Technical certification offers specialized, practical skills that are directly applicable to specific industries, enabling faster entry into the workforce. University degrees provide broader theoretical knowledge and critical thinking abilities, often opening doors to advanced career opportunities and leadership roles. Choosing between the two depends on career goals, preferred learning styles, and the demands of the chosen field.
Table of Comparison
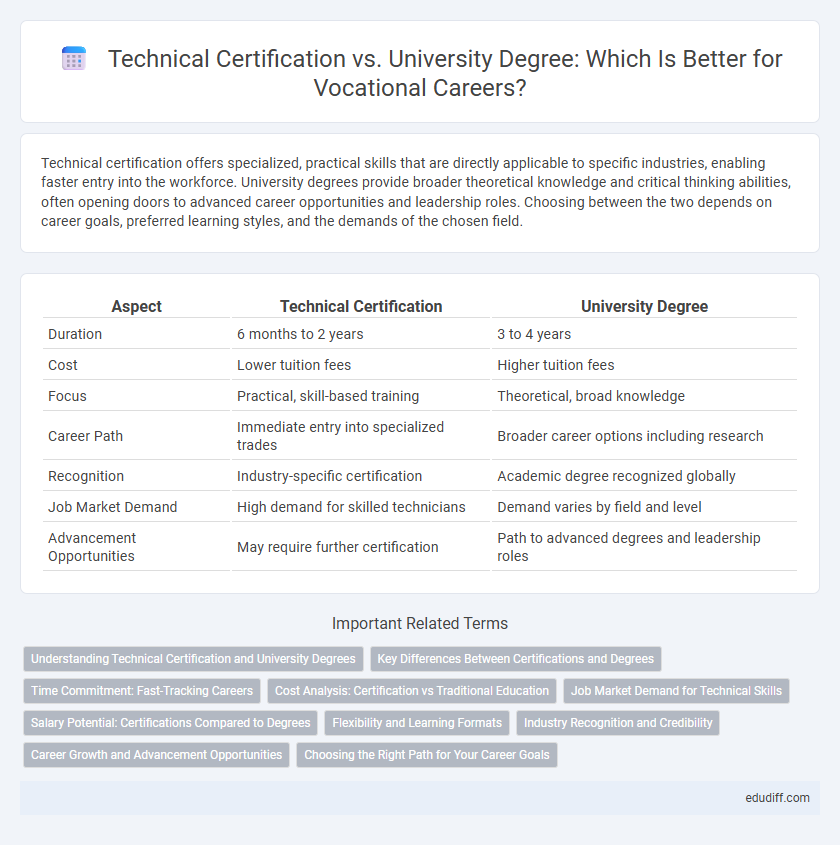
| Aspect | Technical Certification | University Degree |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | 6 months to 2 years | 3 to 4 years |
| Cost | Lower tuition fees | Higher tuition fees |
| Focus | Practical, skill-based training | Theoretical, broad knowledge |
| Career Path | Immediate entry into specialized trades | Broader career options including research |
| Recognition | Industry-specific certification | Academic degree recognized globally |
| Job Market Demand | High demand for skilled technicians | Demand varies by field and level |
| Advancement Opportunities | May require further certification | Path to advanced degrees and leadership roles |
Understanding Technical Certification and University Degrees
Technical certifications validate hands-on skills and specialized knowledge crucial for specific trades or industries, offering quicker entry into the workforce. University degrees provide broader theoretical foundations and critical thinking skills, often required for advanced professional roles and leadership positions. Both pathways enhance employability, but certifications emphasize practical expertise while degrees focus on comprehensive academic learning.
Key Differences Between Certifications and Degrees
Technical certifications focus on specific skills and practical knowledge directly applicable to particular jobs, offering faster completion times and often lower costs compared to university degrees. University degrees provide comprehensive theoretical education, critical thinking development, and broader career opportunities but require longer study periods and greater financial investment. Employers may value certifications for hands-on expertise, while degrees are preferred for roles demanding depth of knowledge and research abilities.
Time Commitment: Fast-Tracking Careers
Technical certifications typically require months to complete, enabling faster entry into the workforce compared to university degrees that often take three to four years. This expedited time commitment allows individuals to gain practical skills and start earning sooner, accelerating career advancement in specialized fields. Employers increasingly value certifications for demonstrating job-ready competencies and up-to-date industry knowledge.
Cost Analysis: Certification vs Traditional Education
Technical certification programs typically cost significantly less than obtaining a traditional university degree, often ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand dollars compared to the tens of thousands spent on college tuition. The shorter duration of certification courses also reduces indirect costs such as lost wages, making them a more affordable and accessible option for many individuals. Employers frequently recognize certifications as proof of practical skills, providing a cost-efficient pathway to career advancement without the financial burden of a four-year degree.
Job Market Demand for Technical Skills
Technical certifications demonstrate specialized skills aligned with current industry standards, often leading to faster employment opportunities in vocational fields. University degrees provide comprehensive theoretical knowledge but may require additional practical experience to meet immediate job market demands for technical proficiency. Employers increasingly prioritize candidates with certified hands-on expertise to address skill gaps in rapidly evolving tech sectors.
Salary Potential: Certifications Compared to Degrees
Technical certifications often lead to higher immediate salary potential in specialized fields such as IT, healthcare, and skilled trades, where employers prioritize hands-on expertise and up-to-date skills. University degrees typically provide broader theoretical knowledge, which can translate into higher long-term earnings in professions like engineering, law, and business management. Salary trajectories for certified professionals may accelerate faster due to industry demand, while degree holders benefit from career advancement options and leadership roles.
Flexibility and Learning Formats
Technical certification programs offer greater flexibility through modular courses and evening or weekend classes tailored to working professionals, enabling faster skill acquisition and immediate industry application. University degrees typically follow rigid semester schedules and full-time commitments, limiting adaptability but providing comprehensive academic exposure and broader theoretical knowledge. Online and hybrid learning formats are increasingly available in both paths, though vocational certifications often lead in delivering practical, hands-on training suited for specific career advancement.
Industry Recognition and Credibility
Technical certifications often provide industry-recognized proof of specific skills and practical expertise, directly aligning with employer demands in fields such as IT, engineering, and healthcare. University degrees, while comprehensive and theoretically focused, may lack the immediate hands-on credibility that certifications offer for specialized roles. Employers frequently prioritize certified professionals for technical positions due to the tangible validation of current industry standards and competencies.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Technical certification often accelerates career growth by providing specialized skills that meet immediate industry demands, making candidates highly employable. University degrees offer broader theoretical knowledge and critical thinking skills, facilitating long-term advancement into managerial or specialized roles. Employers increasingly value technical certifications for their practical relevance, while degrees remain essential for leadership and research-oriented career paths.
Choosing the Right Path for Your Career Goals
Technical certification offers specialized, hands-on skills tailored to specific trades, enabling faster entry into the workforce with practical expertise. University degrees provide comprehensive theoretical foundations and broader career opportunities, often required for advanced professional roles and higher earning potential. Selecting the right path depends on your career goals, industry demands, and the balance between practical skills and academic knowledge desired.
Technical Certification vs University Degree Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com