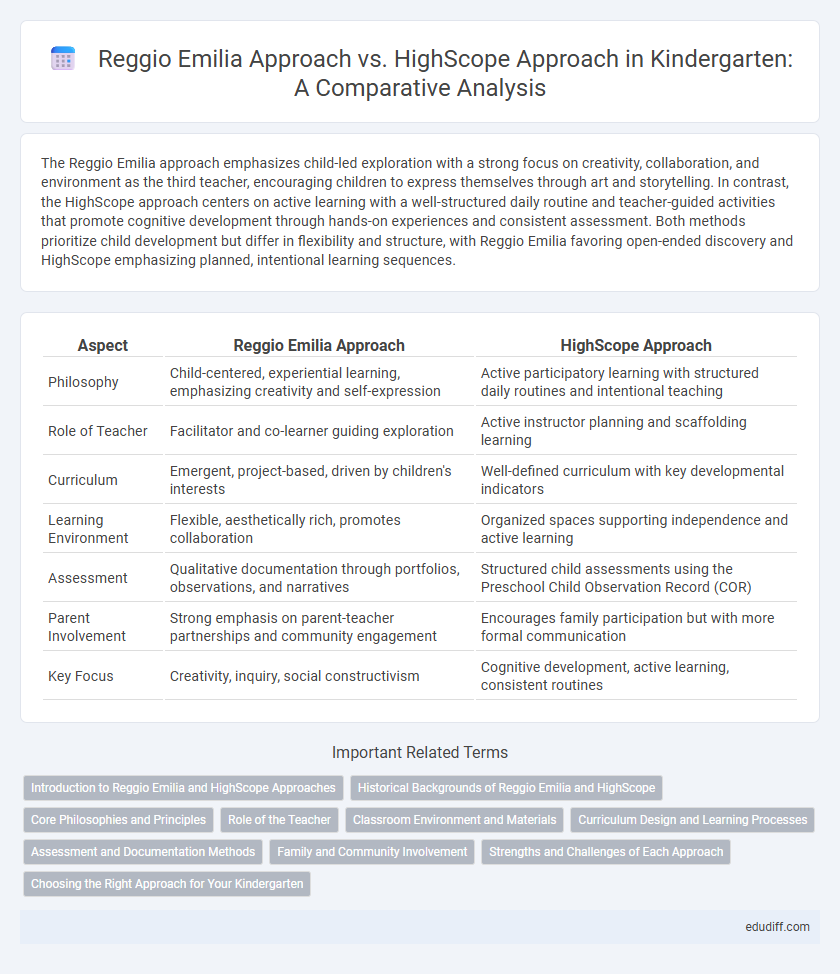
The Reggio Emilia approach emphasizes child-led exploration with a strong focus on creativity, collaboration, and environment as the third teacher, encouraging children to express themselves through art and storytelling. In contrast, the HighScope approach centers on active learning with a well-structured daily routine and teacher-guided activities that promote cognitive development through hands-on experiences and consistent assessment. Both methods prioritize child development but differ in flexibility and structure, with Reggio Emilia favoring open-ended discovery and HighScope emphasizing planned, intentional learning sequences.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Reggio Emilia Approach | HighScope Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Philosophy | Child-centered, experiential learning, emphasizing creativity and self-expression | Active participatory learning with structured daily routines and intentional teaching |
| Role of Teacher | Facilitator and co-learner guiding exploration | Active instructor planning and scaffolding learning |
| Curriculum | Emergent, project-based, driven by children's interests | Well-defined curriculum with key developmental indicators |
| Learning Environment | Flexible, aesthetically rich, promotes collaboration | Organized spaces supporting independence and active learning |
| Assessment | Qualitative documentation through portfolios, observations, and narratives | Structured child assessments using the Preschool Child Observation Record (COR) |
| Parent Involvement | Strong emphasis on parent-teacher partnerships and community engagement | Encourages family participation but with more formal communication |
| Key Focus | Creativity, inquiry, social constructivism | Cognitive development, active learning, consistent routines |
Introduction to Reggio Emilia and HighScope Approaches
The Reggio Emilia approach emphasizes child-led, project-based learning with a strong focus on creativity, collaboration, and the environment as the "third teacher." HighScope centers on active participatory learning through a consistent daily routine and the use of the "plan-do-review" process to foster independence and cognitive development. Both approaches prioritize experiential learning but differ in curriculum structure and the role of adult facilitation.
