A deferral postpones the start of a graduate pet program, allowing admitted students to delay enrollment for a specified period without losing their spot. A leave of absence occurs after enrollment, enabling current students to temporarily pause their studies while maintaining their status. Understanding the policies and duration limits for deferral and leave of absence ensures smooth academic planning and continuity in graduate pet studies.
Table of Comparison
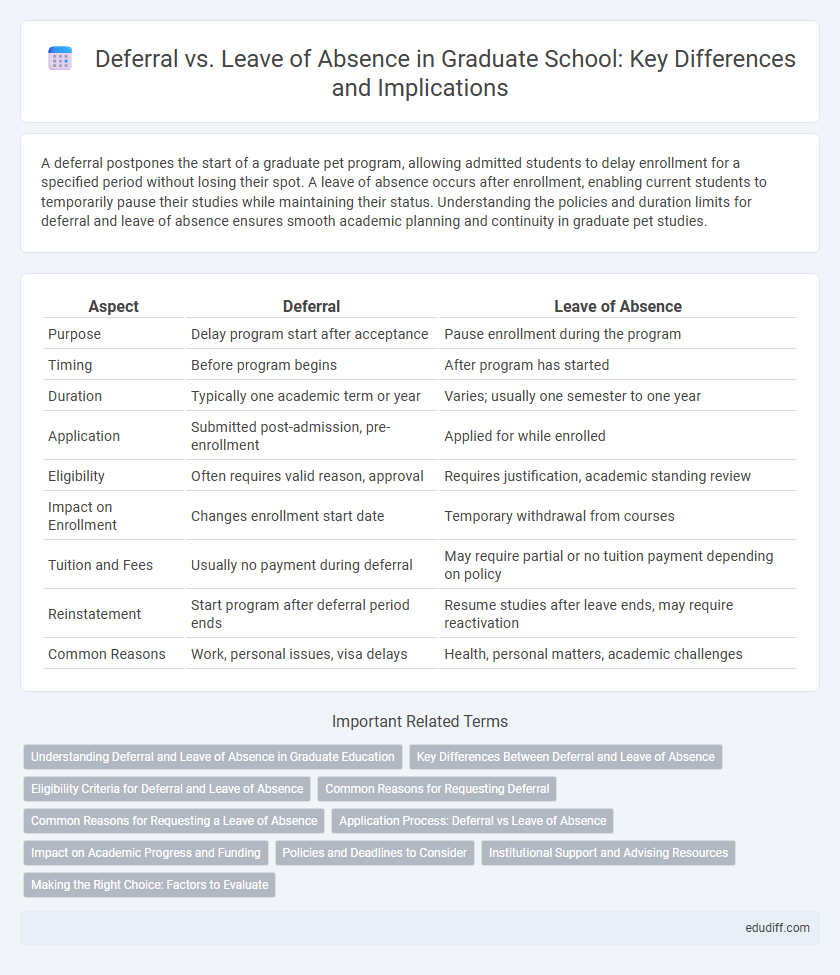
| Aspect | Deferral | Leave of Absence |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Delay program start after acceptance | Pause enrollment during the program |
| Timing | Before program begins | After program has started |
| Duration | Typically one academic term or year | Varies; usually one semester to one year |
| Application | Submitted post-admission, pre-enrollment | Applied for while enrolled |
| Eligibility | Often requires valid reason, approval | Requires justification, academic standing review |
| Impact on Enrollment | Changes enrollment start date | Temporary withdrawal from courses |
| Tuition and Fees | Usually no payment during deferral | May require partial or no tuition payment depending on policy |
| Reinstatement | Start program after deferral period ends | Resume studies after leave ends, may require reactivation |
| Common Reasons | Work, personal issues, visa delays | Health, personal matters, academic challenges |
Understanding Deferral and Leave of Absence in Graduate Education
Deferral in graduate education allows admitted students to postpone their enrollment to a future term without reapplying, typically due to personal, financial, or professional reasons. A Leave of Absence is granted to currently enrolled graduate students who temporarily interrupt their studies, often to manage unforeseen circumstances or pursue opportunities without losing their academic standing. Both options require formal approval from the institution and have specific policies regarding duration, eligibility, and impact on funding or program progression.
