Observation assessment in preschool involves teachers closely monitoring children's behavior, interactions, and developmental progress in natural settings, providing a holistic understanding of each child's strengths and needs. Standardized assessment uses uniform tests designed to measure specific skills against established norms, offering objective data that can be compared across different populations. While observation assessments capture individual learning processes and social development better, standardized assessments provide measurable outcomes essential for tracking overall achievement and identifying potential learning gaps.
Table of Comparison
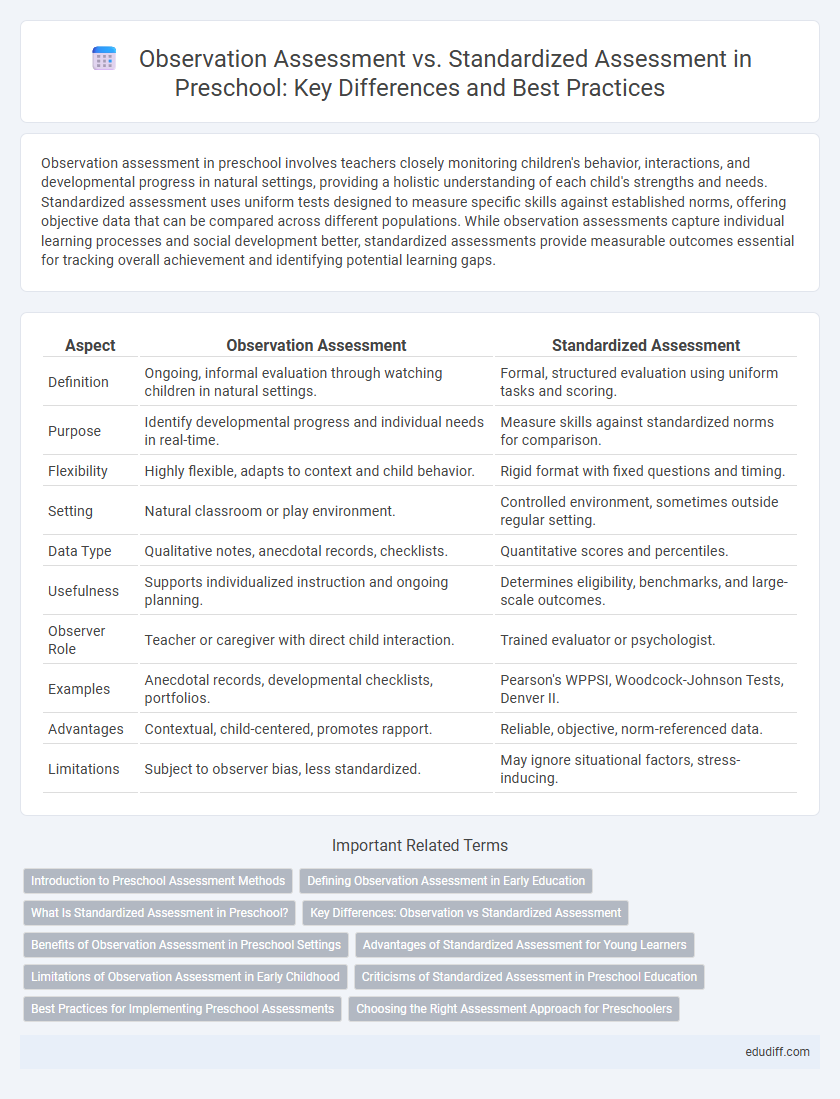
| Aspect | Observation Assessment | Standardized Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ongoing, informal evaluation through watching children in natural settings. | Formal, structured evaluation using uniform tasks and scoring. |
| Purpose | Identify developmental progress and individual needs in real-time. | Measure skills against standardized norms for comparison. |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, adapts to context and child behavior. | Rigid format with fixed questions and timing. |
| Setting | Natural classroom or play environment. | Controlled environment, sometimes outside regular setting. |
| Data Type | Qualitative notes, anecdotal records, checklists. | Quantitative scores and percentiles. |
| Usefulness | Supports individualized instruction and ongoing planning. | Determines eligibility, benchmarks, and large-scale outcomes. |
| Observer Role | Teacher or caregiver with direct child interaction. | Trained evaluator or psychologist. |
| Examples | Anecdotal records, developmental checklists, portfolios. | Pearson's WPPSI, Woodcock-Johnson Tests, Denver II. |
| Advantages | Contextual, child-centered, promotes rapport. | Reliable, objective, norm-referenced data. |
| Limitations | Subject to observer bias, less standardized. | May ignore situational factors, stress-inducing. |
Introduction to Preschool Assessment Methods
Observation assessment in preschool involves educators systematically watching children in natural settings, capturing developmental milestones and social interactions without artificial testing pressures. Standardized assessment uses structured tools with uniform procedures to measure specific skills against established norms, providing quantifiable data on early childhood development. Combining both methods offers a comprehensive understanding of a child's learning progress and developmental needs.
