Montessori and Waldorf preschools emphasize child-centered learning but differ in their approaches; Montessori uses structured, hands-on activities to foster independence, while Waldorf focuses on imaginative play and artistic expression to develop creativity. Montessori classrooms feature carefully designed materials promoting self-directed exploration, whereas Waldorf environments prioritize natural materials and rhythmic routines to support holistic development. Both methods aim to nurture social, emotional, and cognitive skills, adapting to children's individual growth within supportive learning communities.
Table of Comparison
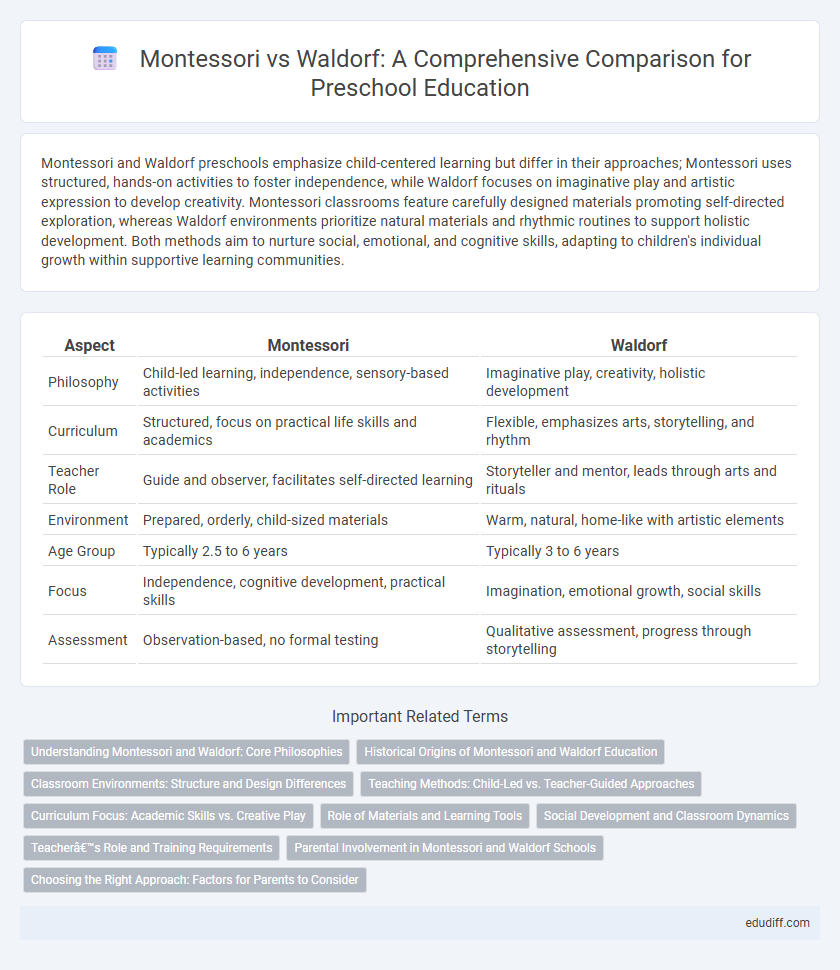
| Aspect | Montessori | Waldorf |
|---|---|---|
| Philosophy | Child-led learning, independence, sensory-based activities | Imaginative play, creativity, holistic development |
| Curriculum | Structured, focus on practical life skills and academics | Flexible, emphasizes arts, storytelling, and rhythm |
| Teacher Role | Guide and observer, facilitates self-directed learning | Storyteller and mentor, leads through arts and rituals |
| Environment | Prepared, orderly, child-sized materials | Warm, natural, home-like with artistic elements |
| Age Group | Typically 2.5 to 6 years | Typically 3 to 6 years |
| Focus | Independence, cognitive development, practical skills | Imagination, emotional growth, social skills |
| Assessment | Observation-based, no formal testing | Qualitative assessment, progress through storytelling |
Understanding Montessori and Waldorf: Core Philosophies
Montessori education emphasizes self-directed learning, hands-on activities, and fostering independence through carefully prepared environments that encourage exploration and practical life skills. Waldorf education centers on holistic development, integrating imagination, creativity, and rhythm through storytelling, arts, and experiential learning aligned with developmental stages. Both approaches prioritize child-centered learning but differ markedly in their methods and educational goals.
