Experiential learning in adult pet education emphasizes hands-on interaction and real-world practice, fostering deeper understanding and retention compared to didactic learning's lecture-based approach. Engaging pets through experiential methods such as training sessions and play enhances behavioral responses and communication more effectively. This immersive process supports adaptability and reinforces learning in natural environments.
Table of Comparison
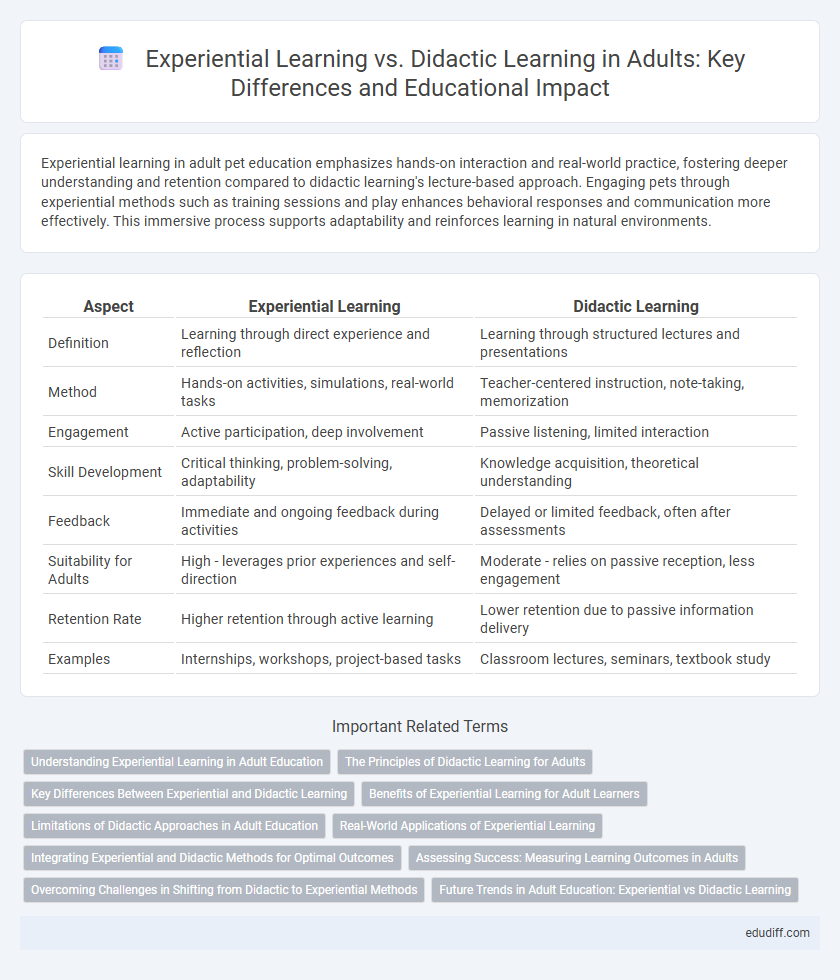
| Aspect | Experiential Learning | Didactic Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through direct experience and reflection | Learning through structured lectures and presentations |
| Method | Hands-on activities, simulations, real-world tasks | Teacher-centered instruction, note-taking, memorization |
| Engagement | Active participation, deep involvement | Passive listening, limited interaction |
| Skill Development | Critical thinking, problem-solving, adaptability | Knowledge acquisition, theoretical understanding |
| Feedback | Immediate and ongoing feedback during activities | Delayed or limited feedback, often after assessments |
| Suitability for Adults | High - leverages prior experiences and self-direction | Moderate - relies on passive reception, less engagement |
| Retention Rate | Higher retention through active learning | Lower retention due to passive information delivery |
| Examples | Internships, workshops, project-based tasks | Classroom lectures, seminars, textbook study |
Understanding Experiential Learning in Adult Education
Experiential learning in adult education emphasizes active participation, where learners engage directly with real-world experiences to construct knowledge and develop practical skills. This approach contrasts with didactic learning by prioritizing reflection and critical thinking over passive reception of information, which enhances retention and application in professional and personal contexts. Adults benefit from experiential learning through problem-solving, collaboration, and hands-on activities that align with their existing knowledge and life experiences.
