Extended School Year (ESY) services provide specialized instruction and support beyond the regular school year to prevent regression in students with special needs. These services are tailored to individual education plans (IEPs) and focus on maintaining skills acquired during the regular school year. Regular School Year programs offer standard educational instruction, while ESY emphasizes continuity and reinforcement for students requiring extra support.
Table of Comparison
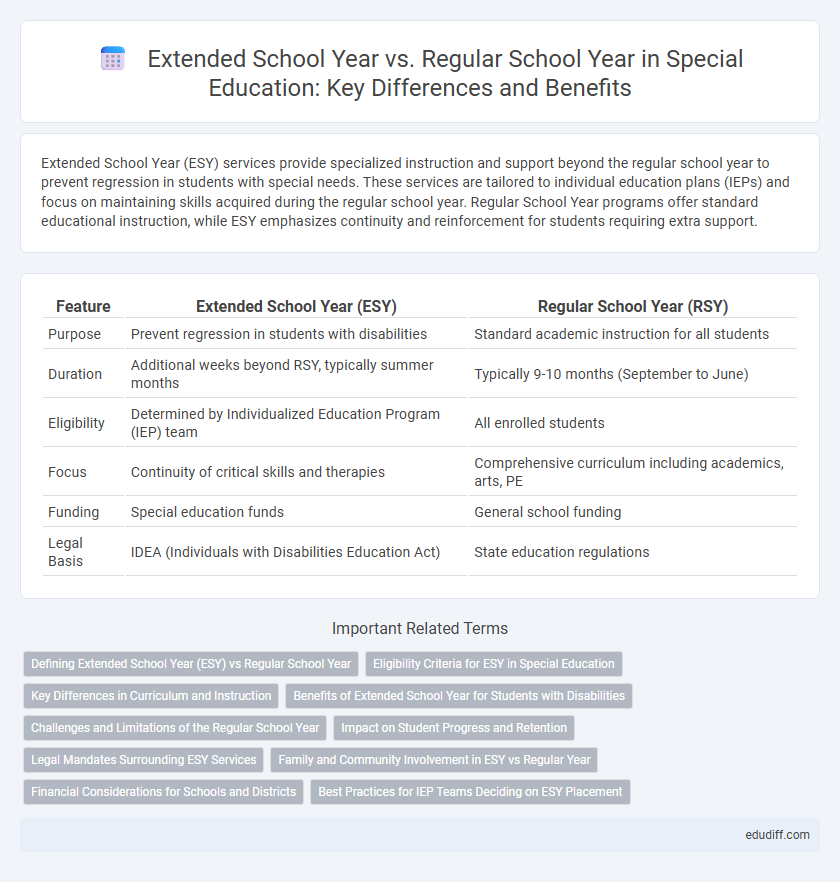
| Feature | Extended School Year (ESY) | Regular School Year (RSY) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevent regression in students with disabilities | Standard academic instruction for all students |
| Duration | Additional weeks beyond RSY, typically summer months | Typically 9-10 months (September to June) |
| Eligibility | Determined by Individualized Education Program (IEP) team | All enrolled students |
| Focus | Continuity of critical skills and therapies | Comprehensive curriculum including academics, arts, PE |
| Funding | Special education funds | General school funding |
| Legal Basis | IDEA (Individuals with Disabilities Education Act) | State education regulations |
Defining Extended School Year (ESY) vs Regular School Year
Extended School Year (ESY) refers to specially designed educational services provided beyond the traditional nine- to ten-month school calendar, aimed at preventing significant regression of skills in students with disabilities. The Regular School Year (RSY) typically spans around 180 instructional days, adhering to a fixed schedule that may not address the individual needs of all students, especially those requiring continuous support. ESY programs focus on maintaining critical academic, social, and functional skills without the loss of progress during extended breaks.
