Inquiry-based learning encourages students to explore questions and discover solutions independently, fostering critical thinking and deep understanding. Direct instruction provides clear, structured guidance from the teacher, ensuring foundational knowledge is effectively conveyed. Combining both methods can enhance student engagement and improve learning outcomes by balancing exploration with clear explanations.
Table of Comparison
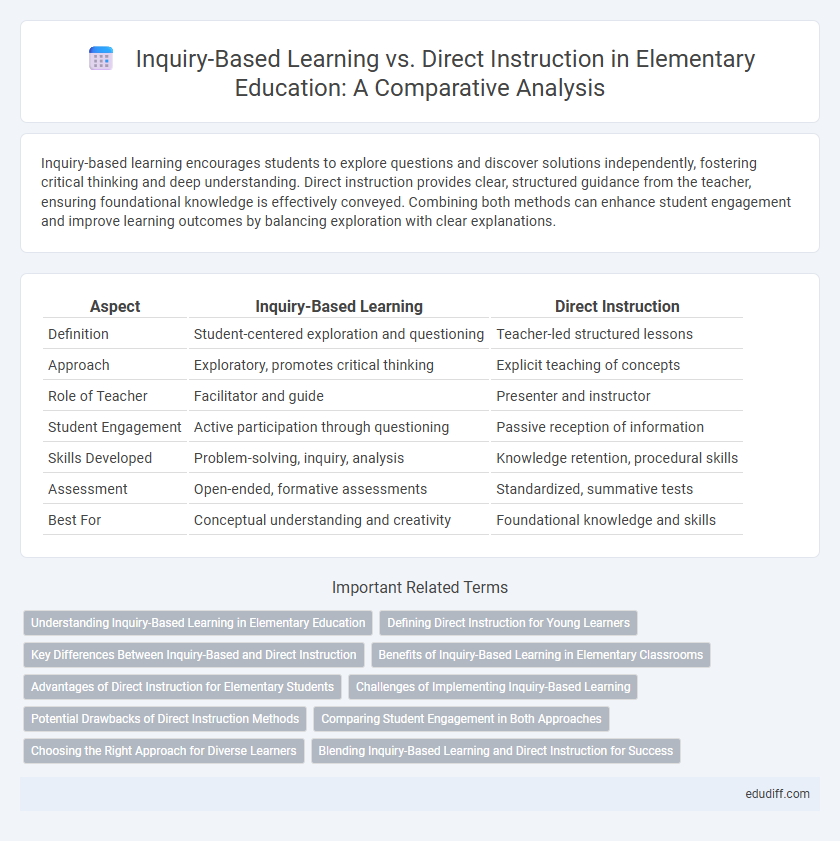
| Aspect | Inquiry-Based Learning | Direct Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-centered exploration and questioning | Teacher-led structured lessons |
| Approach | Exploratory, promotes critical thinking | Explicit teaching of concepts |
| Role of Teacher | Facilitator and guide | Presenter and instructor |
| Student Engagement | Active participation through questioning | Passive reception of information |
| Skills Developed | Problem-solving, inquiry, analysis | Knowledge retention, procedural skills |
| Assessment | Open-ended, formative assessments | Standardized, summative tests |
| Best For | Conceptual understanding and creativity | Foundational knowledge and skills |
Understanding Inquiry-Based Learning in Elementary Education
Inquiry-Based Learning in elementary education emphasizes student curiosity and active exploration, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills through hands-on activities and collaborative projects. This approach encourages children to ask questions, investigate, and draw conclusions, which deepens conceptual understanding and promotes engagement. Compared to direct instruction, inquiry-based learning supports deeper retention and application of knowledge by making learning relevant and student-centered.
Defining Direct Instruction for Young Learners
Direct Instruction for young learners emphasizes structured, teacher-led lessons where clear, explicit teaching of foundational skills occurs through step-by-step guidance and practice. This approach ensures mastery of basic concepts by breaking down complex tasks into manageable parts, allowing immediate feedback and correction. It supports early skill acquisition critical for reading, math, and social development in elementary education.
Key Differences Between Inquiry-Based and Direct Instruction
Inquiry-based learning emphasizes student exploration and active problem-solving, fostering critical thinking and deeper understanding through hands-on activities and open-ended questions. Direct instruction relies on structured, teacher-led lessons with clear objectives, step-by-step guidance, and immediate feedback to ensure mastery of specific skills and knowledge. The key difference lies in student autonomy and discovery in inquiry-based learning versus teacher control and explicit teaching in direct instruction.
Benefits of Inquiry-Based Learning in Elementary Classrooms
Inquiry-Based Learning in elementary classrooms fosters critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving skills by encouraging students to explore and ask questions actively. This approach enhances student engagement and motivation, leading to deeper understanding and retention of knowledge compared to traditional Direct Instruction methods. Research shows that inquiry-based strategies improve collaboration and communication skills, preparing young learners for future academic success and lifelong learning.
Advantages of Direct Instruction for Elementary Students
Direct instruction provides clear, structured guidance that helps elementary students grasp foundational concepts quickly and efficiently. It reduces cognitive load by breaking down complex tasks into manageable steps, fostering confidence and mastery. Consistent routines and explicit feedback in direct instruction enhance student engagement and academic performance in early learning stages.
Challenges of Implementing Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning in elementary education faces challenges such as limited classroom time, which restricts deep exploration of topics. Teachers often require extensive training to effectively guide students' open-ended questions and manage diverse learning paces. Resource constraints, including access to appropriate materials and technology, further complicate the practical implementation of inquiry-based methods.
Potential Drawbacks of Direct Instruction Methods
Direct instruction methods can limit students' creativity and critical thinking by emphasizing rote memorization and passive learning. This approach may reduce opportunities for students to explore concepts deeply or develop problem-solving skills. Over-reliance on teacher-led explanations can also hinder student engagement and reduce motivation to discover knowledge independently.
Comparing Student Engagement in Both Approaches
Inquiry-based learning fosters higher student engagement by encouraging active exploration and critical thinking, allowing elementary students to connect concepts with real-world experiences. Direct instruction provides structured guidance, which can boost engagement through clear expectations and immediate feedback but may limit opportunities for creative problem-solving. Research shows that combining both methods maximizes engagement by balancing student autonomy with teacher support, enhancing motivation and deeper understanding.
Choosing the Right Approach for Diverse Learners
Inquiry-Based Learning encourages elementary students to explore concepts through hands-on activities and critical thinking, fostering deeper understanding and curiosity. Direct Instruction provides clear, structured guidance, which benefits learners needing explicit explanations and step-by-step support. Selecting the right approach depends on individual student needs, with flexible integration enhancing engagement and academic success in diverse classrooms.
Blending Inquiry-Based Learning and Direct Instruction for Success
Blending Inquiry-Based Learning with Direct Instruction in elementary classrooms fosters a balanced approach that promotes critical thinking alongside foundational skill development. This combination allows teachers to guide students through structured lessons while encouraging exploration and curiosity, enhancing engagement and deep understanding. Research indicates that integrating both methods improves student achievement by catering to diverse learning styles and supporting knowledge retention.
Inquiry-Based Learning vs Direct Instruction Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com