Undergraduate advisors provide academic planning, course selection guidance, and degree requirement clarification to ensure students meet graduation criteria. Faculty mentors offer personalized support, career advice, and research opportunities that align with students' academic interests and professional goals. Both roles are essential for undergraduate success but serve distinct purposes in a student's academic journey.
Table of Comparison
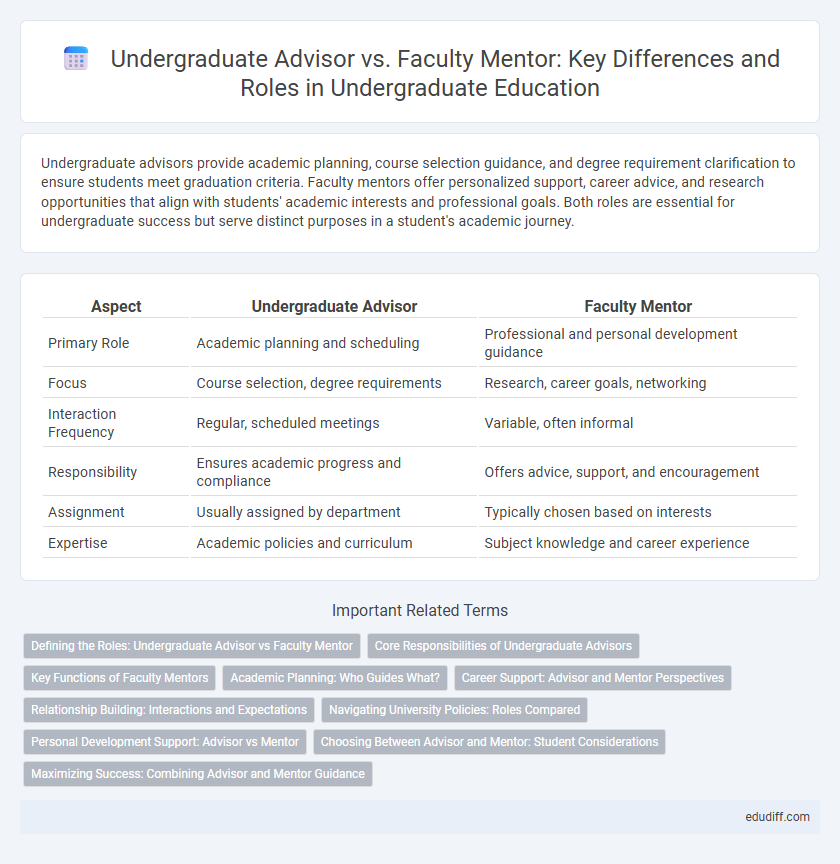
| Aspect | Undergraduate Advisor | Faculty Mentor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Academic planning and scheduling | Professional and personal development guidance |
| Focus | Course selection, degree requirements | Research, career goals, networking |
| Interaction Frequency | Regular, scheduled meetings | Variable, often informal |
| Responsibility | Ensures academic progress and compliance | Offers advice, support, and encouragement |
| Assignment | Usually assigned by department | Typically chosen based on interests |
| Expertise | Academic policies and curriculum | Subject knowledge and career experience |
Defining the Roles: Undergraduate Advisor vs Faculty Mentor
Undergraduate advisors primarily guide students through academic planning, course selection, and ensuring degree requirements are met, while faculty mentors offer personalized support focused on professional development, research opportunities, and career advice. Advisors typically have formal responsibilities tied to institutional policies, whereas faculty mentors provide informal, relationship-based guidance to foster intellectual growth. Distinguishing these roles helps students leverage both resources effectively throughout their undergraduate experience.
Core Responsibilities of Undergraduate Advisors
Undergraduate advisors primarily guide students in course selection, academic planning, and meeting degree requirements to ensure timely graduation. They offer personalized support by monitoring academic progress, addressing university policies, and connecting students with campus resources. Faculty mentors focus more on professional development and research opportunities, while undergraduate advisors emphasize structured academic success and administrative guidance.
Key Functions of Faculty Mentors
Faculty mentors provide personalized academic guidance, support career development, and foster professional growth through regular meetings and tailored advice. They assist undergraduates in navigating complex academic requirements, exploring research opportunities, and building networks within their field. Unlike undergraduate advisors who focus primarily on course selection and administrative tasks, faculty mentors offer deeper engagement in students' intellectual and personal development.
Academic Planning: Who Guides What?
Undergraduate advisors primarily guide students through course selection, degree requirements, and registration processes to ensure timely academic progression. Faculty mentors focus on long-term academic and career goals, providing insights into research opportunities, professional development, and graduate school preparation. This division of roles helps students balance immediate academic responsibilities with broader career planning.
Career Support: Advisor and Mentor Perspectives
Undergraduate advisors provide structured career guidance by offering insights into academic planning and connecting students with internship opportunities specific to their field of study. Faculty mentors offer personalized support, leveraging their professional networks to facilitate research experiences and career advancement tailored to individual student goals. Both roles are essential for comprehensive career development, combining formal academic advising with personalized mentorship to enhance student success.
Relationship Building: Interactions and Expectations
Undergraduate advisors provide structured guidance focused on academic planning, degree requirements, and career advice through regular scheduled meetings that emphasize goal setting and progress tracking. Faculty mentors foster more personalized, informal relationships that encourage intellectual growth, research collaboration, and professional development, often initiating interactions based on shared interests beyond coursework. Both roles involve building trust and open communication, but advisors maintain a more transactional dynamic while mentors cultivate long-term, supportive connections.
Navigating University Policies: Roles Compared
Undergraduate advisors provide structured guidance on navigating university policies, course requirements, and academic regulations to ensure students meet graduation criteria. Faculty mentors offer personalized support, interpreting policies within the context of a student's specific academic and research goals to facilitate informed decision-making. Both roles are essential for helping undergraduates understand institutional rules and leverage them effectively throughout their academic journey.
Personal Development Support: Advisor vs Mentor
An undergraduate advisor primarily offers academic guidance, course selection assistance, and degree planning to help students meet graduation requirements efficiently. In contrast, a faculty mentor provides personalized support for personal development by fostering career exploration, networking opportunities, and professional growth beyond the curriculum. The mentor's role emphasizes building a long-term, trusting relationship that encourages self-reflection and confidence in navigating academic and life challenges.
Choosing Between Advisor and Mentor: Student Considerations
Undergraduate students should evaluate their goals when choosing between an advisor and a faculty mentor, as advisors primarily assist with academic planning and degree requirements, while mentors offer personalized guidance on professional development and research opportunities. Students seeking structured support to navigate course selections and graduation criteria benefit from an advisor, whereas those aiming for career insights and skill-building often find greater value in a faculty mentor relationship. Understanding these distinct roles helps students make informed decisions aligned with their academic and career aspirations.
Maximizing Success: Combining Advisor and Mentor Guidance
Undergraduate advisors provide structured academic planning and ensure adherence to degree requirements, while faculty mentors offer personalized career advice and research opportunities that foster professional growth. Leveraging both roles maximizes student success by integrating formal curriculum guidance with tailored mentorship. This dual support system enhances academic performance, development of skills, and preparation for post-graduate endeavors.
Undergraduate Advisor vs Faculty Mentor Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com