Competency-based learning emphasizes mastery of specific skills and knowledge at an individual pace, allowing learners to progress upon demonstrating proficiency. Time-based learning structures education around fixed schedules, where all students move forward at the same pace regardless of skill acquisition. Vocational programs adopting competency-based approaches better prepare students for real-world job demands by tailoring instruction to their unique learning needs and professional standards.
Table of Comparison
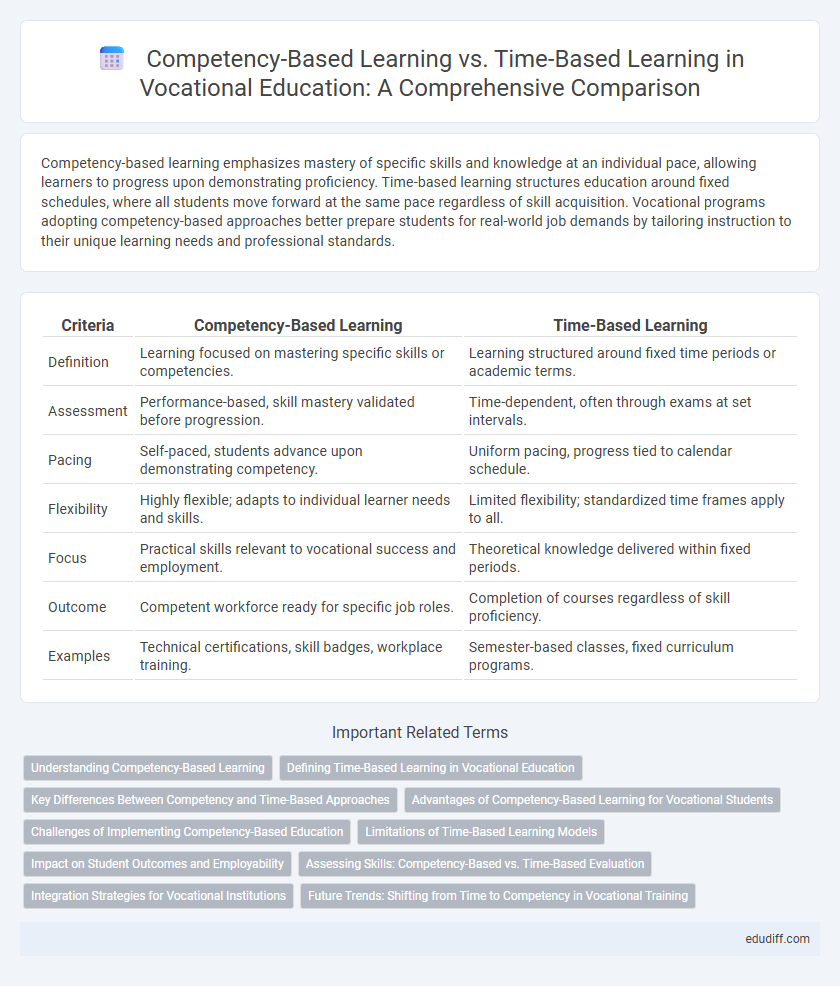
| Criteria | Competency-Based Learning | Time-Based Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning focused on mastering specific skills or competencies. | Learning structured around fixed time periods or academic terms. |
| Assessment | Performance-based, skill mastery validated before progression. | Time-dependent, often through exams at set intervals. |
| Pacing | Self-paced, students advance upon demonstrating competency. | Uniform pacing, progress tied to calendar schedule. |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible; adapts to individual learner needs and skills. | Limited flexibility; standardized time frames apply to all. |
| Focus | Practical skills relevant to vocational success and employment. | Theoretical knowledge delivered within fixed periods. |
| Outcome | Competent workforce ready for specific job roles. | Completion of courses regardless of skill proficiency. |
| Examples | Technical certifications, skill badges, workplace training. | Semester-based classes, fixed curriculum programs. |
Understanding Competency-Based Learning
Competency-based learning prioritizes the mastery of specific skills and knowledge over the amount of time spent in instruction, enabling learners to progress upon demonstrating proficiency. This approach aligns with vocational education by ensuring that students acquire practical abilities directly relevant to their career goals. Emphasizing competency assessment allows for personalized learning paths, increasing engagement and effectiveness in skill acquisition.
