Peer mentoring fosters collaborative learning and mutual support among colleagues, enhancing professional growth through shared experiences and feedback. Traditional supervision typically involves hierarchical oversight, emphasizing evaluation and compliance with established standards. Emphasizing peer mentoring can lead to increased engagement, skill development, and a more dynamic professional environment compared to conventional supervisory methods.
Table of Comparison
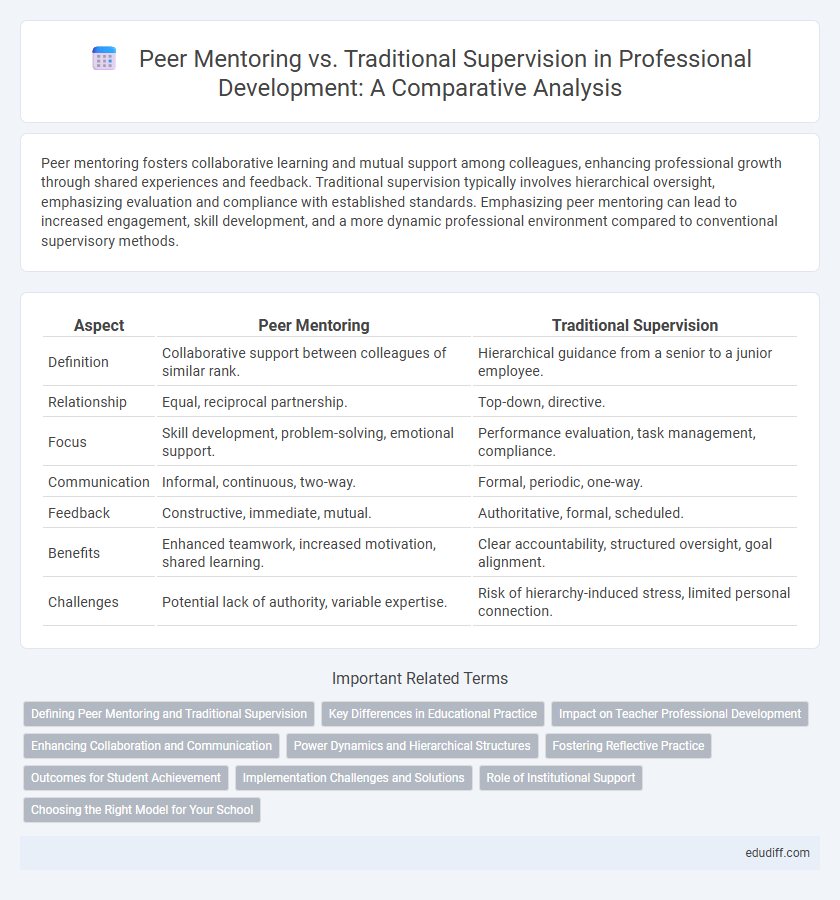
| Aspect | Peer Mentoring | Traditional Supervision |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collaborative support between colleagues of similar rank. | Hierarchical guidance from a senior to a junior employee. |
| Relationship | Equal, reciprocal partnership. | Top-down, directive. |
| Focus | Skill development, problem-solving, emotional support. | Performance evaluation, task management, compliance. |
| Communication | Informal, continuous, two-way. | Formal, periodic, one-way. |
| Feedback | Constructive, immediate, mutual. | Authoritative, formal, scheduled. |
| Benefits | Enhanced teamwork, increased motivation, shared learning. | Clear accountability, structured oversight, goal alignment. |
| Challenges | Potential lack of authority, variable expertise. | Risk of hierarchy-induced stress, limited personal connection. |
Defining Peer Mentoring and Traditional Supervision
Peer mentoring involves a collaborative relationship where individuals at similar professional levels provide guidance, support, and feedback to each other, fostering mutual growth and development. Traditional supervision is a hierarchical structure in which a more experienced supervisor directs, evaluates, and manages the performance and progress of their subordinate. Both approaches aim to enhance skills and productivity but differ significantly in dynamics, authority, and interaction style.
