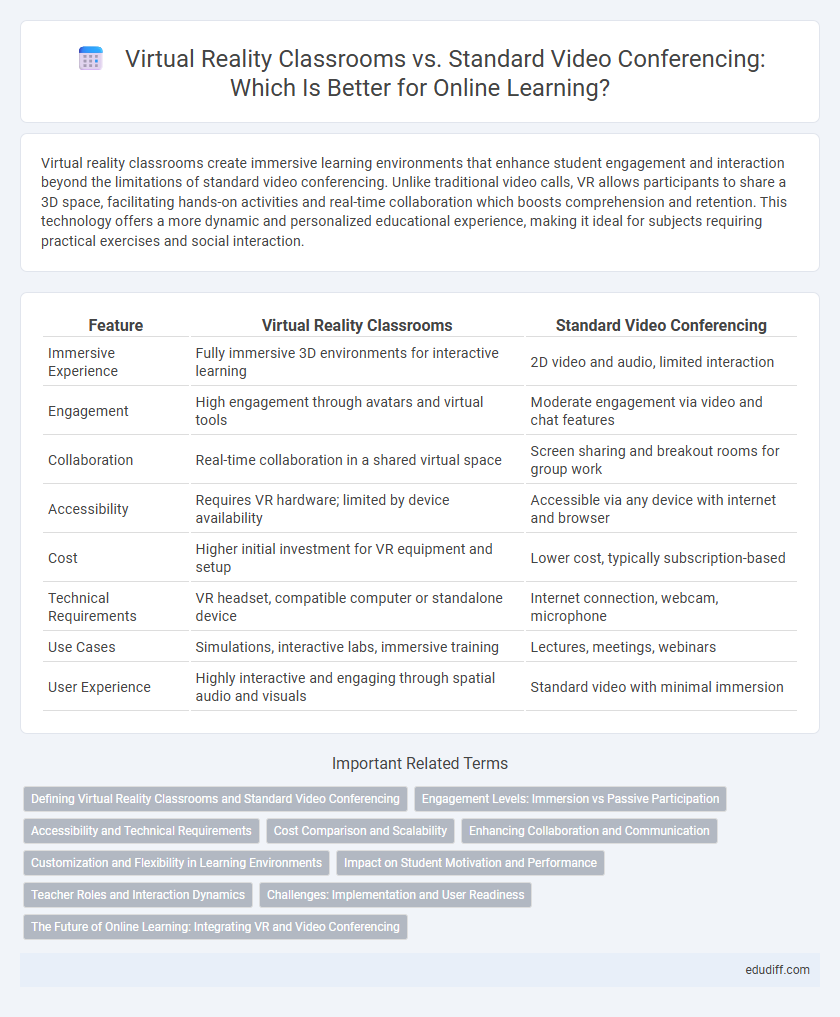
Virtual reality classrooms create immersive learning environments that enhance student engagement and interaction beyond the limitations of standard video conferencing. Unlike traditional video calls, VR allows participants to share a 3D space, facilitating hands-on activities and real-time collaboration which boosts comprehension and retention. This technology offers a more dynamic and personalized educational experience, making it ideal for subjects requiring practical exercises and social interaction.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Virtual Reality Classrooms | Standard Video Conferencing |
|---|---|---|
| Immersive Experience | Fully immersive 3D environments for interactive learning | 2D video and audio, limited interaction |
| Engagement | High engagement through avatars and virtual tools | Moderate engagement via video and chat features |
| Collaboration | Real-time collaboration in a shared virtual space | Screen sharing and breakout rooms for group work |
| Accessibility | Requires VR hardware; limited by device availability | Accessible via any device with internet and browser |
| Cost | Higher initial investment for VR equipment and setup | Lower cost, typically subscription-based |
| Technical Requirements | VR headset, compatible computer or standalone device | Internet connection, webcam, microphone |
| Use Cases | Simulations, interactive labs, immersive training | Lectures, meetings, webinars |
| User Experience | Highly interactive and engaging through spatial audio and visuals | Standard video with minimal immersion |
Defining Virtual Reality Classrooms and Standard Video Conferencing
Virtual Reality Classrooms create immersive, interactive learning environments using 3D avatars and spatial audio, enabling real-time collaboration and presence beyond traditional screen interfaces. Standard Video Conferencing platforms facilitate remote communication through video and audio streams on flat screens, often limited to grid views and basic interaction tools. VR classrooms enhance engagement by simulating physical classrooms, while video conferencing focuses primarily on direct visual and audio communication.