Key Differences Between Deferral and Leave of Absence
Deferral refers to postponing the start of a graduate program before enrollment, while a Leave of Absence is a temporary break taken after a student has already begun the program. Key differences include timing--deferral occurs pre-admission, leave of absence occurs mid-enrollment--and purpose, where deferral often addresses admission or personal scheduling issues, whereas leave of absence typically accommodates health, family, or academic reasons. Institutional policies vary, but deferral usually requires a formal request before matriculation, and leave of absence demands approval during active enrollment, with distinct implications for tuition, financial aid, and academic progression.
Eligibility Criteria for Deferral and Leave of Absence
Eligibility criteria for deferral typically require graduate students to have an accepted admission offer but need to delay enrollment due to personal, medical, or professional reasons, often limited to one academic term or year. Leave of absence eligibility generally applies to currently enrolled graduate students facing temporary circumstances such as health issues, family emergencies, or military service, with institutions requiring formal approval and documentation. Both deferral and leave of absence policies usually mandate timely application submission and adherence to specific deadlines set by the graduate program or university registrar.
Common Reasons for Requesting Deferral
Common reasons for requesting a deferral in graduate programs include personal health issues, financial constraints, and unexpected professional opportunities. Students may also seek deferral due to family emergencies, visa or immigration delays, and the need for additional preparation before starting their studies. Universities often require documentation to support these valid reasons when approving deferral requests.
Common Reasons for Requesting a Leave of Absence
Graduate students commonly request a leave of absence due to personal health issues, family emergencies, or unforeseen financial difficulties. Academic challenges such as the need for additional time to complete research or address program requirements also frequently prompt such requests. Leaves of absence enable students to pause their studies without losing enrollment status, preserving their ability to return and finish their graduate programs.
Application Process: Deferral vs Leave of Absence
The application process for deferral typically requires submitting a formal request before the program start date, accompanied by valid reasons such as personal, health, or financial issues, and may include supporting documents for approval by the admissions office. Leave of absence applications occur after enrollment and demand completion of institutional forms, justification for the leave period, and adherence to deadlines set by the registrar or academic affairs. Both processes involve different procedural requirements, processing times, and potential impacts on academic progression and financial aid eligibility.
Impact on Academic Progress and Funding
Deferral delays enrollment, preserving funding eligibility but postponing academic progress, while a Leave of Absence temporarily pauses studies without affecting current funding status but may require reapplication for financial aid. Graduate students opting for deferral typically maintain guaranteed funding for their starting term, whereas leaves may risk loss of scholarships or assistantships depending on institutional policies. Careful consideration of program timelines and funding requirements is crucial to minimizing disruption in degree completion and financial support.
Policies and Deadlines to Consider
Graduate programs often differentiate between deferral and leave of absence policies, with deferral allowing admitted students to delay enrollment typically for one academic year and requiring formal approval before a specified deadline. Leave of absence policies apply to current students seeking a temporary break from their studies, usually necessitating documentation and adherence to program-specific deadlines to maintain enrollment status. Understanding each policy's timelines and requirements is crucial to avoid losing admission offers or facing readmission complications.
Institutional Support and Advising Resources
Institutions typically offer comprehensive advising resources to guide graduate students through the deferral or leave of absence process, ensuring individualized support based on academic and personal circumstances. Deferral policies often involve specific deadlines and documentation, with advisors helping to align delayed enrollment or project timelines with institutional requirements. Leave of absence options provide structured academic breaks, where advisors coordinate with students to plan re-entry and maintain access to university services and resources during the interim.
Making the Right Choice: Factors to Evaluate
Graduate students must carefully evaluate factors such as program policies, financial implications, and academic goals when choosing between deferral and leave of absence. Deferral typically allows a student to postpone enrollment before starting, maintaining admission status without active participation, whereas a leave of absence usually permits temporary withdrawal during active enrollment with the intent to resume studies later. Considering personal circumstances, the impact on funding or scholarships, and potential effects on graduation timelines is crucial for making the right choice.
Deferral vs Leave of Absence Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com