Plagiarism undermines academic integrity by presenting someone else's work as your own, violating the principles of honesty and originality essential in undergraduate studies. Upholding academic integrity requires proper citation and a commitment to producing authentic work that reflects your understanding. Academic institutions enforce strict policies to discourage plagiarism and promote ethical scholarship among students.
Table of Comparison
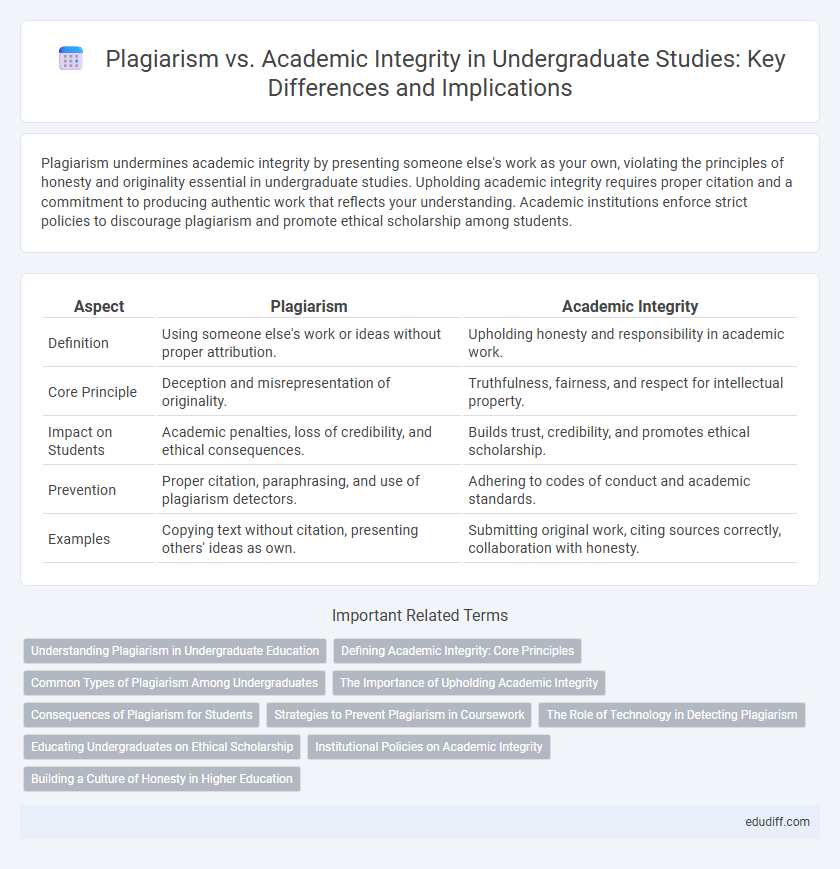
| Aspect | Plagiarism | Academic Integrity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Using someone else's work or ideas without proper attribution. | Upholding honesty and responsibility in academic work. |
| Core Principle | Deception and misrepresentation of originality. | Truthfulness, fairness, and respect for intellectual property. |
| Impact on Students | Academic penalties, loss of credibility, and ethical consequences. | Builds trust, credibility, and promotes ethical scholarship. |
| Prevention | Proper citation, paraphrasing, and use of plagiarism detectors. | Adhering to codes of conduct and academic standards. |
| Examples | Copying text without citation, presenting others' ideas as own. | Submitting original work, citing sources correctly, collaboration with honesty. |
Understanding Plagiarism in Undergraduate Education
Understanding plagiarism in undergraduate education involves recognizing it as the unauthorized use or close imitation of someone else's work presented as one's own, which undermines academic integrity. Effective prevention requires educating students on proper citation methods, the importance of original thought, and institutional policies against academic dishonesty. Upholding academic integrity cultivates a culture of trust, fosters genuine learning, and protects the value of the educational system.
Defining Academic Integrity: Core Principles
Academic integrity encompasses honesty, trust, fairness, respect, and responsibility within the academic community, ensuring that all work submitted by undergraduate students is genuinely their own. Upholding these core principles prevents plagiarism, which is the unauthorized use or imitation of another's intellectual property without proper acknowledgment. Maintaining academic integrity promotes a culture of ethical scholarship and fosters the credibility and value of academic achievements.
Common Types of Plagiarism Among Undergraduates
Common types of plagiarism among undergraduates include direct copying of text without citation, paraphrasing someone else's ideas without proper attribution, and submitting purchased or recycled papers. Self-plagiarism, where students reuse their previous work without acknowledgment, is also prevalent. Understanding these forms is crucial for fostering academic integrity and ensuring original scholarship in higher education.
The Importance of Upholding Academic Integrity
Upholding academic integrity is crucial in maintaining the authenticity and credibility of undergraduate education by preventing plagiarism, which undermines original thought and intellectual growth. Academic integrity fosters a culture of trust, fairness, and respect within the academic community, ensuring that all students are evaluated based on their genuine efforts and knowledge. Institutions that emphasize academic integrity contribute to the development of ethical scholars prepared for professional challenges and lifelong learning.
Consequences of Plagiarism for Students
Plagiarism can lead to severe academic penalties including failing grades, suspension, or expulsion, significantly damaging a student's academic record. Institutions may also impose restrictions on enrollment or revoke degrees if plagiarism is discovered post-graduation. Beyond formal consequences, plagiarism undermines a student's credibility and can negatively impact future academic and professional opportunities.
Strategies to Prevent Plagiarism in Coursework
Implementing thorough citation practices and using plagiarism detection software are critical strategies to prevent plagiarism in undergraduate coursework. Encouraging original thought through formative assessments and clear guidelines reinforces academic integrity among students. Providing workshops on proper research methods and time management skills further reduces the risk of unintentional plagiarism.
The Role of Technology in Detecting Plagiarism
Technology plays a pivotal role in detecting plagiarism by utilizing advanced algorithms and artificial intelligence to compare student submissions against vast databases of academic content, websites, and previous papers. Tools like Turnitin and Grammarly provide educators with detailed similarity reports, helping maintain academic integrity by identifying unoriginal work swiftly and accurately. These technological solutions not only deter students from plagiarizing but also promote a culture of originality and ethical scholarship in undergraduate education.
Educating Undergraduates on Ethical Scholarship
Educating undergraduates on ethical scholarship emphasizes the importance of academic integrity by clearly distinguishing plagiarism from original work, fostering a culture of honesty and respect for intellectual property. Universities implement specialized workshops, honor codes, and digital tools like Turnitin to teach students proper citation practices and the ethical use of sources. Developing these skills early ensures students uphold scholarly standards throughout their academic and professional careers.
Institutional Policies on Academic Integrity
Institutional policies on academic integrity establish strict guidelines to prevent plagiarism, defining it as the unauthorized use or close imitation of another's work without proper attribution. Universities implement mandatory educational programs and use plagiarism detection software to uphold these standards and foster original scholarship. Enforcement measures often include disciplinary actions such as academic probation, failure of assignments, or suspension, emphasizing the institution's commitment to ethical academic conduct.
Building a Culture of Honesty in Higher Education
Fostering academic integrity in undergraduate programs is essential for cultivating a culture of honesty in higher education institutions. Clear policies on plagiarism, combined with education on proper citation practices and ethical research standards, empower students to value original work and intellectual property. Universities that prioritize transparency and accountability create environments where ethical scholarship thrives, enhancing the credibility of academic degrees and the institution's reputation.
Plagiarism vs Academic integrity Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com