Career and Technical Education (CTE) equips high school students with practical skills and hands-on experience tailored to specific industries, enhancing their readiness for direct entry into the workforce or specialized training programs. General Education offers a broad academic foundation emphasizing critical thinking, communication, and theoretical knowledge across various subjects, preparing students for college and diverse career paths. Balancing CTE and General Education enables students to develop both specialized competencies and a well-rounded intellectual base for future success.
Table of Comparison
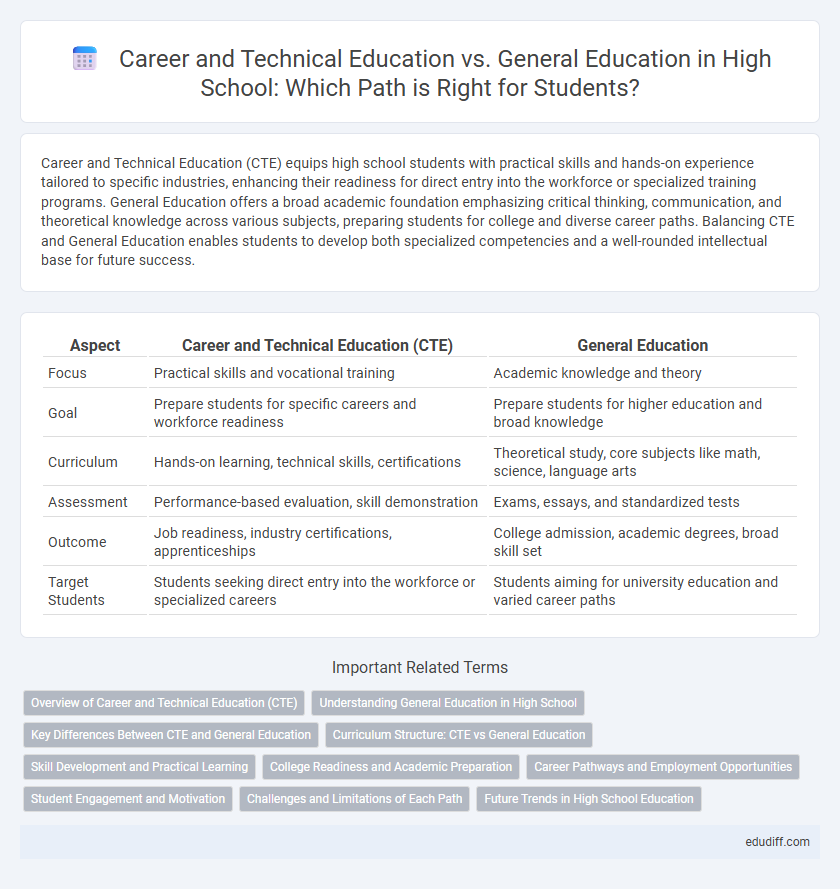
| Aspect | Career and Technical Education (CTE) | General Education |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Practical skills and vocational training | Academic knowledge and theory |
| Goal | Prepare students for specific careers and workforce readiness | Prepare students for higher education and broad knowledge |
| Curriculum | Hands-on learning, technical skills, certifications | Theoretical study, core subjects like math, science, language arts |
| Assessment | Performance-based evaluation, skill demonstration | Exams, essays, and standardized tests |
| Outcome | Job readiness, industry certifications, apprenticeships | College admission, academic degrees, broad skill set |
| Target Students | Students seeking direct entry into the workforce or specialized careers | Students aiming for university education and varied career paths |
Overview of Career and Technical Education (CTE)
Career and Technical Education (CTE) equips high school students with practical skills and industry-specific knowledge, preparing them for immediate employment or further education in specialized fields such as healthcare, information technology, and manufacturing. CTE programs combine classroom instruction with hands-on training, emphasizing real-world applications and career readiness. These programs contribute to workforce development by aligning curricula with labor market demands and offering certifications that enhance students' employability.
