Technical certification offers specialized skills and hands-on experience that directly align with industry demands, often leading to faster employment and career advancement. Traditional degrees provide a broad educational foundation and critical thinking abilities, which are valued in managerial and research roles. Both paths complement each other but choosing between them depends on career goals, time commitment, and specific job requirements.
Table of Comparison
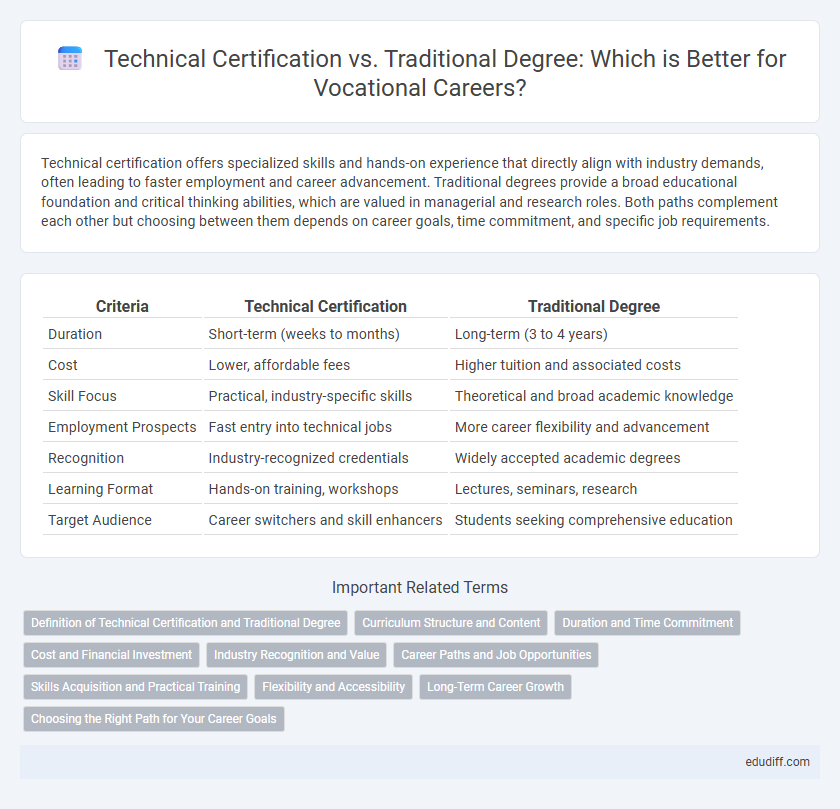
| Criteria | Technical Certification | Traditional Degree |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | Short-term (weeks to months) | Long-term (3 to 4 years) |
| Cost | Lower, affordable fees | Higher tuition and associated costs |
| Skill Focus | Practical, industry-specific skills | Theoretical and broad academic knowledge |
| Employment Prospects | Fast entry into technical jobs | More career flexibility and advancement |
| Recognition | Industry-recognized credentials | Widely accepted academic degrees |
| Learning Format | Hands-on training, workshops | Lectures, seminars, research |
| Target Audience | Career switchers and skill enhancers | Students seeking comprehensive education |
Definition of Technical Certification and Traditional Degree
Technical certification validates specific skills and expertise acquired through focused training programs or practical experience, often aligned with industry standards. Traditional degrees, such as associate's, bachelor's, or master's degrees, represent comprehensive academic education covering a broader theoretical foundation across multiple disciplines. Both pathways serve distinct purposes, with certifications emphasizing job-ready competencies and degrees providing in-depth knowledge and critical thinking skills.
Curriculum Structure and Content
Technical certification programs emphasize hands-on skills and industry-specific technologies, offering a streamlined curriculum tailored to current job market demands. Traditional degrees provide a broader educational foundation, incorporating theoretical knowledge, general education courses, and elective subjects alongside core technical material. Employers often value technical certifications for their direct applicability, while traditional degrees are recognized for cultivating critical thinking and comprehensive problem-solving abilities.
Duration and Time Commitment
Technical certification programs typically require a shorter duration, often ranging from a few weeks to several months, allowing faster entry into the workforce compared to traditional degrees. Traditional degree programs usually take two to four years, demanding a greater time commitment with comprehensive coursework and general education requirements. Choosing technical certification minimizes training time, enabling quicker skills application in vocational fields.
Cost and Financial Investment
Technical certification programs generally require significantly lower financial investment compared to traditional degrees, often costing a fraction of the tuition fees. These certifications offer focused, skill-specific training that can lead to quicker entry into the workforce and less accumulated student debt. In contrast, traditional degrees involve higher costs due to extended study duration, encompassing tuition, accommodation, and ancillary expenses.
Industry Recognition and Value
Technical certifications often hold higher industry recognition due to their practical focus and alignment with current job market demands, enabling faster skill validation in specialized fields like IT, engineering, and healthcare. Traditional degrees provide a broad educational foundation but may require additional experience or certifications to achieve the same level of industry-specific credibility. Employers increasingly prioritize certifications for their direct applicability and proof of up-to-date expertise, enhancing career advancement opportunities.
Career Paths and Job Opportunities
Technical certification offers specialized skills tailored to specific industries, leading to faster entry into high-demand career paths such as IT support, cybersecurity, and advanced manufacturing. Traditional degrees provide a broad educational foundation, opening opportunities in management, research, and roles requiring comprehensive theoretical knowledge. Job market trends reveal that employers increasingly value certifications for technical roles but often prefer degrees for leadership and strategic positions.
Skills Acquisition and Practical Training
Technical certifications emphasize hands-on skills acquisition and practical training tailored to industry needs, enabling faster entry into the workforce. Traditional degrees often focus on theoretical knowledge with limited direct application, which can delay proficiency in technical tasks. Employers increasingly value certification holders for their verified competencies and job-ready abilities in specific trades.
Flexibility and Accessibility
Technical certifications offer greater flexibility and accessibility compared to traditional degrees, allowing learners to acquire specialized skills through shorter, focused programs often available online or part-time. These certifications enable faster entry into the workforce and are frequently updated to reflect current industry standards. In contrast, traditional degrees require longer commitments and can be less adaptable to changing career goals or personal schedules.
Long-Term Career Growth
Technical certifications provide specialized skills that align closely with evolving industry demands, often accelerating entry into high-growth sectors such as IT, healthcare, and engineering. Traditional degrees offer a broad educational foundation and critical thinking abilities that support versatility and adaptability over decades of career development. Combining certifications with a degree can maximize long-term career growth by ensuring both deep technical expertise and comprehensive theoretical knowledge.
Choosing the Right Path for Your Career Goals
Technical certifications offer specialized skills and practical knowledge that align closely with specific job roles, often leading to quicker employment and higher adaptability in rapidly evolving industries. Traditional degrees provide a broad educational foundation, critical thinking skills, and theoretical understanding valuable for long-term career growth and leadership positions. Selecting the right path depends on career goals, industry demands, and the balance between hands-on expertise and academic depth required for advancement.
Technical certification vs Traditional degree Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com