Eligibility Criteria for ESY in Special Education
Eligibility criteria for Extended School Year (ESY) services in Special Education typically require a demonstrated need for continued instruction beyond the Regular School Year to prevent substantial regression of acquired skills. Determining factors include the severity of the student's disability, history of regression and recoupment rates during breaks, and whether the student is emerging critical life skills or at a pivotal stage of skill acquisition. Individualized Education Program (IEP) teams utilize data-driven assessments and progress monitoring to establish ESY eligibility, ensuring tailored support aligned with each student's unique educational needs.
Key Differences in Curriculum and Instruction
Extended School Year (ESY) programs provide individualized instruction tailored to prevent significant regression in students with disabilities, focusing on reinforcing previously mastered skills rather than introducing new curriculum content. Regular School Year (RSY) instruction covers standard academic goals with a broader scope, emphasizing progressive skill development and comprehensive curriculum coverage. ESY sessions typically operate on a condensed schedule with high-intensity support, while RSY follows the full academic calendar with standard instructional pacing.
Benefits of Extended School Year for Students with Disabilities
Extended School Year (ESY) services provide crucial academic support that prevents regression for students with disabilities, ensuring continuous skill development beyond the Regular School Year. These services address individualized education plan (IEP) goals by offering tailored instruction and related services, helping maintain progress and enhance learning retention. ESY promotes stability in academic performance and supports behavioral and social skills growth, minimizing summer learning loss and facilitating smoother transitions between school years.
Challenges and Limitations of the Regular School Year
The regular school year often presents challenges for students requiring special education due to limited instructional time and insufficient opportunities for skill retention and growth. Interruptions during lengthy summer breaks can lead to significant regression in critical academic and social skills, impacting student progress. The rigid schedule and standardized curriculum frequently fail to accommodate the individualized needs of students eligible for Extended School Year (ESY) services.
Impact on Student Progress and Retention
Extended School Year (ESY) services provide targeted instruction beyond the Regular School Year (RSY) to prevent significant regression in students with disabilities, promoting continuous academic progress. ESY focuses on maintaining critical skills during breaks, reducing the risk of skill loss and enhancing long-term retention compared to RSY alone. Research indicates that students receiving ESY demonstrate improved consistency in achievement and reduced learning gaps, supporting sustained educational growth.
Legal Mandates Surrounding ESY Services
Extended School Year (ESY) services are legally mandated under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) to ensure students with disabilities receive uninterrupted special education during school breaks. ESY eligibility is determined based on regression and recoupment criteria, emphasizing the necessity of continuous support for maintaining educational progress. Failure to provide ESY services when warranted may result in violations of a student's Free Appropriate Public Education (FAPE) rights.
Family and Community Involvement in ESY vs Regular Year
Family and community involvement in Extended School Year (ESY) programs often intensifies compared to the regular school year, as ESY services target students with individualized needs requiring consistent support beyond typical schedules. ESY fosters collaborative efforts between educators, families, and community resources to maintain progress and prevent skill regression during breaks. Regular school years offer broader opportunities for engagement through diverse extracurricular activities and school events, yet ESY emphasizes focused, goal-oriented partnerships to meet specific educational objectives.
Financial Considerations for Schools and Districts
Extended School Year (ESY) programs incur higher financial costs for schools and districts compared to the regular school year due to additional staffing, transportation, and facility expenses. Budget allocation must account for these increased operational costs while ensuring compliance with Individualized Education Program (IEP) mandates to provide appropriate services. Strategic financial planning is essential to balance limited resources and optimize support for students requiring ESY services.
Best Practices for IEP Teams Deciding on ESY Placement
IEP teams determine Extended School Year (ESY) eligibility by analyzing regression and recoupment data to identify if a student's skills significantly decline during breaks in instruction. Best practices involve individualized assessments, collaboration with families, and alignment with evidence-based criteria outlined in IDEA to ensure ESY services support the student's critical educational needs. Maintaining thorough documentation and regularly reviewing progress fosters effective decision-making that prioritizes continuity of learning beyond the Regular School Year.
Extended School Year vs Regular School Year Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com