Instructional coaching offers personalized guidance to improve specific teaching strategies, while peer mentoring emphasizes mutual support and collaborative growth among colleagues. Professional pet educators benefit from instructional coaching by receiving targeted feedback tailored to their unique classroom challenges. Peer mentoring fosters a community of practice, encouraging shared experiences and collective problem-solving within the professional pet industry.
Table of Comparison
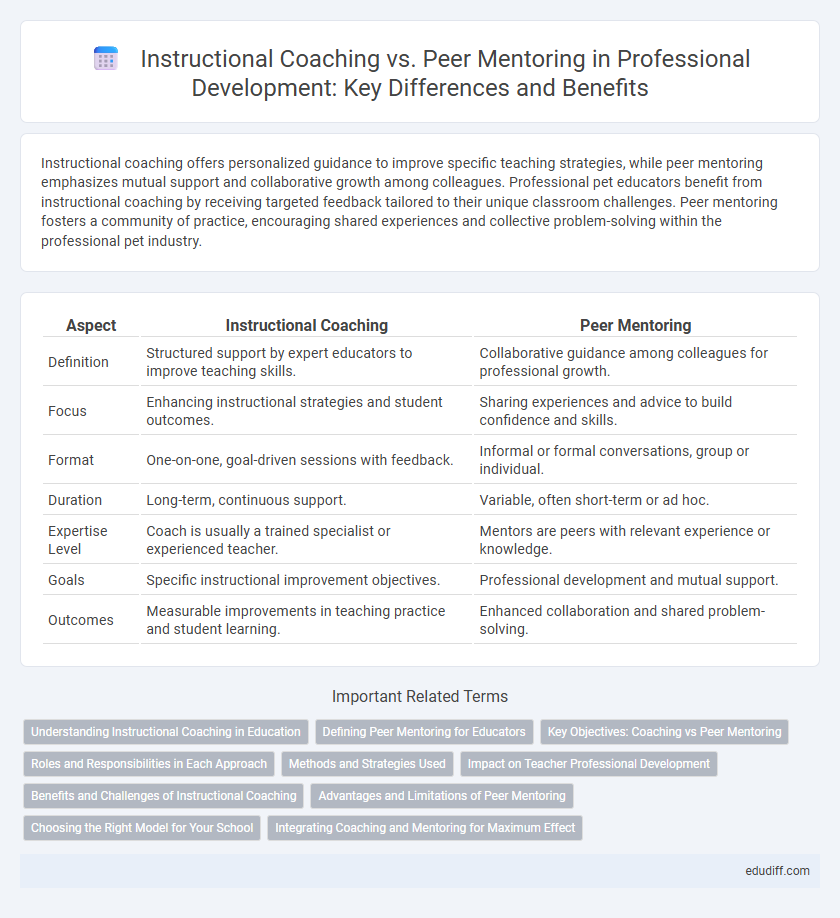
| Aspect | Instructional Coaching | Peer Mentoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured support by expert educators to improve teaching skills. | Collaborative guidance among colleagues for professional growth. |
| Focus | Enhancing instructional strategies and student outcomes. | Sharing experiences and advice to build confidence and skills. |
| Format | One-on-one, goal-driven sessions with feedback. | Informal or formal conversations, group or individual. |
| Duration | Long-term, continuous support. | Variable, often short-term or ad hoc. |
| Expertise Level | Coach is usually a trained specialist or experienced teacher. | Mentors are peers with relevant experience or knowledge. |
| Goals | Specific instructional improvement objectives. | Professional development and mutual support. |
| Outcomes | Measurable improvements in teaching practice and student learning. | Enhanced collaboration and shared problem-solving. |
Understanding Instructional Coaching in Education
Instructional coaching in education involves a structured partnership between an expert coach and a teacher aimed at improving instructional practices through observation, feedback, and targeted professional development. This approach emphasizes data-driven strategies and personalized support to enhance student learning outcomes and teacher efficacy. Unlike peer mentoring, which often relies on collaborative guidance among equals, instructional coaching is typically led by a trained specialist focused on specific pedagogical improvements.
