Technical training offers hands-on experience and practical skills tailored to specific trades, enabling faster entry into the workforce. Academic education emphasizes theoretical knowledge and critical thinking, preparing students for a broad range of professions and advanced studies. Choosing between the two depends on career goals, learning preferences, and industry demands.
Table of Comparison
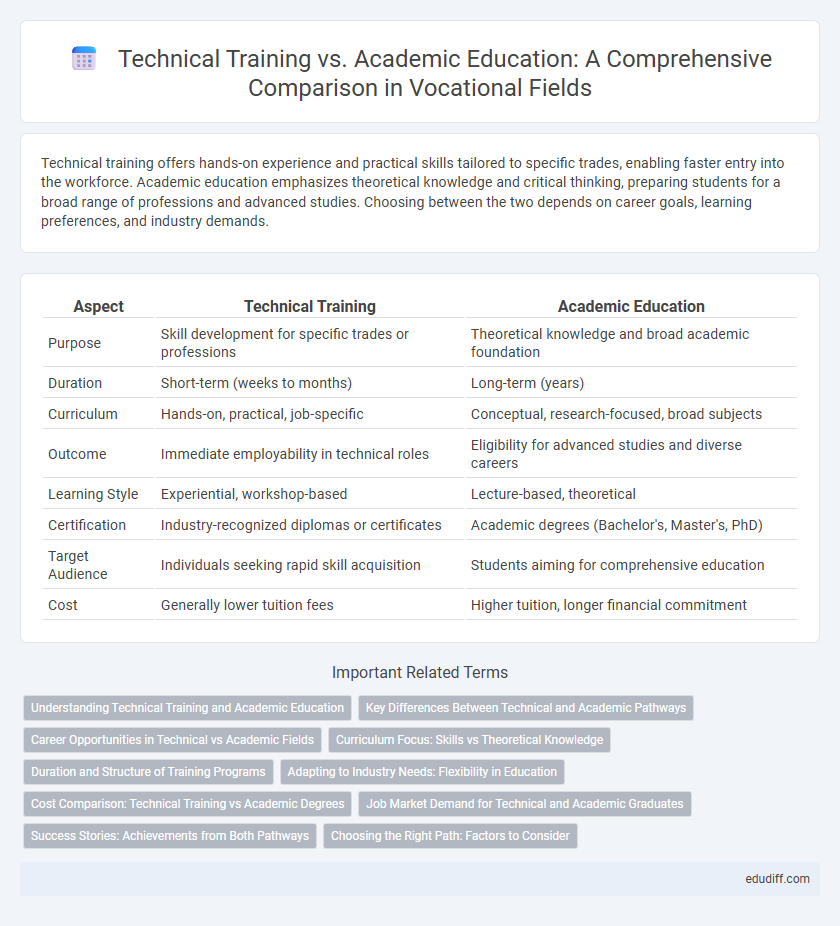
| Aspect | Technical Training | Academic Education |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Skill development for specific trades or professions | Theoretical knowledge and broad academic foundation |
| Duration | Short-term (weeks to months) | Long-term (years) |
| Curriculum | Hands-on, practical, job-specific | Conceptual, research-focused, broad subjects |
| Outcome | Immediate employability in technical roles | Eligibility for advanced studies and diverse careers |
| Learning Style | Experiential, workshop-based | Lecture-based, theoretical |
| Certification | Industry-recognized diplomas or certificates | Academic degrees (Bachelor's, Master's, PhD) |
| Target Audience | Individuals seeking rapid skill acquisition | Students aiming for comprehensive education |
| Cost | Generally lower tuition fees | Higher tuition, longer financial commitment |
Understanding Technical Training and Academic Education
Technical training emphasizes hands-on skills and practical knowledge directly applicable to specific trades or industries, enhancing job readiness and productivity. Academic education focuses on theoretical understanding, critical thinking, and broad-based knowledge that provides foundational concepts across various disciplines. Both pathways offer distinct advantages for career development, with technical training delivering specialized expertise and academic education fostering analytical and adaptable problem-solving abilities.
