Higher education institutions face a critical choice between open access and selective admission policies, each impacting student diversity and academic standards differently. Open access promotes inclusivity by allowing a broader range of students to enroll, fostering equal opportunity and social mobility. Selective admission, on the other hand, aims to maintain high academic standards by admitting students based on performance, which can enhance institutional reputation but may limit diversity.
Table of Comparison
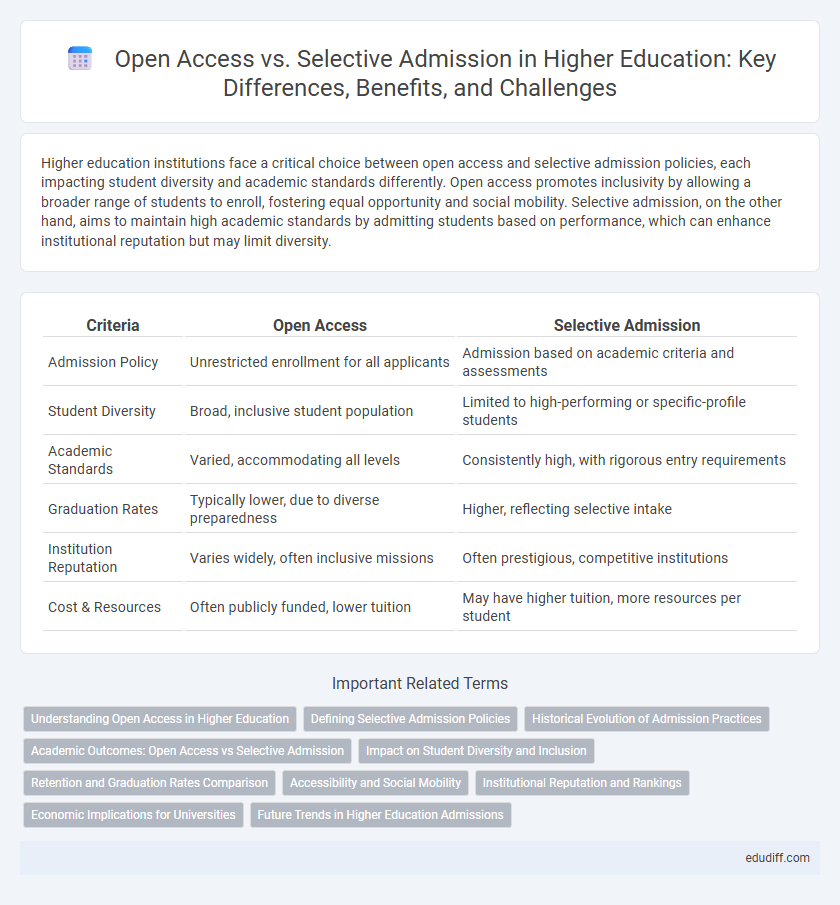
| Criteria | Open Access | Selective Admission |
|---|---|---|
| Admission Policy | Unrestricted enrollment for all applicants | Admission based on academic criteria and assessments |
| Student Diversity | Broad, inclusive student population | Limited to high-performing or specific-profile students |
| Academic Standards | Varied, accommodating all levels | Consistently high, with rigorous entry requirements |
| Graduation Rates | Typically lower, due to diverse preparedness | Higher, reflecting selective intake |
| Institution Reputation | Varies widely, often inclusive missions | Often prestigious, competitive institutions |
| Cost & Resources | Often publicly funded, lower tuition | May have higher tuition, more resources per student |
Understanding Open Access in Higher Education
Open Access in higher education eliminates traditional admission barriers, allowing broader student participation regardless of prior academic achievement. This approach promotes inclusivity and diversity by providing equal opportunity for enrollment across various socioeconomic backgrounds. Open Access institutions often emphasize support services and flexible learning pathways to enhance student success and retention.
Defining Selective Admission Policies
Selective admission policies prioritize applicants based on academic achievements, standardized test scores, and extracurricular involvement to ensure a highly qualified student body. These criteria aim to balance institutional capacity with maintaining rigorous academic standards and enhancing student success rates. Such policies often include holistic reviews that consider personal statements and recommendation letters to evaluate candidates beyond numeric metrics.
Historical Evolution of Admission Practices
Early higher education institutions predominantly practiced selective admission, focusing on elite criteria rooted in social status and classical education. The 20th century marked a gradual shift toward open access policies aimed at democratizing education and expanding opportunities for underrepresented groups. This historical evolution reflects ongoing tensions between maintaining academic standards and promoting inclusivity in university admissions.
Academic Outcomes: Open Access vs Selective Admission
Open Access institutions promote inclusivity and diversity, resulting in a broader range of academic backgrounds and potential performance variability among students. Selective Admission enhances overall academic outcomes by enrolling candidates with stronger prior achievements, thus fostering a more competitive and high-achieving learning environment. Research indicates selective entry correlates with higher graduation rates and improved standardized test scores within higher education.
Impact on Student Diversity and Inclusion
Open Access policies significantly enhance student diversity and inclusion by removing traditional barriers such as standardized test requirements and rigid admission criteria, thereby allowing a broader spectrum of socio-economic backgrounds and academic abilities to enroll. Selective Admission practices often prioritize academic metrics, which can inadvertently exclude underrepresented groups and limit access for students from marginalized communities. Institutions adopting Open Access models report increased enrollment of students from diverse ethnicities, economic statuses, and first-generation college backgrounds, fostering a more inclusive academic environment.
Retention and Graduation Rates Comparison
Selective admission policies often correlate with higher retention and graduation rates due to the ability to admit students with stronger academic preparedness and motivation. Open access institutions typically experience lower retention and graduation rates, as they enroll a more diverse student body with varying levels of academic readiness and external challenges. Data from the National Center for Education Statistics reveals that four-year graduation rates average around 60% for selective institutions, compared to approximately 30-40% for open access colleges.
Accessibility and Social Mobility
Open Access policies enhance higher education accessibility by allowing all qualified students to enroll, promoting greater social mobility and reducing barriers linked to socioeconomic status. Selective Admission restricts enrollment based on academic criteria, potentially limiting opportunities for underrepresented groups and reinforcing existing inequalities. Expanding access through Open Access institutions correlates with increased diversity and upward social mobility, crucial for equitable knowledge dissemination.
Institutional Reputation and Rankings
Open Access policies can enhance an institution's reputation by broadening research visibility and citation impact, which positively influences global rankings. Selective Admission processes often elevate perceived academic quality and exclusivity, attracting high-caliber students and faculty that contribute to institutional prestige. Balancing open accessibility with rigorous admission criteria is critical for universities aiming to improve both reputation and ranking metrics in competitive higher education landscapes.
Economic Implications for Universities
Open Access policies reduce barriers for prospective students, potentially increasing enrollment and university revenue through higher tuition income and expanded course offerings. Selective Admission controls enrollment size, maintaining resource allocation and potentially driving higher tuition rates per student, which supports investment in quality education and research output. Economic implications also include varying impacts on operational costs, with Open Access demanding scalable infrastructure while Selective Admission emphasizes targeted spending on high-achieving cohorts.
Future Trends in Higher Education Admissions
Future trends in higher education admissions emphasize increasing adoption of open access policies to democratize learning opportunities and reduce barriers for underrepresented groups. Selective admission processes are evolving to incorporate holistic criteria, including digital portfolios and AI-driven assessments, enhancing fairness and predictive success metrics. Institutions leveraging hybrid models balance inclusivity with academic standards, responding to growing demand for flexible, competency-based education pathways.
Open Access vs Selective Admission Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com