The Principles of Didactic Learning for Adults
Didactic learning for adults emphasizes structured content delivery, clear objectives, and instructor-led guidance to facilitate knowledge acquisition. This approach relies heavily on repetition, assessment, and formal instruction to reinforce understanding and retention. It is most effective when learners require foundational knowledge or are preparing for standardized evaluations.
Key Differences Between Experiential and Didactic Learning
Experiential learning emphasizes active engagement through real-world experiences, promoting deeper understanding and retention by involving learners in practical tasks and reflection. Didactic learning relies on structured, instructor-led teaching methods focused on information delivery, often through lectures and reading materials, emphasizing theoretical knowledge acquisition. Key differences include the learner's role as participant versus passive receiver, the method of knowledge construction through experience or instruction, and the resulting impact on critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Benefits of Experiential Learning for Adult Learners
Experiential learning empowers adult learners by promoting active engagement, critical thinking, and real-world problem-solving skills, which enhance retention and application of knowledge. This approach leverages hands-on activities and reflection, making learning more relevant and meaningful compared to traditional didactic methods. Adults benefit from experiential learning through increased motivation, improved self-confidence, and the ability to transfer skills directly to professional and personal contexts.
Limitations of Didactic Approaches in Adult Education
Didactic learning in adult education often limits engagement by emphasizing passive information transfer rather than active participation, which hinders retention and application of knowledge. This approach fails to accommodate diverse learning styles and prior experiences, reducing relevance and motivation among adult learners. The lack of critical reflection and problem-solving opportunities restricts the development of practical skills essential for real-world adult learning contexts.
Real-World Applications of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning immerses adults in hands-on tasks that mirror real-world challenges, fostering practical skills and critical thinking beyond theoretical knowledge. This approach enhances retention and problem-solving abilities by engaging learners in authentic environments such as internships, simulations, and project-based assignments. Real-world applications of experiential learning bridge the gap between academic concepts and workplace demands, ensuring that adult learners develop competencies directly transferable to their professional roles.
Integrating Experiential and Didactic Methods for Optimal Outcomes
Integrating experiential and didactic learning methods enhances adult education by combining hands-on practice with structured theoretical instruction, promoting deeper comprehension and skill retention. Experiential learning engages learners through real-world scenarios and active reflection, while didactic approaches provide foundational knowledge and clear frameworks. Employing a blended strategy leverages the strengths of both, leading to improved critical thinking, application, and long-term mastery in adult learners.
Assessing Success: Measuring Learning Outcomes in Adults
Assessing success in adult learning requires evaluating both experiential and didactic approaches by measuring knowledge retention, skill application, and behavioral change. Experiential learning often leads to higher engagement and practical skill mastery, reflected in improved problem-solving and decision-making outcomes. Didactic learning effectiveness is typically measured through tests and quizzes, while experiential methods demand performance-based assessments to capture real-world competency.
Overcoming Challenges in Shifting from Didactic to Experiential Methods
Overcoming challenges in shifting from didactic to experiential learning requires addressing resistance to change among adult learners and educators accustomed to traditional lecture formats. Implementing hands-on activities, real-world simulations, and reflective practices enhances engagement and retention while providing practical skill development. Continuous support, feedback, and adaptable curriculum design facilitate a smoother transition, ensuring learners gain confidence in active participation and critical thinking competencies.
Future Trends in Adult Education: Experiential vs Didactic Learning
Future trends in adult education emphasize a shift toward experiential learning, leveraging hands-on, real-world applications to enhance retention and skill mastery. Didactic learning remains essential for foundational knowledge but increasingly integrates with experiential methods to foster critical thinking and adaptability. Emerging technologies like virtual reality and AI-driven simulations are expected to further transform experiential learning, offering immersive environments that personalize education for adult learners.
Experiential Learning vs Didactic Learning Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com