Defining Peer Mentoring for Educators
Peer mentoring for educators involves experienced teachers providing guidance, support, and feedback to colleagues to enhance instructional practices and professional growth. This collaborative relationship promotes shared learning, reflection, and problem-solving within a supportive professional community. Peer mentoring emphasizes mutual respect and ongoing dialogue, fostering continuous improvement and teacher efficacy.
Key Objectives: Coaching vs Peer Mentoring
Instructional coaching primarily aims to enhance teaching practices by providing personalized, evidence-based feedback focused on improving student outcomes and professional growth. Peer mentoring emphasizes collaborative support, fostering mutual development through shared experiences, problem-solving, and reflective dialogue among colleagues. Both approaches prioritize continuous improvement but differ as coaching centers on guided performance enhancement, while mentoring builds relational trust and peer-led learning.
Roles and Responsibilities in Each Approach
Instructional coaching centers on personalized, skill-specific support where coaches provide targeted feedback, model best practices, and facilitate reflective teaching to enhance instructional quality. Peer mentoring emphasizes mutual growth through collaborative dialogue, shared experiences, and reciprocal guidance, fostering a supportive learning community among educators. Coaches typically hold formal positions with defined goals aligned to school strategies, whereas peer mentors operate more informally, building trust and professional relationships over time.
Methods and Strategies Used
Instructional coaching employs data-driven feedback, observation cycles, and targeted modeling to enhance teacher practices, emphasizing personalized professional development. Peer mentoring relies on collaborative dialogue, shared experiences, and reflective questioning to foster mutual growth and instructional improvement. Both methods utilize goal-setting and progress monitoring but differ in their structural focus--coaching centers on expert guidance while mentoring leverages reciprocal support.
Impact on Teacher Professional Development
Instructional coaching delivers targeted, evidence-based feedback that accelerates skill mastery and directly improves classroom practices, leading to measurable gains in student outcomes. Peer mentoring fosters collaborative reflection and sharing of diverse teaching strategies, enhancing professional growth through mutual support and ongoing dialogue. Both methods contribute significantly to teacher development, but instructional coaching shows a stronger correlation with sustained instructional improvements and data-driven decision making.
Benefits and Challenges of Instructional Coaching
Instructional coaching enhances teaching effectiveness through personalized, data-driven feedback, fostering continuous educator growth and improved student outcomes. Challenges include the need for sustained time commitment, overcoming resistance to change, and ensuring coaches possess strong interpersonal and pedagogical skills. This tailored support contrasts with peer mentoring, which relies more on collaborative sharing and mutual experience but may lack the structured guidance of coaching.
Advantages and Limitations of Peer Mentoring
Peer mentoring fosters a collaborative environment where experienced colleagues provide personalized support, enhancing practical skill development and boosting confidence. It encourages mutual growth and knowledge exchange but may lack the structured guidance and formal assessment found in instructional coaching. Limitations include potential variability in mentor expertise and inconsistent feedback quality, which can affect the mentee's progress and learning outcomes.
Choosing the Right Model for Your School
Selecting the optimal development approach hinges on evaluating your school's goals, staff experience, and culture; instructional coaching delivers personalized expert guidance to improve teaching practices, while peer mentoring fosters collaborative growth among equals. Schools aiming to elevate specific instructional skills benefit from the targeted feedback and goal-setting intrinsic to coaching, whereas peer mentoring enhances community and shared accountability through reciprocal support. Aligning the model with your institution's priorities ensures sustainable professional growth and measurable impact on student achievement.
Integrating Coaching and Mentoring for Maximum Effect
Integrating instructional coaching and peer mentoring enhances professional development by combining personalized skill-building with collaborative knowledge sharing, fostering continuous improvement and reflective practice. Instructional coaching targets specific instructional techniques through data-driven feedback, while peer mentoring leverages shared experiences to cultivate supportive learning communities. Blending these approaches maximizes teacher efficacy and student outcomes by addressing both technical proficiency and relational growth.
Instructional Coaching vs Peer Mentoring Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com