Engagement Levels: Immersion vs Passive Participation
Virtual reality classrooms provide immersive environments that significantly enhance student engagement by enabling interactive, experiential learning opportunities beyond traditional screen-based video conferencing. Unlike standard video conferencing, which often results in passive participation due to limited sensory input and reduced spatial presence, VR classrooms foster active involvement through realistic simulations and collaborative virtual spaces. Research indicates that immersive virtual reality increases attention retention and motivation, making it a superior tool for maintaining high engagement levels in online education.
Accessibility and Technical Requirements
Virtual reality classrooms require advanced hardware such as VR headsets and high-performance computers, creating higher technical barriers compared to standard video conferencing, which only needs a basic webcam and internet connection. Accessibility is more limited in VR environments due to cost and user adaptability, whereas video conferencing platforms offer broad compatibility across devices, including smartphones and tablets. These differences significantly impact scalability and inclusivity in remote education settings.
Cost Comparison and Scalability
Virtual reality classrooms require significant upfront investment for VR hardware and software development but offer enhanced scalability by supporting immersive, interactive learning environments that can accommodate numerous users simultaneously without physical space limitations. Standard video conferencing tools are generally more cost-effective initially, relying on existing devices and internet connections, but face scalability challenges such as bandwidth constraints and reduced engagement in large groups. Evaluating long-term cost efficiency involves balancing the high initial VR setup expenses against the ongoing limitations and potential lower engagement costs of video conferencing platforms.
Enhancing Collaboration and Communication
Virtual reality classrooms transform online learning by enabling immersive, spatial interactions that mimic physical presence, fostering more natural communication and collaborative problem-solving. Unlike standard video conferencing, VR integrates 3D environments where participants can engage in dynamic gestures and real-time spatial awareness, significantly boosting engagement and teamwork efficiency. Enhanced tools such as shared virtual whiteboards and interactive simulations further elevate collaboration, making VR classrooms a powerful alternative for deeper, more effective educational interactions.
Customization and Flexibility in Learning Environments
Virtual reality classrooms offer immersive customization options that allow educators to design interactive, 3D learning spaces tailored to specific subjects and student needs, enhancing engagement and retention. Unlike standard video conferencing platforms, which provide limited layout and interaction flexibility, VR environments enable real-time spatial arrangement adjustments and personalized avatar features that support diverse learning styles. This flexibility fosters a more dynamic educational experience, promoting active participation and collaboration beyond traditional screen-based settings.
Impact on Student Motivation and Performance
Virtual Reality Classrooms create immersive learning environments that significantly boost student motivation by enabling interactive and engaging experiences compared to standard video conferencing. Studies show VR increases retention rates by up to 30% through experiential learning, while traditional video calls often lead to passive participation and distractions. Enhanced presence and real-time collaboration in VR enhance focus and improve overall academic performance in remote education settings.
Teacher Roles and Interaction Dynamics
Virtual Reality Classrooms transform teacher roles by enabling immersive, interactive environments where instructors can engage students through spatial presence and real-time gesture recognition, unlike standard video conferencing which limits interaction to 2D screens and passive communication. The dynamic nature of VR promotes active learning and collaboration, fostering deeper student engagement and more natural social interactions compared to the constrained audio-visual channels typical of video calls. VR technology supports diverse teaching strategies such as simulations and role-playing, enhancing pedagogical effectiveness beyond the static, lecture-focused formats of traditional video conferencing platforms.
Challenges: Implementation and User Readiness
Virtual reality classrooms face significant implementation challenges such as high costs for specialized hardware and the need for robust internet infrastructure, which limits accessibility compared to standard video conferencing. User readiness is hindered by the steep learning curve associated with immersive VR technology and varying levels of digital literacy among students and educators. Standard video conferencing platforms benefit from widespread familiarity and minimal setup, but they lack the immersive engagement that VR offers for remote learning environments.
The Future of Online Learning: Integrating VR and Video Conferencing
Virtual reality classrooms offer immersive, interactive environments that enhance student engagement far beyond traditional video conferencing capabilities. Combining VR with video conferencing technology enables seamless collaboration, real-time feedback, and personalized learning experiences tailored to diverse educational needs. This integration promises to revolutionize online learning by bridging physical gaps and fostering deeper cognitive connection through multi-sensory stimulation and social presence.
Virtual Reality Classrooms vs Standard Video Conferencing Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com