Scaffolded learning in preschool supports children's development by providing tailored guidance that gradually decreases as they gain independence, enhancing critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Direct instruction focuses on explicit teaching of specific skills and knowledge, ensuring clear objectives and immediate feedback. Combining both approaches creates a balanced environment that fosters autonomy while maintaining structured learning.
Table of Comparison
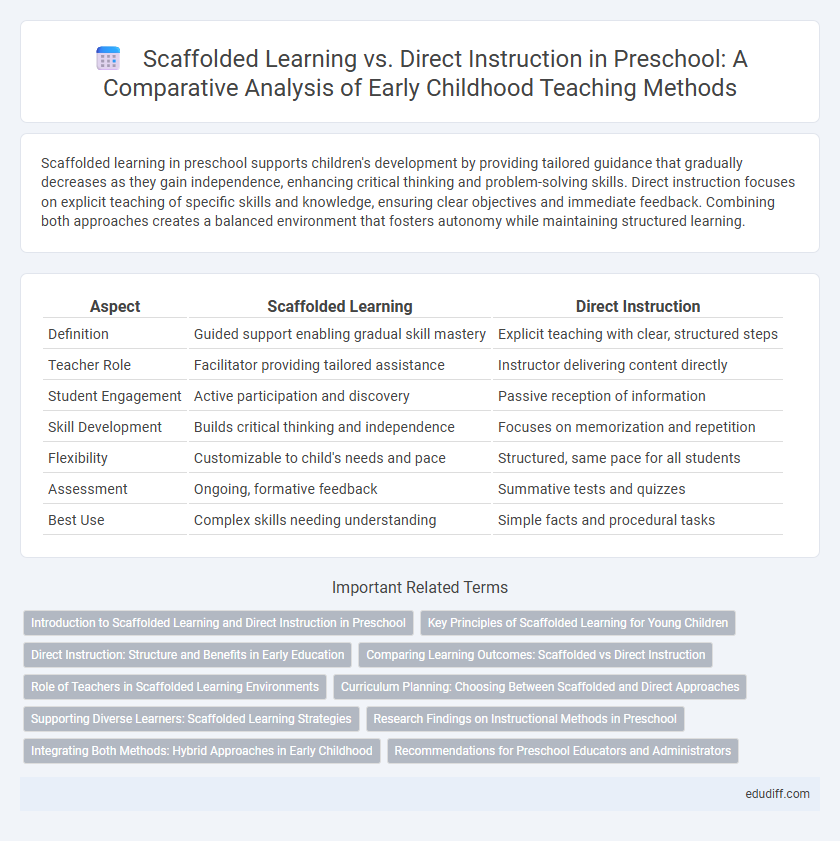
| Aspect | Scaffolded Learning | Direct Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Guided support enabling gradual skill mastery | Explicit teaching with clear, structured steps |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator providing tailored assistance | Instructor delivering content directly |
| Student Engagement | Active participation and discovery | Passive reception of information |
| Skill Development | Builds critical thinking and independence | Focuses on memorization and repetition |
| Flexibility | Customizable to child's needs and pace | Structured, same pace for all students |
| Assessment | Ongoing, formative feedback | Summative tests and quizzes |
| Best Use | Complex skills needing understanding | Simple facts and procedural tasks |
Introduction to Scaffolded Learning and Direct Instruction in Preschool
Scaffolded learning in preschool involves providing tailored support that gradually fades as children develop skills, encouraging independent problem-solving and critical thinking. Direct instruction emphasizes clear, structured teaching with explicit guidance, focusing on specific learning objectives and ensuring mastery through repetition and practice. Both approaches play a crucial role in early childhood education by addressing diverse learning needs and fostering cognitive development.
Key Principles of Scaffolded Learning for Young Children
Scaffolded learning in preschool emphasizes providing tailored support that matches a child's current developmental level, gradually withdrawing aid as independence grows. Key principles include guided participation, where adults model and assist activities, and zone of proximal development, focusing on tasks just beyond the child's unassisted abilities. This approach contrasts with direct instruction by fostering active problem-solving and critical thinking through interactive, collaborative experiences.
