Resource rooms provide specialized support within a general education setting, allowing students to receive targeted instruction while remaining integrated with peers. Self-contained classrooms offer a more structured environment designed for students with significant needs, providing intensive, individualized attention throughout the school day. Choosing between these options depends on the student's unique academic and social requirements for optimal development.
Table of Comparison
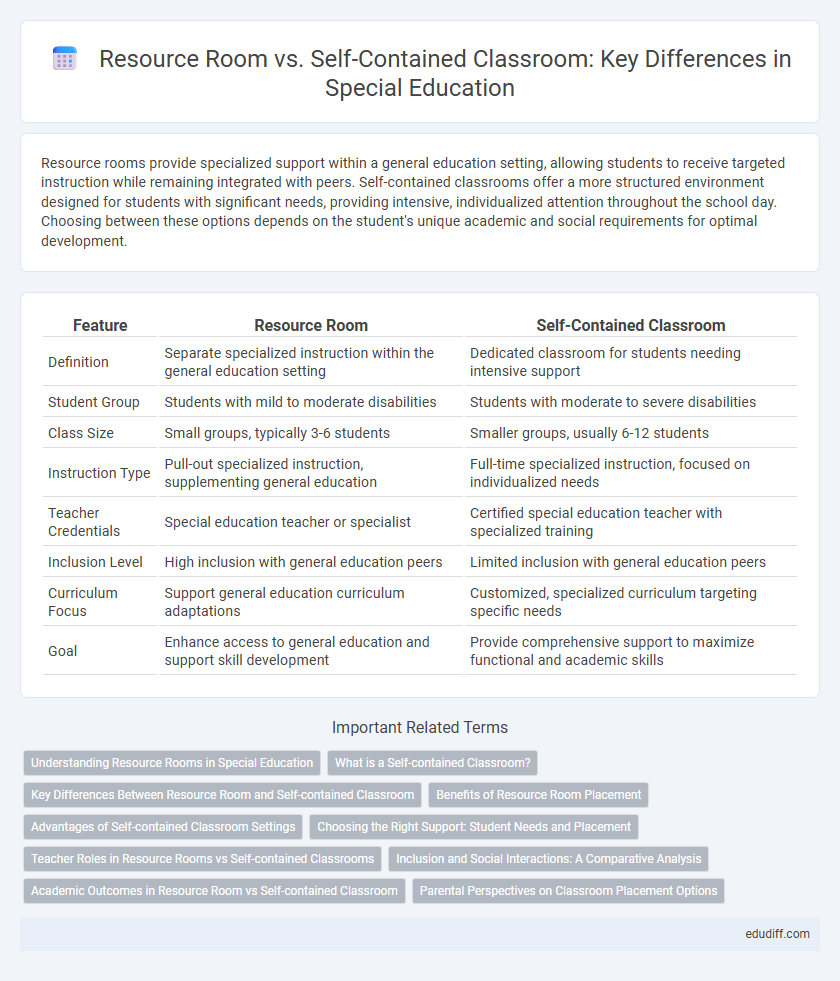
| Feature | Resource Room | Self-Contained Classroom |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Separate specialized instruction within the general education setting | Dedicated classroom for students needing intensive support |
| Student Group | Students with mild to moderate disabilities | Students with moderate to severe disabilities |
| Class Size | Small groups, typically 3-6 students | Smaller groups, usually 6-12 students |
| Instruction Type | Pull-out specialized instruction, supplementing general education | Full-time specialized instruction, focused on individualized needs |
| Teacher Credentials | Special education teacher or specialist | Certified special education teacher with specialized training |
| Inclusion Level | High inclusion with general education peers | Limited inclusion with general education peers |
| Curriculum Focus | Support general education curriculum adaptations | Customized, specialized curriculum targeting specific needs |
| Goal | Enhance access to general education and support skill development | Provide comprehensive support to maximize functional and academic skills |
Understanding Resource Rooms in Special Education
Resource Rooms in special education provide targeted support to students with disabilities while allowing them to participate in general education classrooms for the majority of the day. These rooms offer tailored instruction in specific areas such as reading, math, or social skills, helping students build competencies alongside their peers. Resource Rooms promote inclusion by balancing individualized attention with opportunities for mainstream interaction, distinguishing them from self-contained classrooms that serve as separate settings for comprehensive support.
