Independent study allows graduate students to explore topics at their own pace with minimal supervision, fostering self-discipline and personalized learning. Directed study involves more structured guidance from faculty, providing targeted expertise and regular feedback to deepen understanding of specialized subjects. Choosing between these options depends on a student's learning style, academic goals, and desire for autonomy versus mentorship.
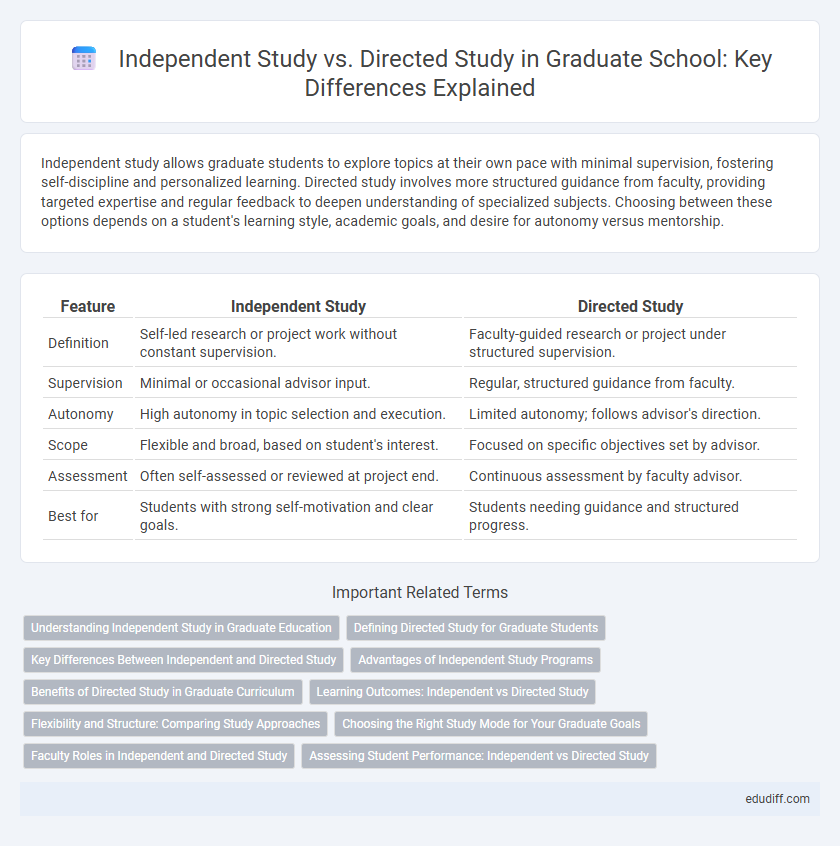
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Independent Study | Directed Study |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Self-led research or project work without constant supervision. | Faculty-guided research or project under structured supervision. |
| Supervision | Minimal or occasional advisor input. | Regular, structured guidance from faculty. |
| Autonomy | High autonomy in topic selection and execution. | Limited autonomy; follows advisor's direction. |
| Scope | Flexible and broad, based on student's interest. | Focused on specific objectives set by advisor. |
| Assessment | Often self-assessed or reviewed at project end. | Continuous assessment by faculty advisor. |
| Best for | Students with strong self-motivation and clear goals. | Students needing guidance and structured progress. |
Understanding Independent Study in Graduate Education
Independent study in graduate education empowers students to pursue specialized research topics under minimal supervision, fostering critical thinking and self-discipline essential for advanced academic success. Unlike directed study, which involves structured guidance from faculty and predetermined objectives, independent study allows for greater autonomy in designing research scope and methodologies. This approach enhances deep subject matter expertise and prepares graduates for professional or doctoral-level research challenges.
Defining Directed Study for Graduate Students
Directed Study for graduate students involves structured, faculty-supervised research or coursework tailored to specific academic interests, typically with predetermined objectives and regular mentor guidance. Unlike Independent Study, Directed Study requires more direct interaction with a professor to ensure alignment with program requirements and learning outcomes. This format supports in-depth exploration of specialized topics while maintaining academic rigor through consistent oversight.
Key Differences Between Independent and Directed Study
Independent study allows graduate students to design and pursue their own research projects with minimal faculty supervision, fostering autonomy and self-motivation. Directed study involves structured guidance from a faculty advisor who provides tailored support, direction, and feedback throughout the research process. The key difference lies in the level of oversight, where independent study emphasizes student-driven inquiry and directed study ensures more faculty involvement and academic accountability.
Advantages of Independent Study Programs
Independent Study programs offer graduate students the flexibility to tailor their coursework according to individual research interests, promoting deeper subject mastery and critical thinking skills. These programs encourage self-discipline and time management, essential qualities for successful academic and professional careers. Access to diverse resources and personalized mentorship enhances the overall learning experience, fostering innovation and academic independence.
Benefits of Directed Study in Graduate Curriculum
Directed Study in graduate curriculum offers structured guidance from faculty, enhancing academic rigor and ensuring alignment with program goals. It facilitates in-depth exploration of specialized topics while promoting critical thinking through regular feedback and mentorship. This approach also supports tailored learning objectives, fostering professional skills applicable to research or industry settings.
Learning Outcomes: Independent vs Directed Study
Independent Study fosters self-directed learning, critical thinking, and time management, allowing graduate students to explore topics deeply based on personal interests and pace. Directed Study provides structured guidance and clear objectives from faculty, ensuring focused mastery of specific concepts and skills aligned with curriculum standards. Both approaches enhance graduate-level competencies but differ in autonomy and instructor involvement, impacting the depth and style of learning outcomes.
Flexibility and Structure: Comparing Study Approaches
Independent study offers graduate students the flexibility to tailor research topics and schedules, fostering self-motivation and personalized learning paths. Directed study provides a more structured environment with guidance from faculty advisors, ensuring focused progress and resource support. Both approaches cater to different learning styles and academic goals by balancing autonomy and oversight.
Choosing the Right Study Mode for Your Graduate Goals
Independent Study offers graduate students flexibility to explore specialized topics deeply while developing self-discipline and research skills. Directed Study provides structured guidance from faculty, ideal for those seeking close mentorship and targeted academic support. Selecting between these modes depends on your graduate goals, learning style, and need for supervision to maximize academic growth and research outcomes.
Faculty Roles in Independent and Directed Study
Faculty roles in Independent Study involve mentoring students through self-designed research projects, providing guidance on methodology and resource selection while allowing significant autonomy. In Directed Study, faculty direct the curriculum and learning objectives more explicitly, offering structured supervision and regular assessments to ensure academic progress. Both approaches require faculty to balance support with fostering student independence, tailoring their involvement to the needs of graduate students.
Assessing Student Performance: Independent vs Directed Study
Assessing student performance in independent study relies heavily on self-motivation, critical thinking, and the ability to meet deadlines without constant supervision, often evaluated through portfolios, reflective journals, and project outcomes. Directed study assessments emphasize structured guidance and frequent instructor feedback, with evaluations based on targeted assignments, progress reports, and direct performance metrics. Independent study demands higher self-regulation, whereas directed study benefits from continuous instructor involvement, impacting the assessment criteria and learning outcomes in graduate education.
Independent Study vs Directed Study Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com