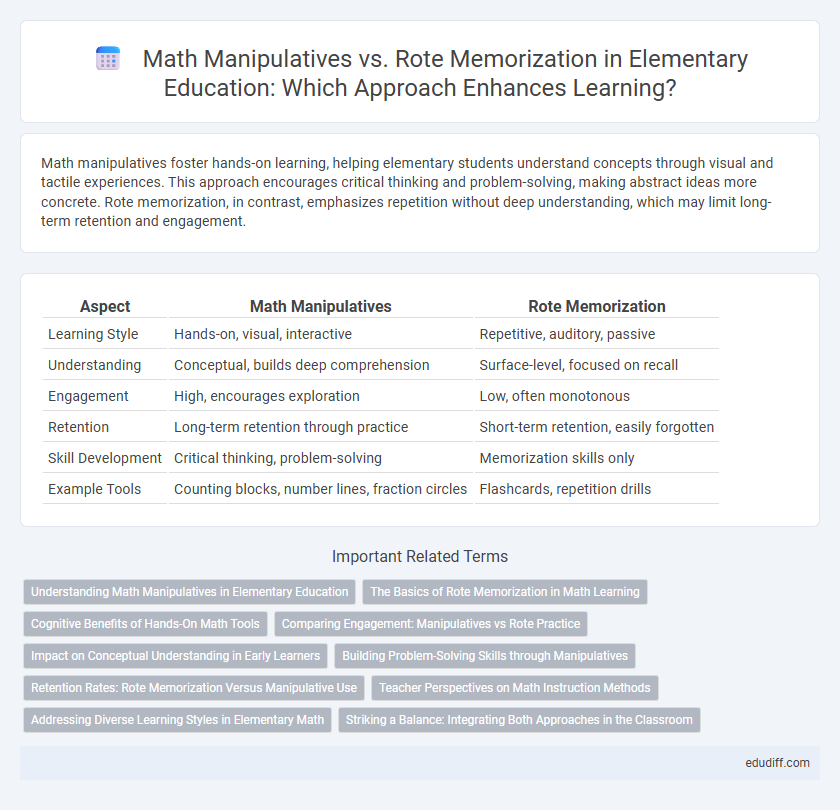
Math manipulatives foster hands-on learning, helping elementary students understand concepts through visual and tactile experiences. This approach encourages critical thinking and problem-solving, making abstract ideas more concrete. Rote memorization, in contrast, emphasizes repetition without deep understanding, which may limit long-term retention and engagement.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Math Manipulatives | Rote Memorization |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Style | Hands-on, visual, interactive | Repetitive, auditory, passive |
| Understanding | Conceptual, builds deep comprehension | Surface-level, focused on recall |
| Engagement | High, encourages exploration | Low, often monotonous |
| Retention | Long-term retention through practice | Short-term retention, easily forgotten |
| Skill Development | Critical thinking, problem-solving | Memorization skills only |
| Example Tools | Counting blocks, number lines, fraction circles | Flashcards, repetition drills |
Understanding Math Manipulatives in Elementary Education
Math manipulatives in elementary education enhance conceptual understanding by providing hands-on experiences that make abstract math concepts tangible. Using objects like blocks, counters, and shapes helps students visualize addition, subtraction, and fractions, fostering deeper cognitive connections than rote memorization alone. This tactile approach supports differentiated learning styles and improves problem-solving skills by encouraging exploration and interaction with mathematical ideas.
The Basics of Rote Memorization in Math Learning
Rote memorization in math learning involves repetitive practice to quickly recall basic facts such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. This method builds foundational fluency but may limit deeper conceptual understanding and problem-solving skills. Effective math instruction balances rote memorization with hands-on manipulatives to enhance both memory and comprehension.
Cognitive Benefits of Hands-On Math Tools
Hands-on math tools enhance cognitive development by promoting active engagement and concrete understanding of abstract concepts, which strengthens problem-solving skills and memory retention. Manipulatives like blocks and counters provide sensory experiences that support spatial reasoning and logical thinking, aiding in the transfer of knowledge to new mathematical situations. In contrast, rote memorization often limits deep comprehension, making manipulatives essential for fostering meaningful math learning in elementary education.
Comparing Engagement: Manipulatives vs Rote Practice
Math manipulatives increase engagement by providing hands-on, tactile experiences that help elementary students visualize and understand abstract concepts. In contrast, rote memorization often leads to passive learning, where students repeat information without deeper comprehension. Using manipulatives fosters active participation and critical thinking, making math lessons more interactive and effective for young learners.
Impact on Conceptual Understanding in Early Learners
Math manipulatives significantly enhance conceptual understanding in early learners by providing tangible experiences that connect abstract mathematical ideas to real-world objects. In contrast, rote memorization often leads to superficial learning, limiting the ability to apply concepts in varied contexts. Research indicates that early exposure to hands-on tools like blocks and counters promotes deeper cognitive engagement and long-term retention of foundational math skills.
Building Problem-Solving Skills through Manipulatives
Math manipulatives enhance elementary students' understanding by providing hands-on experiences that foster critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Unlike rote memorization, manipulatives allow learners to explore mathematical concepts visually and physically, leading to deeper comprehension and long-term retention. Using tools such as blocks, counters, and number lines supports the development of analytical skills and encourages flexible thinking in solving math problems.
Retention Rates: Rote Memorization Versus Manipulative Use
Math manipulatives improve retention rates by engaging multiple senses, allowing students to understand concepts through hands-on experience rather than memorizing facts. Research shows that students using manipulatives retain information longer and apply math skills more effectively compared to those relying on rote memorization. Utilizing tools like blocks, counters, and visual aids strengthens conceptual understanding and supports long-term learning in elementary math education.
Teacher Perspectives on Math Instruction Methods
Teachers recognize that math manipulatives enhance conceptual understanding by allowing students to visualize and physically interact with mathematical concepts. In contrast, rote memorization tends to focus on repetition without deep comprehension, which can limit students' ability to apply math skills in varied contexts. Educators emphasize manipulatives as a tool to promote critical thinking, problem-solving, and long-term retention in elementary math instruction.
Addressing Diverse Learning Styles in Elementary Math
Math manipulatives enhance comprehension by providing tactile and visual experiences that cater to kinesthetic and spatial learners, making abstract concepts tangible. Rote memorization, while useful for reinforcing basic math facts, often neglects the needs of students who benefit from interactive and hands-on learning approaches. Integrating manipulatives in elementary math instruction effectively addresses diverse learning styles, improving engagement and mastery of foundational numeracy skills.
Striking a Balance: Integrating Both Approaches in the Classroom
Integrating math manipulatives with rote memorization fosters deeper conceptual understanding and efficient recall in elementary classrooms. Hands-on tools like counting blocks and number lines enhance students' grasp of abstract concepts, while memorization of math facts ensures quick problem-solving skills. Striking a balance between these methods supports diverse learning styles and promotes long-term mathematical proficiency.
Math Manipulatives vs Rote Memorization Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com