Defining Observation Assessment in Early Education
Observation assessment in early education involves systematically watching and recording children's behaviors, skills, and interactions in natural settings to gauge developmental progress. This method captures authentic learning moments, providing educators with qualitative data tailored to each child's unique growth patterns. Unlike standardized assessments, observation assessments emphasize individual context and flexibility, fostering a comprehensive understanding of preschoolers' abilities.
What Is Standardized Assessment in Preschool?
Standardized assessment in preschool involves using uniform procedures and scoring methods to evaluate children's development and learning outcomes. These assessments provide objective data on skills such as language, motor abilities, and cognitive functions, enabling comparisons across different children or groups. The consistent format and administration ensure reliability and validity, supporting informed decisions about early intervention and educational planning.
Key Differences: Observation vs Standardized Assessment
Observation assessment in preschool involves continuous, naturalistic monitoring of children's behavior and development within their everyday environment, capturing authentic learning processes and social interactions. Standardized assessment uses structured tools with uniform procedures and scoring criteria to evaluate specific skills or knowledge against established benchmarks, providing quantifiable data for comparison. Key differences include the flexible, qualitative insights gained from observation versus the objective, quantitative results derived from standardized assessment instruments.
Benefits of Observation Assessment in Preschool Settings
Observation assessment in preschool settings provides a natural and authentic way to evaluate children's developmental progress, capturing nuanced social, emotional, and cognitive behaviors in real-time. This approach allows educators to tailor learning experiences based on individual strengths and needs, fostering personalized growth. Unlike standardized assessments, observation reduces test anxiety and provides a comprehensive understanding of a child's abilities within their everyday environment.
Advantages of Standardized Assessment for Young Learners
Standardized assessment in preschool provides consistent, objective measures of young learners' developmental progress, allowing educators to identify specific strengths and areas needing support. These assessments enable reliable comparisons across diverse populations and early childhood programs, ensuring equitable evaluation standards. Data from standardized tools facilitate targeted instructional planning and track growth longitudinally to inform individualized learning strategies.
Limitations of Observation Assessment in Early Childhood
Observation assessment in early childhood often lacks consistency and objectivity, as it depends heavily on the subjective interpretations of educators. This method can miss subtle developmental delays due to its informal nature and variability in observation frequency. Unlike standardized assessments, observation assessment may not provide comprehensive data for tracking progress or making comparisons across populations.
Criticisms of Standardized Assessment in Preschool Education
Standardized assessments in preschool education face criticism for failing to capture the developmental nuances and individual learning styles of young children. These assessments often rely on rigid criteria that overlook social-emotional growth and creativity, key components of early childhood development. Critics argue that standardized tests may induce stress and limit teachers' ability to tailor instruction based on personalized observations.
Best Practices for Implementing Preschool Assessments
Effective preschool assessments balance observation assessment and standardized assessment to support comprehensive child development evaluation. Observation assessment captures natural interactions and developmental milestones through teacher-led, real-time documentation, while standardized assessments provide objective data for developmental benchmarks using validated tools. Best practices for implementing preschool assessments emphasize integrating observational data with standardized results, ongoing educator training, cultural responsiveness, and involving families to create individualized learning strategies and accurate progress tracking.
Choosing the Right Assessment Approach for Preschoolers
Observation assessment in preschool offers a naturalistic and ongoing evaluation of children's developmental progress, capturing social, emotional, and cognitive skills in a familiar environment. Standardized assessment provides structured, norm-referenced benchmarks to measure specific academic abilities but may not fully reflect a child's practical learning or behavior. Selecting the right assessment approach depends on the child's unique needs, the purpose of evaluation, and the educator's goal to support individualized development and instructional planning.
Observation Assessment vs Standardized Assessment Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com