Emergent curriculum prioritizes child-led learning by adapting activities based on students' interests and developmental needs, fostering creativity and engagement. Prescribed curriculum follows a fixed set of objectives and content determined by educational authorities, ensuring consistency and measurable outcomes across classrooms. Balancing these approaches can support both individualized exploration and standardized learning goals in primary education.
Table of Comparison
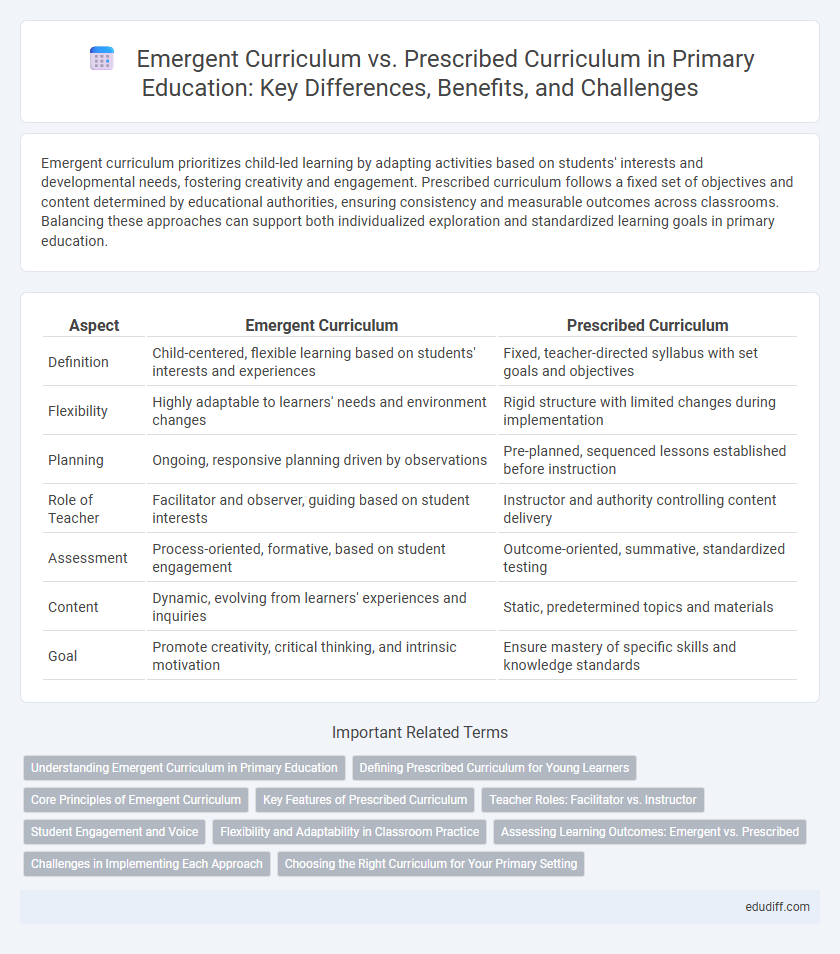
| Aspect | Emergent Curriculum | Prescribed Curriculum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Child-centered, flexible learning based on students' interests and experiences | Fixed, teacher-directed syllabus with set goals and objectives |
| Flexibility | Highly adaptable to learners' needs and environment changes | Rigid structure with limited changes during implementation |
| Planning | Ongoing, responsive planning driven by observations | Pre-planned, sequenced lessons established before instruction |
| Role of Teacher | Facilitator and observer, guiding based on student interests | Instructor and authority controlling content delivery |
| Assessment | Process-oriented, formative, based on student engagement | Outcome-oriented, summative, standardized testing |
| Content | Dynamic, evolving from learners' experiences and inquiries | Static, predetermined topics and materials |
| Goal | Promote creativity, critical thinking, and intrinsic motivation | Ensure mastery of specific skills and knowledge standards |
Understanding Emergent Curriculum in Primary Education
Emergent curriculum in primary education emphasizes child-centered learning, allowing themes and activities to develop based on students' interests and experiences. This approach fosters creativity, critical thinking, and engagement by integrating real-life contexts and promoting collaboration among learners. Teachers act as facilitators, observing and responding to children's needs rather than following a fixed set of predetermined objectives.