Key Differences Between Technical and Academic Pathways
Technical training emphasizes hands-on skills and practical knowledge tailored for specific trades or industries, enabling faster workforce entry. Academic education provides a broader theoretical foundation across disciplines, promoting critical thinking and research capabilities. Key differences include the curriculum focus, learning methods, and career readiness outcomes, with technical pathways prioritizing immediate job skills and academic pathways fostering long-term intellectual development.
Career Opportunities in Technical vs Academic Fields
Technical training equips individuals with hands-on skills and practical knowledge directly applicable to specific trades, leading to faster entry into the workforce and high demand in sectors such as manufacturing, information technology, and healthcare. Academic education, often theory-based, provides a broader foundation across disciplines, fostering critical thinking and research abilities crucial for careers in academia, engineering, and scientific innovation. Career opportunities in technical fields tend to offer immediate employment and specialized roles, whereas academic pathways often lead to advanced positions requiring higher degrees and long-term professional development.
Curriculum Focus: Skills vs Theoretical Knowledge
Technical training emphasizes practical skills development tailored to specific trades or industries, ensuring learners gain hands-on experience directly applicable to job requirements. Academic education prioritizes theoretical knowledge and conceptual understanding, fostering critical thinking and broad intellectual foundations across multiple disciplines. This distinction reflects the vocational aim of technical training to prepare students for immediate employment versus academic education's focus on long-term intellectual growth.
Duration and Structure of Training Programs
Technical training programs typically offer shorter, more intensive courses designed to develop specific practical skills within weeks or months, emphasizing hands-on experience. Academic education generally spans several years, combining theoretical knowledge with broader subject areas and structured semesters or terms. The streamlined duration and focused structure of technical training enable faster workforce entry compared to the comprehensive approach of academic programs.
Adapting to Industry Needs: Flexibility in Education
Technical training emphasizes practical skills tailored to current industry demands, ensuring rapid adaptation to evolving technologies and job requirements. Academic education often follows a more theoretical curriculum, which may lack immediate responsiveness to market shifts. Flexibility in vocational education allows programs to update content regularly, aligning graduate competencies with real-world industry standards and enhancing employability.
Cost Comparison: Technical Training vs Academic Degrees
Technical training typically incurs lower costs compared to academic degrees, with average tuition fees for vocational programs ranging from $1,000 to $10,000, whereas traditional college degrees can cost between $20,000 and $60,000 or more. Shorter program durations in technical training reduce expenses related to living costs and lost income, making vocational education a more affordable option for skill acquisition and career entry. The cost-benefit ratio of technical training often results in faster returns on investment due to quicker workforce entry and targeted skill development.
Job Market Demand for Technical and Academic Graduates
Technical training equips graduates with specialized skills directly aligned with current job market demands in industries such as manufacturing, IT, and healthcare, resulting in higher employment rates and faster job placement. Academic education provides a broad theoretical foundation, promoting critical thinking and adaptability, which is valuable for long-term career growth and roles requiring advanced research or management expertise. Employers increasingly seek candidates with practical technical competencies combined with academic knowledge to meet evolving technological and operational challenges.
Success Stories: Achievements from Both Pathways
Technical training produces skilled professionals who excel in hands-on roles within industries such as manufacturing, IT, and healthcare, contributing to rapid workforce integration and high job placement rates. Academic education fosters critical thinking and research skills, leading to innovations and leadership positions in sectors like engineering, education, and technology development. Success stories from both pathways highlight individual achievements, entrepreneurial ventures, and advancements that drive economic growth and societal progress.
Choosing the Right Path: Factors to Consider
Choosing between technical training and academic education depends on career goals, learning preferences, and industry demands. Technical training emphasizes hands-on skills and immediate job readiness in fields like manufacturing, IT, and healthcare, while academic education provides theoretical knowledge suitable for research, management, and professions requiring advanced degrees. Consider job market trends, earning potential, and personal aptitude to determine whether a vocational certificate, associate degree, or traditional academic path aligns best with your professional aspirations.
Technical Training vs Academic Education Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com