Defining Time-Based Learning in Vocational Education
Time-based learning in vocational education structures training according to fixed schedules, where students advance after completing set hours rather than demonstrating specific competencies. This approach emphasizes seat time and standardized curricula, often leading to variable skill mastery among learners. It contrasts with competency-based models that prioritize demonstrated abilities and mastery over elapsed time.
Key Differences Between Competency and Time-Based Approaches
Competency-based learning measures student progress through demonstrated mastery of specific skills and knowledge, allowing personalized pacing and targeted assessments that reflect real-world vocational demands. Time-based learning relies on fixed instructional hours and standardized timelines, often emphasizing seat time over actual skill acquisition. The key difference lies in outcome-driven proficiency assessment versus uniform time allocation, impacting flexibility, learner motivation, and alignment with industry needs.
Advantages of Competency-Based Learning for Vocational Students
Competency-based learning allows vocational students to progress upon mastering specific skills, ensuring personalized pacing and practical proficiency essential for industry demands. This approach enhances job readiness by emphasizing real-world application and measurable outcomes rather than seat time, aligning education with employer expectations. Employers benefit from graduates who have demonstrated tangible competencies, reducing training costs and increasing workforce effectiveness.
Challenges of Implementing Competency-Based Education
Implementing competency-based education (CBE) often faces challenges such as the need for personalized assessment systems that accurately measure skill mastery rather than time spent. Institutions must invest in training educators to design flexible curricula that accommodate diverse learner paces and backgrounds. Additionally, integrating CBE requires overcoming administrative barriers linked to traditional time-based enrollment and credit hour regulations.
Limitations of Time-Based Learning Models
Time-based learning models often fail to accommodate individual learner differences and pacing, leading to gaps in skill mastery and reduced vocational readiness. These models emphasize seat time rather than demonstrated competency, which can result in graduates who are underprepared for real-world vocational demands. Employers increasingly seek workers with proven capabilities, highlighting the limitations of traditional time-based frameworks in vocational education.
Impact on Student Outcomes and Employability
Competency-based learning enhances student outcomes by prioritizing mastery of skills and real-world application, leading to higher employability rates as graduates meet specific industry standards. Time-based learning often results in varied skill acquisition due to fixed durations, potentially leaving gaps in job readiness. Employers increasingly favor competency-based credentials for their alignment with workforce demands and measurable performance.
Assessing Skills: Competency-Based vs. Time-Based Evaluation
Competency-based learning evaluates students by demonstrating mastery of specific skills and knowledge, ensuring readiness for real-world tasks. Time-based learning measures progress through fixed instructional hours or semesters, which may not reflect actual skill acquisition. Assessing skills in vocational education favors competency-based evaluation for its focus on measurable outcomes and personalized pacing.
Integration Strategies for Vocational Institutions
Vocational institutions can enhance skill mastery by integrating competency-based learning with time-based frameworks, ensuring students progress upon demonstrating proficiency rather than fixed schedules. Blending modular assessments with flexible timelines supports personalized learning paths while maintaining accreditation standards. Leveraging digital platforms for real-time competency tracking facilitates seamless transitions between theory and hands-on practice, optimizing workforce readiness.
Future Trends: Shifting from Time to Competency in Vocational Training
Competency-based learning in vocational training emphasizes mastery of skills and real-world application, preparing learners for dynamic job markets more effectively than traditional time-based approaches. Future trends indicate a shift toward personalized pacing and assessment methods that validate actual competencies rather than hours spent in training. This evolution aligns vocational education with industry demands for adaptable, job-ready professionals equipped to navigate rapidly changing technologies and workflows.
Competency-based learning vs Time-based learning Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com