Postgraduate PET programs offer cohort-based models that foster collaborative learning, structured timelines, and peer support, enhancing student engagement and consistency. Non-cohort formats provide flexible scheduling and individualized pacing, accommodating diverse professional and personal commitments without fixed group progression. Choosing between cohort and non-cohort relies on balancing the need for community-driven learning against the demand for flexible study options in postgraduate PET education.
Table of Comparison
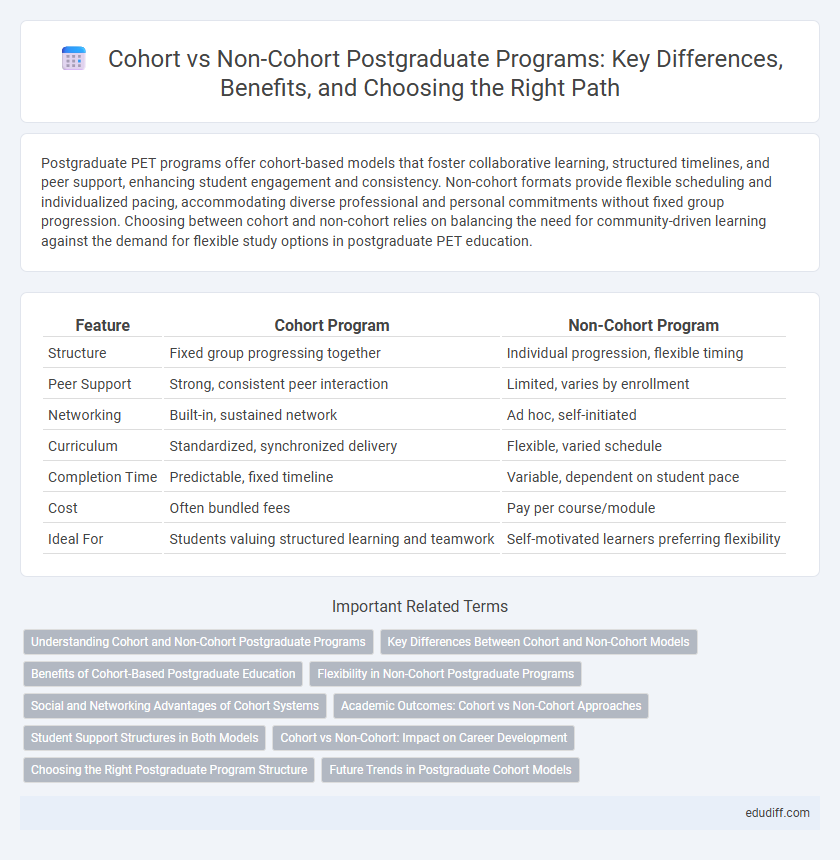
| Feature | Cohort Program | Non-Cohort Program |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Fixed group progressing together | Individual progression, flexible timing |
| Peer Support | Strong, consistent peer interaction | Limited, varies by enrollment |
| Networking | Built-in, sustained network | Ad hoc, self-initiated |
| Curriculum | Standardized, synchronized delivery | Flexible, varied schedule |
| Completion Time | Predictable, fixed timeline | Variable, dependent on student pace |
| Cost | Often bundled fees | Pay per course/module |
| Ideal For | Students valuing structured learning and teamwork | Self-motivated learners preferring flexibility |
Understanding Cohort and Non-Cohort Postgraduate Programs
Cohort postgraduate programs group students who start and progress through their studies together, fostering collaboration and consistent peer support. Non-cohort programs offer flexible start dates and individual pacing, catering to students balancing professional or personal commitments. Understanding these differences helps postgraduate students choose the format that best aligns with their learning style and schedule.
Key Differences Between Cohort and Non-Cohort Models
Cohort models in postgraduate education group students who start and progress through a program together, fostering collaborative learning and peer support, whereas non-cohort models allow for flexible entry and individualized pacing. Cohort systems emphasize structured schedules, shared milestones, and consistent peer interaction, which can enhance motivation and retention. Non-cohort models prioritize flexibility and personalization, accommodating diverse schedules but potentially reducing peer networking and constant peer accountability.
Benefits of Cohort-Based Postgraduate Education
Cohort-based postgraduate education fosters collaborative learning and strong peer networks, which enhance academic performance and professional opportunities. Structured progression within a cohort promotes accountability and consistent support, leading to higher retention and completion rates. Exposure to diverse perspectives within the group accelerates critical thinking skills and prepares students for complex real-world challenges.
Flexibility in Non-Cohort Postgraduate Programs
Non-cohort postgraduate programs offer greater flexibility by allowing students to start at multiple points throughout the year rather than following a fixed schedule. This structure accommodates diverse professional and personal commitments, enabling learners to progress at their own pace. Flexibility in non-cohort models supports customized learning paths and often provides access to asynchronous content, making advanced education more accessible.
Social and Networking Advantages of Cohort Systems
Cohort systems in postgraduate programs foster strong social connections and collaborative networking opportunities by grouping students into stable, interactive communities throughout their study period. These structured interactions encourage peer support, knowledge sharing, and the formation of professional networks that often extend beyond graduation. Non-cohort systems typically lack the consistency and shared experience, making it harder to build lasting relationships and collaborative opportunities.
Academic Outcomes: Cohort vs Non-Cohort Approaches
Cohort-based postgraduate programs foster collaborative learning and sustained peer support, often leading to higher retention rates and improved academic performance compared to non-cohort structures. Research indicates cohort students exhibit greater engagement, timely completion rates, and enhanced critical thinking skills due to structured group interactions and shared curriculum pacing. Non-cohort models, while offering flexibility, tend to face challenges in maintaining consistent motivation and peer connection, impacting overall academic outcomes negatively.
Student Support Structures in Both Models
Cohort postgraduate programs provide structured support through peer networks and coordinated academic advising, enhancing collaboration and consistent guidance. Non-cohort models offer flexible support tailored to individual student needs, often relying on personalized mentoring and diverse resource accessibility. Both structures aim to optimize student success, but cohorts emphasize community-driven engagement while non-cohorts focus on autonomy and customized support services.
Cohort vs Non-Cohort: Impact on Career Development
Cohort-based postgraduate programs foster strong peer networks and collaborative learning, enhancing professional connections that support career advancement. Non-cohort structures offer flexible pacing but may limit opportunities for collective skill-building and immediate peer feedback, potentially impacting networking potential. Research indicates cohort experiences correlate with higher employment rates and leadership development within specialized fields.
Choosing the Right Postgraduate Program Structure
Choosing the right postgraduate program structure depends on understanding cohort versus non-cohort models, where cohort programs offer structured group progression and consistent peer support, enhancing collaborative learning and networking opportunities. Non-cohort programs provide flexible pacing and individualized study timelines, ideal for professionals balancing work and education. Evaluating personal learning style, career goals, and schedule flexibility is crucial to selecting the optimal postgraduate path.
Future Trends in Postgraduate Cohort Models
Emerging trends in postgraduate education reveal a shift towards flexible cohort models integrating asynchronous learning, enabling diverse student groups to progress together while accommodating individual pacing. Data indicates that hybrid cohort structures driven by AI analytics improve collaboration and retention rates by tailoring peer interactions and academic support. Institutions adopting such models anticipate enhanced scalability and global accessibility, positioning cohort-based learning as a cornerstone in future postgraduate program design.
Cohort vs Non-cohort Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com