RAship offers postgraduate students the opportunity to engage in specialized research projects aligned with their academic interests, often providing deeper domain expertise and stronger mentorship from faculty. TAship primarily involves assisting with course delivery, grading, and student support, which develops teaching skills and enhances communication abilities. Choosing between RAship and TAship depends on career goals, with RAship favoring research-oriented paths and TAship benefiting those pursuing academic teaching roles.
Table of Comparison
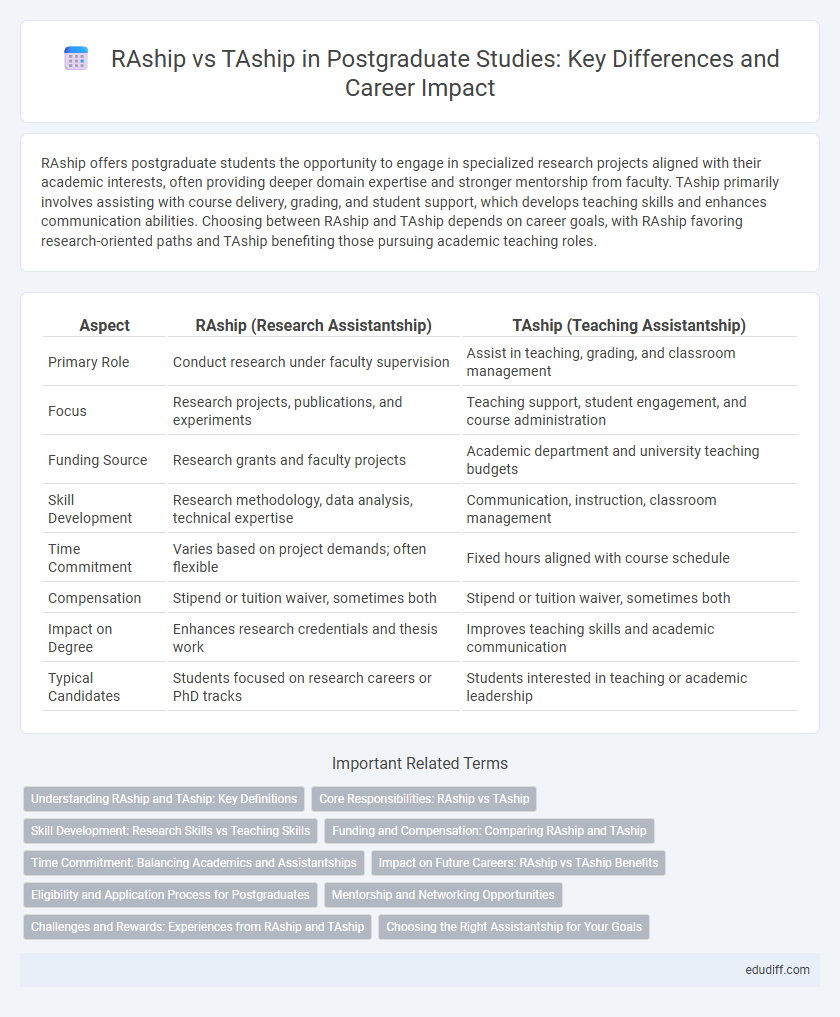
| Aspect | RAship (Research Assistantship) | TAship (Teaching Assistantship) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Conduct research under faculty supervision | Assist in teaching, grading, and classroom management |
| Focus | Research projects, publications, and experiments | Teaching support, student engagement, and course administration |
| Funding Source | Research grants and faculty projects | Academic department and university teaching budgets |
| Skill Development | Research methodology, data analysis, technical expertise | Communication, instruction, classroom management |
| Time Commitment | Varies based on project demands; often flexible | Fixed hours aligned with course schedule |
| Compensation | Stipend or tuition waiver, sometimes both | Stipend or tuition waiver, sometimes both |
| Impact on Degree | Enhances research credentials and thesis work | Improves teaching skills and academic communication |
| Typical Candidates | Students focused on research careers or PhD tracks | Students interested in teaching or academic leadership |
Understanding RAship and TAship: Key Definitions
RAship (Research Assistantship) involves graduate students aiding faculty in research projects, typically receiving stipends and tuition waivers in exchange for research contributions. TAship (Teaching Assistantship) requires students to support undergraduate courses through grading, tutoring, or leading discussions, also providing financial benefits like stipends. Both positions are critical for funding postgraduate education, enhancing academic skills, and offering practical experience within their respective roles.
