Choosing between accredited and non-accredited homeschool programs impacts education quality and college acceptance. Accredited programs follow standardized curricula and undergo rigorous evaluation, ensuring recognized credentials. Non-accredited programs offer flexibility and personalized learning but may face challenges with credit transfer and higher education admissions.
Table of Comparison
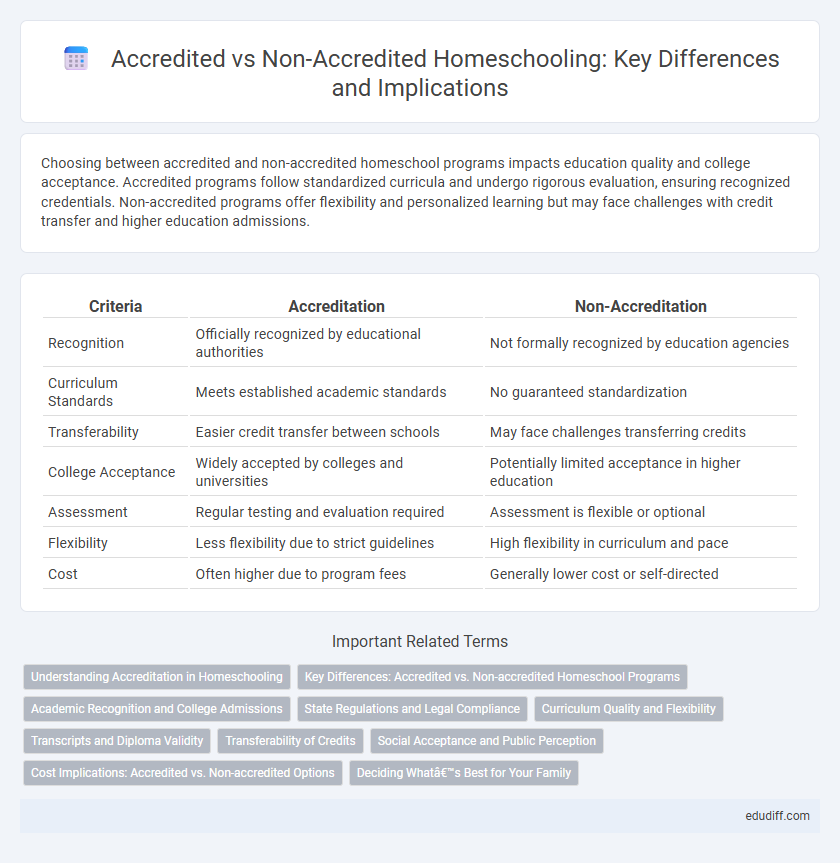
| Criteria | Accreditation | Non-Accreditation |
|---|---|---|
| Recognition | Officially recognized by educational authorities | Not formally recognized by education agencies |
| Curriculum Standards | Meets established academic standards | No guaranteed standardization |
| Transferability | Easier credit transfer between schools | May face challenges transferring credits |
| College Acceptance | Widely accepted by colleges and universities | Potentially limited acceptance in higher education |
| Assessment | Regular testing and evaluation required | Assessment is flexible or optional |
| Flexibility | Less flexibility due to strict guidelines | High flexibility in curriculum and pace |
| Cost | Often higher due to program fees | Generally lower cost or self-directed |
Understanding Accreditation in Homeschooling
Accreditation in homeschooling refers to the formal recognition by an authorized educational body that a homeschool program meets established academic standards and quality benchmarks. Accredited homeschool programs often provide standardized curricula, verified transcripts, and easier acceptance for college admissions or transfer to traditional schools. Non-accredited homeschooling offers more flexibility and customization but may face challenges in credential validation and acceptance by higher education institutions or employers.
Key Differences: Accredited vs. Non-accredited Homeschool Programs
Accredited homeschool programs undergo rigorous evaluation by recognized educational authorities, ensuring adherence to standardized curricula and quality assurance. Non-accredited programs lack formal recognition but often offer flexible, customized learning experiences tailored to individual student needs. Parents choosing between accredited and non-accredited options should consider factors like college acceptance, transcript credibility, and alignment with state homeschooling laws.
Academic Recognition and College Admissions
Accredited homeschool programs provide formal academic recognition accepted by colleges and universities, ensuring transcripts meet standardized criteria for admission. Non-accredited homeschoolers may face challenges proving academic rigor, potentially requiring supplementary documentation or standardized test scores during college applications. Choosing accreditation enhances credibility, streamlining acceptance into higher education institutions and scholarship opportunities.
State Regulations and Legal Compliance
State regulations for homeschooling vary widely, with some requiring accreditation for curriculum providers while others allow non-accredited programs as long as legal reporting and assessment criteria are met. Accreditation can streamline compliance with these regulations, ensuring that educational standards align with state mandates and reducing risks of legal challenges. Homeschool parents should verify their specific state's requirements to maintain proper documentation and avoid enforcement actions related to non-compliance.
Curriculum Quality and Flexibility
Accredited homeschool programs typically ensure curriculum quality by meeting established educational standards and undergoing regular evaluations, providing parents and students with verified academic rigor. Non-accredited programs offer greater flexibility in curriculum design and pacing, allowing customization to individual learning styles and interests but may lack formal recognition from educational institutions. Families must weigh the benefits of standardized quality assurance against personalized education freedom when choosing between accredited and non-accredited homeschooling options.
Transcripts and Diploma Validity
Accredited homeschool programs ensure transcripts and diplomas are widely recognized by colleges, employers, and state education boards, providing clear documentation of academic standards. Non-accredited programs may face challenges in transcript acceptance, often requiring additional verification or evaluation for diploma validity during college admissions or job applications. Families must carefully evaluate accreditation status to ensure credentials meet future educational and professional requirements.
Transferability of Credits
Accredited homeschool programs offer transferability of credits to public and private schools, ensuring smooth transitions for students moving between educational institutions. Non-accredited programs often lack recognized credit validation, which can complicate enrollment or credit acceptance in traditional schools and colleges. Families prioritizing college admission or future school transfers should consider accredited options to guarantee academic recognition.
Social Acceptance and Public Perception
Accredited homeschooling programs often gain higher social acceptance and trust due to recognized standards and quality assurance, which can positively influence public perception and ease college admissions. Non-accredited programs may face skepticism or misunderstanding, impacting social acceptance despite flexible curriculum choices. Public perception favors accredited homeschooling as a credible alternative to traditional education, boosting confidence among employers and educational institutions.
Cost Implications: Accredited vs. Non-accredited Options
Accredited homeschool programs typically involve higher costs due to standardized curriculum fees, administrative expenses, and potential state regulatory compliance, while non-accredited options often offer more affordable, flexible learning materials and reduced overhead. Families choosing accreditation may invest in formal recognition that supports college admissions and transferability of credits, which can justify the higher financial outlay. Non-accredited homeschooling allows cost savings but may require additional effort in portfolio documentation and alternative validation methods for academic achievement.
Deciding What’s Best for Your Family
Choosing between accredited and non-accredited homeschooling options depends on your family's educational goals and future plans for the child. Accredited programs offer recognized standards and easier credit transferability for college admission, while non-accredited curricula provide flexibility and customization tailored to individual learning styles. Evaluating the importance of formal recognition against personalized learning needs helps families determine the best fit for their homeschool journey.
Accreditation vs Non-accreditation Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com