Defining Prescribed Curriculum for Young Learners
A prescribed curriculum for young learners consists of a structured, predefined set of educational objectives, content, and activities designed by educational authorities or curriculum developers. It emphasizes standardized learning outcomes, ensuring consistency and measurable progress across classrooms and schools. This approach often prioritizes specific skill development, assessment benchmarks, and adherence to state or national educational standards.
Core Principles of Emergent Curriculum
Emergent curriculum in primary education centers on child-led exploration, emphasizing flexibility and responsiveness to students' interests and developmental needs. Core principles include fostering creativity, collaboration, and critical thinking through active, experiential learning rather than rigid, predetermined objectives. This approach promotes intrinsic motivation and deeper engagement by valuing students' voices and encouraging adaptation based on ongoing observations and interactions.
Key Features of Prescribed Curriculum
Prescribed curriculum in primary education emphasizes structured content delivery through predetermined learning objectives, standardized assessments, and fixed instructional sequences. It ensures uniformity across classrooms by following state or national standards, promoting consistency in skill acquisition and knowledge benchmarks. Teachers primarily act as facilitators of predefined material, which aids in systematic progress tracking and accountability.
Teacher Roles: Facilitator vs. Instructor
In emergent curriculum, teachers act as facilitators who observe children's interests and guide learning experiences that evolve naturally, fostering creativity and critical thinking. In prescribed curriculum, teachers function as instructors delivering predefined content and structured lessons, ensuring adherence to specific educational standards. This shift in teacher roles significantly impacts student engagement and the adaptability of learning environments.
Student Engagement and Voice
Emergent curriculum prioritizes student engagement by allowing learners' interests and voices to shape the learning process, fostering deeper involvement and motivation. Unlike prescribed curriculum, which follows a fixed plan with predetermined content, emergent curriculum adapts dynamically to students' ideas and questions, promoting creativity and active participation. This approach empowers students to take ownership of their learning, enhancing critical thinking and collaboration skills.
Flexibility and Adaptability in Classroom Practice
Emergent curriculum emphasizes flexibility and adaptability by allowing teachers to respond to students' interests and developmental needs in real time, fostering personalized learning experiences. Prescribed curriculum follows a fixed, standardized sequence of content, limiting the ability to adjust lessons based on classroom dynamics. This contrast makes emergent curriculum particularly effective for primary education, where responsiveness to young learners promotes engagement and deeper understanding.
Assessing Learning Outcomes: Emergent vs. Prescribed
Assessing learning outcomes in emergent curriculum emphasizes observation-based, formative evaluations that capture children's interests and developmental progress in real-time. Prescribed curriculum relies on standardized tests and predetermined benchmarks to measure student achievement against set educational goals. The flexibility of emergent curriculum allows for adaptive assessment methods, fostering a more individualized understanding of student growth compared to the fixed criteria of prescribed curriculum.
Challenges in Implementing Each Approach
Emergent Curriculum presents challenges such as requiring extensive teacher flexibility and observational skills to adapt to children's interests in real-time, often leading to difficulties in planning and resource allocation. Prescribed Curriculum faces obstacles including limited responsiveness to individual student needs and creativity constraints, resulting in potential disengagement and diminished intrinsic motivation. Both approaches demand significant professional development and support to address these implementation complexities effectively.
Choosing the Right Curriculum for Your Primary Setting
Selecting the right curriculum for a primary setting depends on balancing child-centered learning with structured educational goals. Emergent Curriculum fosters creativity and responsiveness to children's interests, promoting engagement and development through exploration and inquiry. Prescribed Curriculum provides a consistent framework ensuring coverage of essential skills and standards, supporting measurable academic progress and preparation for future learning stages.
Emergent Curriculum vs Prescribed Curriculum Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com