Technical schools provide specialized, hands-on training designed to quickly prepare students for specific trades or professions, often leading to certifications or diplomas. Community colleges offer a broader curriculum including associate degrees, general education, and vocational programs, allowing for transfer to four-year universities or entry into the job market. Choosing between technical school and community college depends on career goals, preferred learning styles, and the desired balance between practical skills and academic education.
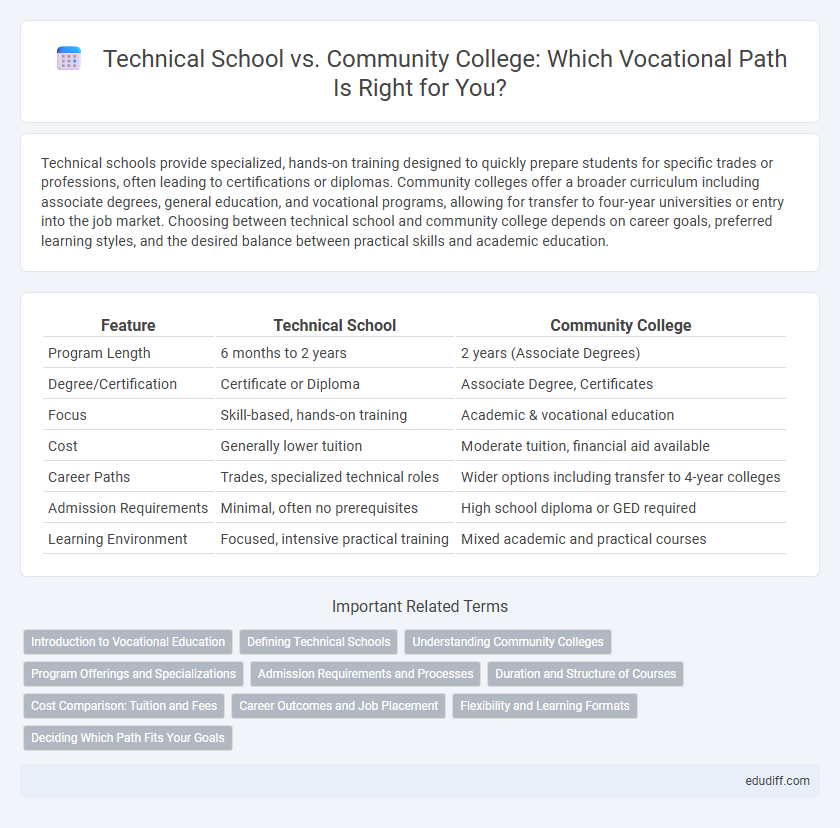
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Technical School | Community College |
|---|---|---|
| Program Length | 6 months to 2 years | 2 years (Associate Degrees) |
| Degree/Certification | Certificate or Diploma | Associate Degree, Certificates |
| Focus | Skill-based, hands-on training | Academic & vocational education |
| Cost | Generally lower tuition | Moderate tuition, financial aid available |
| Career Paths | Trades, specialized technical roles | Wider options including transfer to 4-year colleges |
| Admission Requirements | Minimal, often no prerequisites | High school diploma or GED required |
| Learning Environment | Focused, intensive practical training | Mixed academic and practical courses |
Introduction to Vocational Education
Vocational education provides specialized training that prepares students for specific careers by developing practical skills and technical knowledge. Technical schools offer focused programs in trades and applied technologies, emphasizing hands-on experience to meet industry standards. Community colleges deliver broader vocational curricula combined with academic courses, enabling pathways for certification, associate degrees, and seamless transfer to four-year institutions.
Defining Technical Schools
Technical schools specialize in hands-on training programs designed to develop specific skills for careers in industries such as healthcare, IT, manufacturing, and automotive technology. These institutions offer certificates, diplomas, and associate degrees focused on practical knowledge and direct job preparation. Emphasizing skill competency, technical schools typically provide accelerated courses and industry-recognized certifications tailored to workforce demands.
Understanding Community Colleges
Community colleges offer affordable vocational training and associate degrees tailored to local workforce needs, making them accessible options for technical education. These institutions provide flexible schedules, smaller class sizes, and partnerships with industries to ensure practical skills and certifications ready for immediate employment. Community colleges serve as a bridge to four-year institutions while supporting career-focused programs in fields such as healthcare, information technology, and advanced manufacturing.
Program Offerings and Specializations
Technical schools specialize in hands-on training with focused programs in fields like automotive technology, welding, and medical assisting, offering certificates and diplomas tailored for immediate workforce entry. Community colleges provide a broader range of academic and vocational programs, including allied health, information technology, and business management, with options for associate degrees and transfer pathways to four-year universities. Both institutions deliver career-oriented education, but technical schools emphasize intensive skill development in specific trades, while community colleges balance vocational training with broader educational pursuits.
Admission Requirements and Processes
Technical schools often require a high school diploma or equivalent for admission, along with possible entrance exams or technical skill assessments specific to the program. Community colleges typically have open admission policies, accepting any applicant with a high school diploma or GED, and may offer placement tests to determine appropriate course levels. Both institutions may also require submission of transcripts, application forms, and sometimes interviews or orientation sessions to finalize enrollment.
Duration and Structure of Courses
Technical schools typically offer shorter, intensive programs focused on specific trades or skills, often lasting six months to two years. Community colleges provide more comprehensive curricula with flexible course structures, allowing students to earn associate degrees or certifications usually within two years. Both options emphasize practical training, but technical schools concentrate on rapid workforce entry while community colleges balance vocational education with general academics.
Cost Comparison: Tuition and Fees
Technical schools often have lower tuition and fees compared to community colleges, making them a cost-effective option for specialized vocational training. Community colleges may charge higher overall fees due to broader educational resources and transfer opportunities, potentially increasing total expenses. Evaluating tuition rates, additional fees, and financial aid options is essential for budgeting vocational education effectively.
Career Outcomes and Job Placement
Technical schools emphasize hands-on training and specialized skills tailored to specific industries, often resulting in higher job placement rates in niche markets. Community colleges provide broader academic curricula alongside vocational programs, offering flexible pathways that include associate degrees and transfer opportunities to four-year institutions. Career outcomes from technical schools typically show quicker entry into the workforce with certifications, whereas community colleges deliver diversified options with a balance of technical proficiency and general education.
Flexibility and Learning Formats
Technical schools offer highly flexible learning formats tailored to hands-on, skill-based training, often featuring accelerated programs and night or weekend classes to accommodate working students. Community colleges provide a broader range of flexible options including part-time enrollment, online courses, and hybrid models, supporting diverse academic and career pathways. Both institutions prioritize adaptable schedules, but technical schools emphasize direct vocational preparation while community colleges balance flexibility with academic transfer opportunities.
Deciding Which Path Fits Your Goals
Technical schools offer specialized training focused on specific trades or skills, providing faster entry into the workforce with hands-on experience. Community colleges provide a broader curriculum, including associate degrees and transferable credits for further education, appealing to those seeking flexibility and academic advancement. Evaluating career goals, time commitment, and educational preferences helps determine whether a technical school's targeted approach or a community college's comprehensive program best aligns with your vocational objectives.
Technical School vs Community College Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com