Core Responsibilities: RAship vs TAship
RAship core responsibilities include conducting research, data analysis, and contributing to academic publications, directly supporting faculty projects and advancing knowledge in a specific field. TAship core duties involve assisting with course instruction, grading assignments, leading discussion sections, and providing student support to enhance learning experiences. Both roles demand time management and communication skills but differ primarily in research versus teaching focus.
Skill Development: Research Skills vs Teaching Skills
RAships enhance advanced research competencies, including data analysis, experimental design, and academic writing, crucial for scholarly contributions and innovation. TAships cultivate effective communication, classroom management, and pedagogical strategies essential for fostering student learning and engagement. Choosing between RAship and TAship depends on whether the priority is deepening research expertise or developing teaching proficiency in a postgraduate career.
Funding and Compensation: Comparing RAship and TAship
Research Assistantships (RAships) typically provide higher stipends funded directly by faculty grants, offering students both financial support and valuable research experience. Teaching Assistantships (TAships) usually offer compensation through university funds, often including tuition waivers and salaries aligned with teaching duties and hours. While RAships emphasize research funding and specialized skill development, TAships focus on instructional support with steadier compensation linked to academic calendar commitments.
Time Commitment: Balancing Academics and Assistantships
RAships typically demand 20 hours per week dedicated to research projects, allowing flexibility to align with academic schedules, whereas TAships often require 10-15 hours for grading, leading discussions, and assisting professors. Balancing RAship commitments can enhance research skills but may intensify workload during peak academic periods, while TAships provide structured hours supporting teaching experience. Effective time management ensures postgraduate students maintain academic performance while fulfilling assistantship responsibilities.
Impact on Future Careers: RAship vs TAship Benefits
Research Assistantships (RAships) provide hands-on experience in academic research, enhancing skills highly valued in doctoral programs and research-intensive careers. Teaching Assistantships (TAships) develop communication and leadership abilities, crucial for careers in academia and education. Both RAships and TAships offer unique benefits that significantly impact career trajectories depending on whether the focus is research or teaching.
Eligibility and Application Process for Postgraduates
Eligibility for RAship typically requires a strong research background and alignment with ongoing faculty projects, often necessitating prior experience or specialized skills, while TAship eligibility centers on subject mastery and teaching aptitude, frequently available to a broader range of postgraduates. The RAship application process involves direct faculty contact or department research postings, emphasizing proposal submission and interviews, whereas TAship applications are usually coordinated through departmental teaching offices, requiring course preference submissions and sometimes teaching demonstrations. Both opportunities demand academic excellence but differ in focus, with RAships highlighting research competencies and TAships prioritizing instructional abilities.
Mentorship and Networking Opportunities
RAships offer close mentorship from faculty through collaborative research projects, fostering strong professional relationships that enhance specialized academic growth. TAships provide broader interaction with faculty and peers in teaching environments, facilitating skill development and expanding networking within diverse student groups. Both roles cultivate valuable connections, but RAships emphasize personalized mentorship while TAships focus on community engagement and communication skills.
Challenges and Rewards: Experiences from RAship and TAship
Research Assistantships (RAships) provide hands-on experience in conducting academic research, fostering critical thinking and technical skills, yet often involve high pressure due to strict project deadlines and complex problem-solving demands. Teaching Assistantships (TAships) enhance communication and leadership abilities through direct interaction with students, grading, and delivering tutorials, but can be challenging due to time management and balancing teaching responsibilities with personal studies. Both RAships and TAships offer valuable professional development opportunities, with RAships emphasizing depth of research expertise and TAships strengthening pedagogical and interpersonal competencies.
Choosing the Right Assistantship for Your Goals
RAship positions emphasize research experience and often provide higher stipends, making them ideal for students aiming to deepen expertise and publish in academic journals. TAship roles develop teaching skills and communication abilities, suitable for those considering academic careers or educational leadership. Selecting between RAship and TAship depends on aligning assistantship responsibilities with long-term career aspirations and skill development priorities.
RAship vs TAship Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com