What is a Self-contained Classroom?
A self-contained classroom is an educational setting where students with similar special needs receive instruction exclusively from a special education teacher throughout the entire school day. This classroom model provides personalized support, tailored curriculum, and small class sizes to address individual learning challenges. It fosters a structured environment aimed at enhancing academic, social, and functional skills for students requiring intensive assistance.
Key Differences Between Resource Room and Self-contained Classroom
Resource rooms provide targeted support to students with disabilities while they spend most of their day in general education classrooms, emphasizing skill-building in specific areas. Self-contained classrooms serve students with more intensive needs, offering specialized instruction within a separate setting for the majority of the school day. Key differences include the level of inclusion, intensity of services, and instructional environment tailored to individual student requirements.
Benefits of Resource Room Placement
Resource room placement offers individualized support while allowing students to participate in general education settings, promoting social integration and academic growth. It provides tailored instruction on specific skills within a less restrictive environment, enhancing student confidence and independence. Access to specialized resources and collaborative teaching strategies in resource rooms optimizes learning outcomes for students with diverse needs.
Advantages of Self-contained Classroom Settings
Self-contained classroom settings offer tailored instruction by grouping students with similar special needs, enabling educators to focus on individualized learning goals and provide specialized support. These classrooms foster a structured environment that minimizes distractions and promotes social-emotional development through consistent routines and peer interactions. Concentrated resources and targeted interventions in self-contained classrooms often lead to improved academic outcomes and increased student confidence.
Choosing the Right Support: Student Needs and Placement
Choosing between a Resource Room and a Self-contained Classroom depends on a student's individual learning needs and the level of support required. Resource Rooms offer targeted instruction for specific skills while allowing students to participate in general education classes, promoting inclusion. Self-contained Classrooms provide a structured environment with intensive, specialized support for students with significant disabilities, ensuring personalized attention and resources.
Teacher Roles in Resource Rooms vs Self-contained Classrooms
Teachers in resource rooms primarily provide targeted, individualized instruction to students with specific learning needs, often collaborating with general education teachers to support inclusive education. In contrast, self-contained classroom teachers manage a consistent group of students with similar disabilities, delivering specialized curricula and adaptations tailored to their unique developmental and behavioral requirements. Both roles demand expertise in differentiated instruction, but resource room teachers emphasize consultation and co-teaching, while self-contained teachers have more direct responsibility for comprehensive student management and progress monitoring.
Inclusion and Social Interactions: A Comparative Analysis
Resource rooms offer targeted support within general education settings, promoting greater inclusion and facilitating peer interactions, which enhance social skills among students with special needs. Self-contained classrooms provide specialized environments that may limit exposure to typical peer models, potentially restricting opportunities for social engagement and integration. Research indicates that inclusive settings like resource rooms support improved social outcomes and foster a sense of belonging, critical for holistic development.
Academic Outcomes in Resource Room vs Self-contained Classroom
Resource rooms provide targeted academic support that addresses individual student needs, often resulting in higher individualized achievement compared to self-contained classrooms. Research indicates that students in resource rooms demonstrate improved academic progress, especially in reading and math, due to tailored instruction and integration with general education curriculum. Self-contained classrooms may offer more intensive support but often lag behind resource rooms in promoting academic growth and inclusion within mainstream academic standards.
Parental Perspectives on Classroom Placement Options
Parents often prioritize individualized attention and social integration when comparing Resource Rooms and Self-contained Classrooms for their children with special needs. In Resource Rooms, children receive specialized support while participating in general education settings, which many parents view as beneficial for social development. Alternatively, some parents prefer Self-contained Classrooms for the consistent, intensive instruction tailored to their child's specific learning challenges.
Resource Room vs Self-contained Classroom Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com