Direct Instruction: Structure and Benefits in Early Education
Direct instruction in preschool offers a clear, structured approach where teachers lead lessons with explicit objectives and step-by-step guidance, enhancing children's understanding and skill acquisition. This method supports early learners by providing focused practice and immediate feedback, which promotes mastery of foundational concepts such as literacy and numeracy. Research demonstrates that direct instruction can accelerate cognitive development and improve academic outcomes in early childhood education settings.
Comparing Learning Outcomes: Scaffolded vs Direct Instruction
Scaffolded learning in preschool promotes deeper understanding and long-term retention by progressively building on a child's existing knowledge with guided support, while direct instruction provides clear, structured teaching of specific skills leading to quicker mastery of targeted tasks. Studies show scaffolded approaches enhance critical thinking and problem-solving abilities more effectively than direct instruction, which excels in delivering foundational knowledge efficiently. Effective preschool curricula often blend scaffolded learning's developmental benefits with direct instruction's clarity to optimize diverse learning outcomes.
Role of Teachers in Scaffolded Learning Environments
Teachers in scaffolded learning environments actively guide preschoolers by providing tailored support that adapts to each child's developmental level, encouraging exploration and problem-solving. They create responsive interactions that gradually fade assistance as children gain confidence and skills, fostering independence and critical thinking. This dynamic role contrasts with direct instruction, where teachers primarily deliver explicit knowledge with less emphasis on individualized support.
Curriculum Planning: Choosing Between Scaffolded and Direct Approaches
Scaffolded learning in preschool curriculum planning emphasizes building on children's prior knowledge and gradually increasing complexity through guided support, fostering deeper understanding and independent skills. Direct instruction focuses on structured, explicit teaching of specific skills and content, providing clear, step-by-step guidance to ensure mastery of foundational concepts. Educators must balance these approaches based on developmental needs, learning objectives, and classroom dynamics to optimize early childhood education outcomes.
Supporting Diverse Learners: Scaffolded Learning Strategies
Scaffolded learning in preschool employs tailored support systems such as guided questioning, visual aids, and step-by-step task breakdowns that align with the cognitive and linguistic levels of diverse learners. This approach fosters active engagement and gradual skill mastery, accommodating learners with varying abilities including those with language delays or learning differences. Scaffolded techniques create a flexible learning environment that contrasts with the one-size-fits-all nature of direct instruction, ensuring inclusivity and personalized growth opportunities.
Research Findings on Instructional Methods in Preschool
Research findings on instructional methods in preschool reveal that scaffolded learning significantly enhances children's cognitive development by providing tailored support that gradually fades as competence increases. Studies indicate this approach fosters critical thinking and problem-solving skills more effectively than direct instruction, which often emphasizes rote memorization and passive learning. Meta-analyses confirm scaffolded learning promotes higher engagement and deeper understanding, essential for early childhood educational success.
Integrating Both Methods: Hybrid Approaches in Early Childhood
Hybrid approaches in early childhood education combine scaffolded learning and direct instruction to enhance cognitive and social development in preschoolers. Scaffolded learning supports individualized guidance and encourages exploration, while direct instruction provides clear, structured teaching of fundamental skills. Integrating both methods maximizes engagement, deepens understanding, and fosters critical thinking by balancing child-led discovery with teacher-led explanations.
Recommendations for Preschool Educators and Administrators
Preschool educators and administrators should implement scaffolded learning by gradually building on children's existing skills, providing tailored support that promotes autonomy and critical thinking. Direct instruction methods are effective for teaching foundational skills such as letter recognition and number sense, requiring clear, concise guidance and repetition. Combining scaffolded learning with direct instruction offers a balanced approach, enhancing early childhood cognitive development and fostering social-emotional growth in preschool settings.
Scaffolded learning vs Direct instruction Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com