Understanding General Education in High School
General education in high school provides a broad foundation across core subjects such as math, science, English, and social studies, essential for developing critical thinking and communication skills. This comprehensive approach equips students with versatile knowledge necessary for college readiness and various career paths. Emphasizing general education helps students build adaptable competencies that support lifelong learning and informed citizenship.
Key Differences Between CTE and General Education
Career and Technical Education (CTE) emphasizes hands-on skills and industry-specific training in fields like healthcare, information technology, and manufacturing, preparing students directly for the workforce. General Education focuses on broad academic knowledge across subjects such as math, science, and literature, promoting critical thinking and college readiness. The key difference lies in CTE's practical, career-oriented curriculum versus General Education's theoretical, academic approach.
Curriculum Structure: CTE vs General Education
Career and Technical Education (CTE) curriculum emphasizes hands-on, skill-based training aligned with specific industries, integrating real-world applications and certifications within courses. General Education focuses on a broad academic foundation, covering subjects like math, science, language arts, and social studies to promote critical thinking and cognitive development. CTE programs often combine technical instruction with core academic content, whereas General Education maintains a traditional subject-based structure aiming for overall intellectual growth.
Skill Development and Practical Learning
Career and Technical Education (CTE) emphasizes hands-on skill development and practical learning tailored to specific trades or professions, enabling students to gain real-world experience and job readiness. General Education focuses on broad academic knowledge, critical thinking, and theoretical understanding across diverse subjects, which builds foundational skills but offers less direct application. Integrating CTE with General Education fosters comprehensive skill acquisition, balancing technical proficiency with intellectual growth essential for career adaptability.
College Readiness and Academic Preparation
Career and Technical Education (CTE) offers high school students practical skills and industry-specific knowledge, enhancing college readiness by aligning academic preparation with workforce demands. General Education provides a broad academic foundation that strengthens critical thinking and problem-solving abilities essential for diverse college disciplines. Integrating CTE with General Education can optimize academic preparation and improve postsecondary success rates by balancing hands-on experience with comprehensive theoretical knowledge.
Career Pathways and Employment Opportunities
Career and Technical Education (CTE) programs provide high school students with specialized training in industries such as healthcare, information technology, and manufacturing, equipping them with practical skills and certifications that directly enhance employability upon graduation. In contrast, General Education focuses on a broad academic curriculum designed to develop critical thinking and foundational knowledge, preparing students for a wide range of college majors and long-term career flexibility. CTE pathways often lead to immediate workforce entry or apprenticeships, while General Education supports diverse career options requiring advanced degrees, together addressing varied student goals in career readiness and academic achievement.
Student Engagement and Motivation
Career and Technical Education (CTE) programs in high schools significantly boost student engagement by offering hands-on, real-world learning experiences aligned with specific career paths. These practical opportunities increase motivation by connecting academic content to tangible goals, enhancing relevance and skill development. In contrast, General Education often emphasizes theoretical knowledge, which may result in lower engagement for students seeking immediate applicability and career preparation.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Path
Career and Technical Education (CTE) often faces challenges such as limited academic breadth and fewer opportunities for advanced theoretical learning compared to General Education, which can restrict students' access to traditional four-year college pathways. General Education programs frequently lack hands-on skill development and practical training, leading to potential gaps in job readiness upon graduation. Both paths struggle with balancing the depth of specialized skills and the flexibility required for evolving career landscapes, impacting long-term student success.
Future Trends in High School Education
Career and Technical Education (CTE) programs are increasingly integrating advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and robotics to better prepare students for evolving job markets. General Education remains essential for developing critical thinking and communication skills, yet schools are blending it with career-focused curricula to offer a more interdisciplinary approach. Future trends emphasize personalized learning pathways and partnerships with industry leaders to ensure students gain relevant skills for high-demand careers.
Career and Technical Education vs General Education Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com