Historical Backgrounds of Reggio Emilia and HighScope
The Reggio Emilia approach originated in post-World War II Italy, developed by Loris Malaguzzi and parents in the town of Reggio Emilia to promote child-centered, community-based education. The HighScope approach emerged in the 1960s in the United States, founded by psychologist David Weikart focused on active participatory learning and cognitive development through structured daily routines. Both approaches have since influenced early childhood education globally, emphasizing different philosophies rooted in their unique historical and cultural contexts.
Core Philosophies and Principles
The Reggio Emilia approach emphasizes child-led exploration, creativity, and collaborative learning, fostering a strong relationship between children, teachers, and environment. HighScope centers on active participatory learning with a consistent daily routine, promoting cognitive development through structured play and adult-child interaction. Both approaches prioritize respect for the child's abilities but differ in flexibility and the role of the adult in guiding experiences.
Role of the Teacher
In the Reggio Emilia approach, teachers act as co-learners and collaborators, facilitating inquiry through open-ended questions and encouraging children's exploration. The HighScope approach positions teachers as active observers and planners who use a structured curriculum to guide children's learning through consistent routines and intentional interactions. Both approaches emphasize the teacher's role in fostering independence but differ in the level of structure and teacher-led guidance.
Classroom Environment and Materials
The Reggio Emilia approach emphasizes natural, open-ended materials that encourage creativity and exploration within a thoughtfully designed space reflecting children's interests. HighScope incorporates well-organized, durable materials arranged in clearly defined areas, promoting structured, active learning through child-initiated activities. Both approaches prioritize an engaging environment but differ in material selection and spatial flexibility to support developmental objectives.
Curriculum Design and Learning Processes
The Reggio Emilia approach emphasizes a child-centered, project-based curriculum that fosters exploration, creativity, and collaboration through emergent themes driven by children's interests. In contrast, the HighScope approach utilizes a structured, research-based curriculum with active participatory learning, incorporating daily routines, planned activities, and consistent assessment to promote cognitive and social development. Both approaches prioritize hands-on learning but differ in flexibility and teacher-led guidance within early childhood education settings.
Assessment and Documentation Methods
The Reggio Emilia approach emphasizes observational assessment and photographic documentation to capture children's learning processes and expressions, fostering reflective discussions among educators and parents. In contrast, the HighScope approach utilizes systematic, daily checklists and child portfolios to track developmental milestones and skill acquisition through structured evaluations. Both methods prioritize comprehensive documentation but differ in focus: Reggio Emilia highlights narrative and visual records, while HighScope centers on objective, criterion-based assessments.
Family and Community Involvement
The Reggio Emilia approach emphasizes strong family and community partnerships, viewing parents as active participants in the educational process and valuing their insights in shaping curriculum. In contrast, the HighScope approach incorporates family engagement through structured communication and collaborative goal-setting to support children's learning and development. Both approaches prioritize meaningful family involvement but differ in their methods of integrating community perspectives into the kindergarten experience.
Strengths and Challenges of Each Approach
The Reggio Emilia approach emphasizes child-led learning and expressive arts, fostering creativity and collaboration, but may challenge educators with its less structured curriculum. The HighScope approach offers a well-defined daily routine and active learning principles, supporting cognitive development and assessment, yet it can limit spontaneity and flexibility in classroom interactions. Both approaches provide valuable frameworks but require careful adaptation to meet diverse learner needs and educational goals.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Kindergarten
Selecting the right approach for your kindergarten depends on the educational philosophy and developmental goals you prioritize. The Reggio Emilia approach emphasizes student-led exploration, collaboration, and creativity through expressive arts, fostering strong community ties and personalized learning environments. HighScope focuses on active participatory learning with a structured daily routine and consistent assessment, promoting cognitive and social-emotional development through hands-on experiences and teacher-guided interaction.
Reggio Emilia approach vs HighScope approach Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com