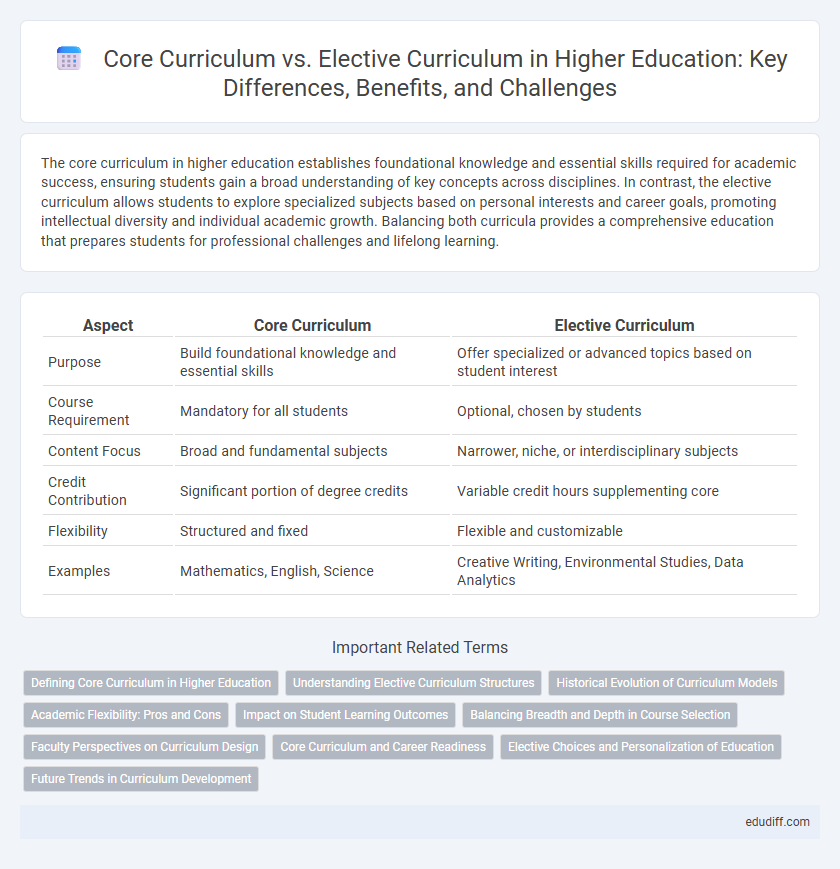
The core curriculum in higher education establishes foundational knowledge and essential skills required for academic success, ensuring students gain a broad understanding of key concepts across disciplines. In contrast, the elective curriculum allows students to explore specialized subjects based on personal interests and career goals, promoting intellectual diversity and individual academic growth. Balancing both curricula provides a comprehensive education that prepares students for professional challenges and lifelong learning.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Core Curriculum | Elective Curriculum |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Build foundational knowledge and essential skills | Offer specialized or advanced topics based on student interest |
| Course Requirement | Mandatory for all students | Optional, chosen by students |
| Content Focus | Broad and fundamental subjects | Narrower, niche, or interdisciplinary subjects |
| Credit Contribution | Significant portion of degree credits | Variable credit hours supplementing core |
| Flexibility | Structured and fixed | Flexible and customizable |
| Examples | Mathematics, English, Science | Creative Writing, Environmental Studies, Data Analytics |
Defining Core Curriculum in Higher Education
Core Curriculum in higher education consists of a structured set of foundational courses designed to provide all students with essential knowledge and critical thinking skills across various disciplines, such as humanities, sciences, and social sciences. This curriculum aims to ensure a well-rounded academic experience, fostering intellectual versatility and a common academic foundation. Unlike elective courses, core requirements are mandatory and serve to prepare students for advanced specialization and professional success.
Understanding Elective Curriculum Structures
Elective curriculum structures provide flexibility by allowing students to choose courses aligned with their interests and career goals, enhancing personalized learning pathways. These curricula often include interdisciplinary options that promote critical thinking and practical skills beyond the core requirements. Understanding the modular framework and credit distribution within elective systems is essential for optimizing academic planning and maximizing educational outcomes.
Historical Evolution of Curriculum Models
The historical evolution of curriculum models reveals a shift from rigid Core Curriculum frameworks, emphasizing classical knowledge and essential disciplines, to more flexible Elective Curriculum systems that prioritize student choice and specialization. Early 20th-century education largely centered around core subjects like literature, mathematics, and science, reflecting societal values and industrial needs. Contemporary models integrate interdisciplinary electives, responding to diverse student interests and evolving workforce demands in higher education.
Academic Flexibility: Pros and Cons
Core Curriculum provides a structured foundation ensuring students acquire essential knowledge across disciplines, enhancing academic consistency and skill development. Elective Curriculum offers academic flexibility, allowing students to tailor their studies to personal interests and career goals, promoting deeper engagement and specialization. However, excessive reliance on electives may lead to gaps in foundational skills, while a rigid core curriculum can limit exploration and adaptability in a rapidly evolving job market.
Impact on Student Learning Outcomes
Core Curriculum establishes foundational knowledge and essential skills that ensure a consistent academic baseline for all students, directly enhancing critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. Elective Curriculum offers personalized learning opportunities, fostering student engagement and motivation by aligning with individual interests and career goals. Balancing both curricula maximizes student learning outcomes by combining comprehensive knowledge acquisition with specialized skill development.
Balancing Breadth and Depth in Course Selection
Balancing breadth and depth in course selection within higher education requires integrating core curriculum that ensures foundational knowledge across disciplines with elective courses that allow students to specialize and explore personal academic interests. Core curricula provide essential skills in critical thinking, communication, and quantitative reasoning, forming a comprehensive academic base. Elective curricula enable deeper engagement in specific fields, fostering expertise and supporting career readiness while maintaining intellectual diversity.
Faculty Perspectives on Curriculum Design
Faculty perspectives on curriculum design emphasize the balance between core curriculum and elective curriculum to foster comprehensive academic development. Core curricula establish foundational knowledge and critical thinking skills across disciplines, while elective curricula provide opportunities for specialization and student-driven learning. Faculty members prioritize alignment with institutional goals, employability, and adaptability to evolving industry standards when shaping curriculum structures.
Core Curriculum and Career Readiness
Core Curriculum provides a foundational knowledge base essential for career readiness by emphasizing critical skills such as communication, problem-solving, and analytical thinking. This structured program ensures students acquire competencies aligned with workforce demands in fields like healthcare, technology, and business. Emphasizing core subjects like math, science, and literacy equips learners with transferable skills vital for professional success and lifelong learning.
Elective Choices and Personalization of Education
Elective curriculum offers students the flexibility to tailor their education based on individual interests and career goals, enhancing engagement and motivation. These courses diversify learning experiences by allowing exploration beyond core requirements, fostering critical thinking and specialized knowledge. Personalized elective choices contribute to holistic development and better preparation for future academic or professional pursuits.
Future Trends in Curriculum Development
Future trends in curriculum development emphasize integrating technology-driven personalized learning within both core and elective curricula to enhance student engagement and skill acquisition. Core curricula are shifting towards interdisciplinary approaches that embed critical thinking, digital literacy, and global competencies essential for the evolving job market. Elective curricula increasingly offer specialized modules in emerging fields such as artificial intelligence, sustainability, and data science, aligning education with industry demands and fostering lifelong learning.
Core Curriculum vs Elective Curriculum Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com