Key Differences in Educational Practice
Peer mentoring fosters collaborative learning by encouraging mutual support and shared experiences among students, enhancing critical thinking and self-directed learning. Traditional supervision relies on hierarchical guidance where an experienced educator directs and evaluates student progress, often emphasizing accountability and adherence to established standards. The key differences lie in the relational dynamics and autonomy, with peer mentoring promoting egalitarian interaction and traditional supervision ensuring structured oversight.
Impact on Teacher Professional Development
Peer mentoring fosters collaborative learning and reflective practice, significantly enhancing teacher professional development by encouraging shared expertise and continuous feedback. Traditional supervision often relies on hierarchical evaluation, which may limit open communication and hinder personalized growth opportunities. Empirical studies indicate that peer mentoring leads to higher teacher engagement, improved instructional strategies, and sustained professional growth compared to conventional supervisory models.
Enhancing Collaboration and Communication
Peer mentoring fosters enhanced collaboration and communication by creating a supportive environment where colleagues share experiences and insights openly, promoting mutual trust and knowledge exchange. In contrast, traditional supervision often emphasizes hierarchical feedback, which can limit open dialogue and reduce opportunities for collaborative problem-solving. Integrating peer mentoring into professional settings encourages continuous learning and a more dynamic interaction among team members, leading to improved teamwork and productivity.
Power Dynamics and Hierarchical Structures
Peer mentoring fosters collaborative learning by minimizing power imbalances and promoting mutual support, contrasting sharply with traditional supervision, which often reinforces hierarchical structures and authority gradients. Power dynamics in traditional supervision can inhibit open communication and limit mentees' autonomy, whereas peer mentoring encourages egalitarian relationships that enhance trust and knowledge exchange. This shift from a top-down approach to a more reciprocal interaction model enhances professional development and intrinsic motivation within organizations.
Fostering Reflective Practice
Peer mentoring fosters reflective practice by encouraging open dialogue, collaborative problem-solving, and shared experiences, which enhance self-awareness and critical thinking skills. Traditional supervision often follows a hierarchical approach, focusing on evaluation and directive feedback that may limit opportunities for mutual reflection and growth. Integrating peer mentoring within professional development frameworks promotes continuous learning and deeper engagement in reflective practice.
Outcomes for Student Achievement
Peer mentoring fosters collaborative learning and critical thinking, resulting in improved student engagement and higher academic achievement compared to traditional supervision. Studies reveal that students involved in peer mentoring programs demonstrate increased motivation, enhanced problem-solving skills, and better retention of subject matter. Traditional supervision often emphasizes evaluation and compliance, which may limit opportunities for personalized feedback and peer-supported growth crucial for student success.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Implementing peer mentoring faces challenges such as inconsistent mentor expertise and limited formal training frameworks, which can impact the quality of guidance provided. Traditional supervision often struggles with hierarchical barriers and time constraints, hindering effective communication and feedback. Solutions include structured mentor training programs for peer mentoring and adopting flexible scheduling with regular check-ins in traditional supervision to enhance support and collaboration.
Role of Institutional Support
Institutional support plays a critical role in enhancing both peer mentoring and traditional supervision by providing structured frameworks, resources, and training that foster effective communication and skill development. In peer mentoring, institutional backing ensures consistent guidelines and recognition, which promote accountability and collaborative learning environments. For traditional supervision, institutional support reinforces authority, establishes clear performance metrics, and facilitates professional growth through formal feedback mechanisms.
Choosing the Right Model for Your School
Peer mentoring fosters collaborative learning and empowers students through shared experiences, enhancing engagement and personal development. Traditional supervision provides structured oversight and expert guidance from experienced staff, ensuring adherence to educational standards and accountability. Schools should assess their culture, resources, and goals to determine whether the supportive, student-centered approach of peer mentoring or the authoritative framework of traditional supervision best aligns with their objectives.
Peer mentoring vs Traditional supervision Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com