Inclusion in special pet care promotes integrated environments where animals with unique needs receive personalized attention alongside others, fostering socialization and well-being. Segregation isolates special pets, potentially limiting their social interactions and preventing holistic care. Emphasizing inclusion supports healthier development and improved emotional states for all pets.
Table of Comparison
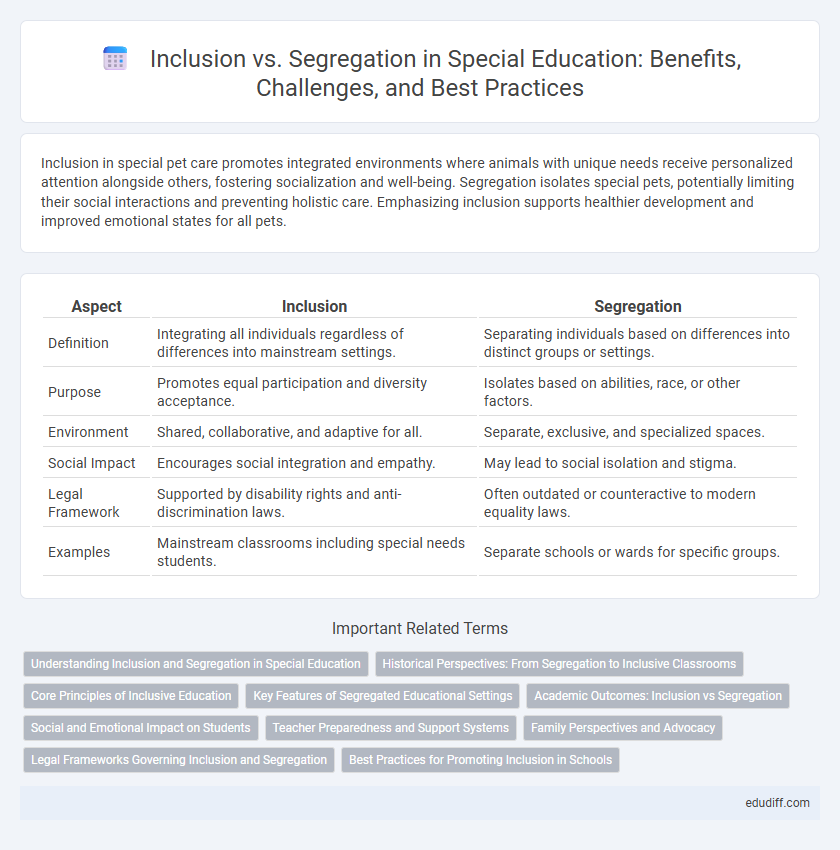
| Aspect | Inclusion | Segregation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrating all individuals regardless of differences into mainstream settings. | Separating individuals based on differences into distinct groups or settings. |
| Purpose | Promotes equal participation and diversity acceptance. | Isolates based on abilities, race, or other factors. |
| Environment | Shared, collaborative, and adaptive for all. | Separate, exclusive, and specialized spaces. |
| Social Impact | Encourages social integration and empathy. | May lead to social isolation and stigma. |
| Legal Framework | Supported by disability rights and anti-discrimination laws. | Often outdated or counteractive to modern equality laws. |
| Examples | Mainstream classrooms including special needs students. | Separate schools or wards for specific groups. |
Understanding Inclusion and Segregation in Special Education
In special education, inclusion refers to integrating students with disabilities into general education classrooms, promoting equal access to learning and social interaction with peers. Segregation involves separate settings or specialized classrooms where students with disabilities receive instruction apart from their non-disabled peers, often limiting opportunities for social integration. Understanding these approaches is crucial for creating effective educational environments that balance academic support and social inclusion for all students.
Historical Perspectives: From Segregation to Inclusive Classrooms
Historical perspectives on education reveal a transformative shift from segregation, where students with disabilities or from marginalized groups were excluded or separated, to inclusive classrooms that embrace diversity and provide equal learning opportunities. Landmark policies such as the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) in the United States played a crucial role in promoting inclusive education by mandating access to free and appropriate public education for all children. This evolution reflects a growing societal recognition of the value of diversity and the importance of accommodating individual needs within mainstream educational settings.
Core Principles of Inclusive Education
Inclusive education centers on the principle that all students, regardless of disabilities or differences, learn together in mainstream classrooms with appropriate support. Core principles include equity, respect for diversity, and providing individualized accommodations to meet each learner's needs. This approach fosters social integration, equal access to quality education, and promotes a sense of belonging for every student.
Key Features of Segregated Educational Settings
Segregated educational settings are characterized by separate classrooms or schools exclusively for students with disabilities, often limiting their interaction with non-disabled peers. These settings typically emphasize specialized instruction tailored to specific disabilities but may lack opportunities for social integration and inclusion. Physical separation and differentiated curricula are core features, impacting both academic and social development outcomes.
Academic Outcomes: Inclusion vs Segregation
Inclusion in classrooms fosters improved academic outcomes by providing students with disabilities access to the general curriculum alongside peers, which enhances learning opportunities and social integration. Segregation often limits exposure to grade-level content and reduces motivation, leading to lower academic achievement and slower skill development. Research indicates inclusive settings promote higher test scores, better attendance, and increased graduation rates compared to segregated environments.
Social and Emotional Impact on Students
Inclusion fosters positive social interactions and emotional well-being among students by promoting a sense of belonging and acceptance within the classroom community. Segregation can heighten feelings of isolation and stigmatization, negatively affecting self-esteem and social skills development. Research indicates that inclusive settings contribute to improved emotional resilience, empathy, and peer relationship building for students with diverse learning needs.
Teacher Preparedness and Support Systems
Effective teacher preparedness in special education hinges on comprehensive training programs that emphasize inclusive instructional strategies and adaptive technologies. Robust support systems, including co-teaching models and collaborative planning, enable educators to address diverse learner needs while minimizing segregation. Research shows that well-prepared teachers with access to ongoing professional development significantly improve academic and social outcomes for students with disabilities in inclusive settings.
Family Perspectives and Advocacy
Families of individuals with special needs emphasize inclusion as a critical factor for social development and emotional well-being, advocating for integrated educational settings that promote diversity and equal opportunities. They highlight the negative impacts of segregation, such as social isolation and limited access to resources, which can hinder personal growth and community participation. Advocacy groups support family voices by pushing for policies and practices that ensure inclusive environments, reinforcing the importance of acceptance and collaboration between families, educators, and policymakers.
Legal Frameworks Governing Inclusion and Segregation
Legal frameworks governing inclusion and segregation play a pivotal role in shaping educational and social environments for individuals with special needs. Laws such as the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) mandate inclusive practices by requiring accommodations and equal access to education and public services, while also outlining criteria for legitimate, non-discriminatory segregation when necessary for safety or specialized support. Court rulings and policy amendments continuously influence these legal standards, ensuring that inclusion remains the preferred approach while segregation is strictly regulated and minimized.
Best Practices for Promoting Inclusion in Schools
Creating inclusive school environments involves implementing Universal Design for Learning (UDL) principles to accommodate diverse learning needs and fostering collaborative teaching strategies that integrate students with disabilities alongside their peers. Establishing clear anti-bullying policies and providing ongoing professional development for educators enhances understanding and support for inclusion. Engaging families and community resources promotes a holistic approach, ensuring equitable access to education and social participation for all students.
Inclusion vs Segregation Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com