Historical Origins of Montessori and Waldorf Education
Montessori education was developed by Dr. Maria Montessori in the early 1900s, emphasizing child-led learning through hands-on activities and natural development. Waldorf education originated from Rudolf Steiner's anthroposophical philosophy in 1919, focusing on holistic development through artistic expression and imaginative play. Both approaches emerged in Europe as innovative responses to traditional education, shaping distinct pedagogical frameworks worldwide.
Classroom Environments: Structure and Design Differences
Montessori classrooms emphasize individual learning stations with open shelving, natural materials, and minimalistic design to promote independence and sensory exploration. Waldorf classrooms feature rich, warm colors, natural textures, and an artistic ambiance that encourages imaginative play and social interaction. Both environments prioritize natural light and child-sized furniture but differ in their focus on structured tasks versus creative expression.
Teaching Methods: Child-Led vs. Teacher-Guided Approaches
Montessori education emphasizes child-led learning, encouraging independence through hands-on activities and self-directed exploration within prepared environments. Waldorf education relies on teacher-guided methods, using structured routines, storytelling, and creative arts to nurture imagination and social development. Both approaches prioritize holistic growth but differ in balancing autonomy with guided instruction.
Curriculum Focus: Academic Skills vs. Creative Play
Montessori preschools emphasize academic skills through structured activities that promote independence, sensory development, and practical life exercises. Waldorf preschools prioritize creative play, imagination, and artistic expression to foster emotional growth and holistic development. This distinction reflects Montessori's focus on cognitive skill-building and Waldorf's commitment to nurturing creativity and social-emotional learning.
Role of Materials and Learning Tools
Montessori preschools utilize carefully designed, hands-on materials that encourage independent exploration and sensory learning, such as bead chains and geometric solids, fostering fine motor skills and concrete understanding of concepts. Waldorf preschools emphasize natural, open-ended materials like wooden toys, wool, and clay, which promote creativity, imagination, and holistic development through unstructured play. The Montessori approach prioritizes structured learning tools with clear educational goals, while Waldorf materials support rhythmic, artistic experiences aligned with child development stages.
Social Development and Classroom Dynamics
Montessori classrooms promote social development through mixed-age groups that encourage peer learning, fostering independence and collaboration. Waldorf education emphasizes imaginative play and community-building activities that nurture empathy and social responsibility among children. Both approaches create distinct classroom dynamics: Montessori with structured, self-directed tasks, while Waldorf offers rhythm and artistic expression to support social skills.
Teacher’s Role and Training Requirements
Montessori teachers undergo specialized training emphasizing observation and guiding children's independent learning, focusing on individualized instruction within prepared environments. Waldorf educators receive comprehensive training in child development, arts, and storytelling, highlighting the teacher's role as a developmental model and creative facilitator. Both approaches require dedicated certification, but Montessori mandates a strict adherence to specific materials and methods, whereas Waldorf training cultivates flexible, holistic teaching through artistic and experiential practices.
Parental Involvement in Montessori and Waldorf Schools
Montessori schools emphasize active parental involvement through regular observations, parent-teacher meetings, and home activities that reinforce classroom learning, fostering a collaborative community focused on the child's independence. Waldorf schools encourage parental engagement via involvement in school festivals, classroom volunteering, and artistic activities that align with the curriculum's focus on creativity and holistic development. Both educational philosophies prioritize meaningful family participation but differ in structure, with Montessori focusing on direct academic support and Waldorf highlighting cultural immersion and community bonding.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors for Parents to Consider
Parents choosing between Montessori and Waldorf preschools should evaluate the learning philosophy alignment, considering Montessori's emphasis on structured self-directed activity versus Waldorf's focus on imaginative play and creativity. Assessing the child's personality and developmental needs helps determine which approach fosters their independence or nurtures emotional and artistic growth more effectively. Availability of trained educators, classroom environment, and parental involvement also play crucial roles in selecting the ideal preschool model.
Montessori vs Waldorf Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com