remote learning relies solely on digital tools, providing flexibility and convenience but potentially limiting real-time socialization and direct guidance. Each approach caters to different needs, balancing engagement, accessibility, and personalized support for pet education.
Table of Comparison
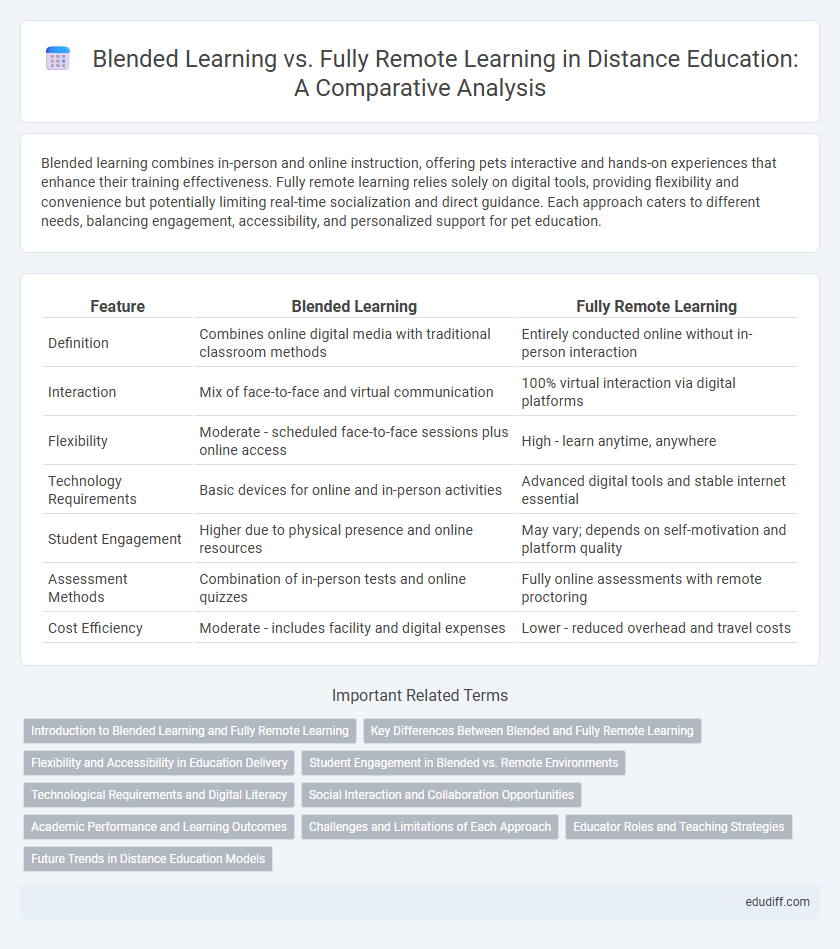
| Feature | Blended Learning | Fully Remote Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines online digital media with traditional classroom methods | Entirely conducted online without in-person interaction |
| Interaction | Mix of face-to-face and virtual communication | 100% virtual interaction via digital platforms |
| Flexibility | Moderate - scheduled face-to-face sessions plus online access | High - learn anytime, anywhere |
| Technology Requirements | Basic devices for online and in-person activities | Advanced digital tools and stable internet essential |
| Student Engagement | Higher due to physical presence and online resources | May vary; depends on self-motivation and platform quality |
| Assessment Methods | Combination of in-person tests and online quizzes | Fully online assessments with remote proctoring |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate - includes facility and digital expenses | Lower - reduced overhead and travel costs |
Introduction to Blended Learning and Fully Remote Learning
Blended learning integrates online digital media with traditional classroom methods, enabling flexible pacing and interactive engagement while maintaining face-to-face instruction. Fully remote learning occurs entirely online, relying on virtual platforms for communication, content delivery, and assessment without physical presence. Both approaches leverage technology but differ in structure, with blended learning offering hybrid flexibility and fully remote learning providing complete geographic independence.
Key Differences Between Blended and Fully Remote Learning
Blended learning combines in-person instruction with online components, allowing students to benefit from direct interaction and digital flexibility, whereas fully remote learning relies exclusively on virtual platforms for all educational activities. Key differences include the level of social engagement, where blended learning fosters face-to-face collaboration, and the mode of content delivery, with remote learning depending entirely on internet connectivity and digital tools. Assessment methods also vary; blended learning often incorporates both traditional and online evaluations, while fully remote learning utilizes digital assessments and online proctoring systems.
Flexibility and Accessibility in Education Delivery
Blended learning combines face-to-face instruction with online components, offering increased flexibility by allowing students to access materials anytime while maintaining direct interaction with instructors. Fully remote learning maximizes accessibility by removing geographical barriers, enabling students from diverse locations to engage in education without commuting. Both models enhance educational delivery but differ in balancing synchronous engagement and autonomous study.
Student Engagement in Blended vs. Remote Environments
Blended learning environments enhance student engagement by combining face-to-face interactions with digital content, fostering collaborative activities and immediate feedback. Fully remote learning relies heavily on virtual tools, which can limit spontaneous peer communication and reduce motivation due to physical isolation. Research shows that engagement metrics such as participation rates and assignment completion are typically higher in blended settings compared to fully remote counterparts.
Technological Requirements and Digital Literacy
Blended learning demands reliable access to both physical classroom technology and online platforms, requiring moderate digital literacy to navigate hybrid systems effectively. Fully remote learning depends heavily on stable internet connections, advanced software tools, and higher digital literacy to manage virtual environments independently. Mastery of video conferencing, learning management systems, and troubleshooting connectivity issues is crucial for success in fully remote settings.
Social Interaction and Collaboration Opportunities
Blended learning combines in-person classes with online components, enhancing social interaction and collaboration through face-to-face discussions and group activities alongside digital tools. Fully remote learning relies on virtual platforms, which can limit spontaneous social exchanges but offers structured collaboration via video calls, chat forums, and shared documents. The hybrid approach fosters stronger peer connections and engagement, while fully remote models require deliberate strategies to maintain social presence and teamwork.
Academic Performance and Learning Outcomes
Blended learning combines in-person and online instruction, often resulting in higher academic performance due to increased engagement and immediate feedback. Fully remote learning relies exclusively on digital platforms, which can challenge student motivation and interaction, sometimes leading to inconsistent learning outcomes. Studies indicate that blended learning environments typically produce better retention and comprehension compared to fully remote models.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Blended learning faces challenges such as inconsistent access to technology and difficulties in balancing in-person and online instruction, which can hinder student engagement and continuity. Fully remote learning struggles with limitations like reduced face-to-face interaction, leading to potential isolation and decreased motivation among learners. Both approaches encounter obstacles in ensuring equitable access to resources, effective communication, and maintaining student accountability.
Educator Roles and Teaching Strategies
Blended learning requires educators to balance in-person engagement with digital facilitation, employing strategies such as flipped classrooms and interactive media to enhance student participation. Fully remote learning demands proficiency in virtual communication tools and adaptive structuring of asynchronous and synchronous sessions to maintain instructional momentum. Both modalities necessitate continuous assessment techniques and personalized feedback mechanisms to support diverse learner needs effectively.
Future Trends in Distance Education Models
Blended learning integrates in-person and online experiences, enhancing flexibility and engagement through synchronous and asynchronous methods, while fully remote learning relies entirely on digital platforms, offering accessibility regardless of location. Emerging trends indicate a rise in adaptive learning technologies and AI-driven personalized content, optimizing student outcomes in both models. Data from recent studies show that hybrid approaches combining face-to-face interaction with remote accessibility are predicted to dominate future distance education landscapes.
Blended learning vs Fully remote learning Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com