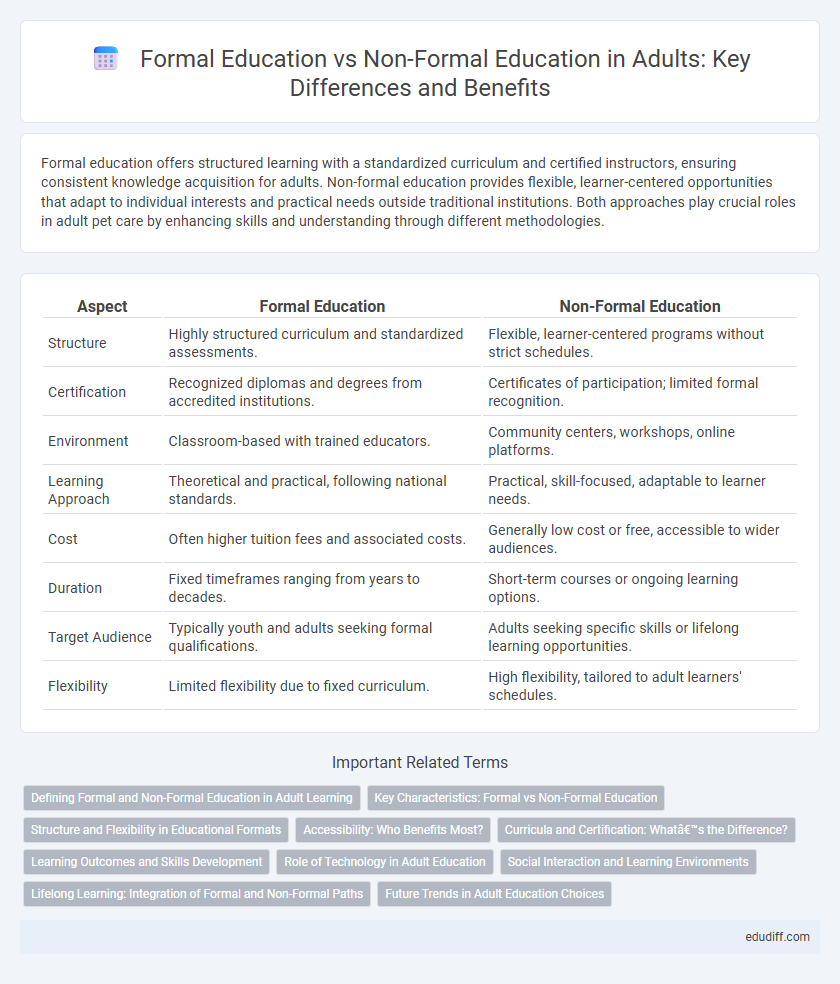
Formal education offers structured learning with a standardized curriculum and certified instructors, ensuring consistent knowledge acquisition for adults. Non-formal education provides flexible, learner-centered opportunities that adapt to individual interests and practical needs outside traditional institutions. Both approaches play crucial roles in adult pet care by enhancing skills and understanding through different methodologies.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Formal Education | Non-Formal Education |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Highly structured curriculum and standardized assessments. | Flexible, learner-centered programs without strict schedules. |
| Certification | Recognized diplomas and degrees from accredited institutions. | Certificates of participation; limited formal recognition. |
| Environment | Classroom-based with trained educators. | Community centers, workshops, online platforms. |
| Learning Approach | Theoretical and practical, following national standards. | Practical, skill-focused, adaptable to learner needs. |
| Cost | Often higher tuition fees and associated costs. | Generally low cost or free, accessible to wider audiences. |
| Duration | Fixed timeframes ranging from years to decades. | Short-term courses or ongoing learning options. |
| Target Audience | Typically youth and adults seeking formal qualifications. | Adults seeking specific skills or lifelong learning opportunities. |
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility due to fixed curriculum. | High flexibility, tailored to adult learners' schedules. |
Defining Formal and Non-Formal Education in Adult Learning
Formal education in adult learning refers to structured programs delivered in institutional settings, such as universities and vocational schools, characterized by a defined curriculum, certification, and standardized assessment. Non-formal education encompasses flexible, learner-centered activities outside traditional institutions, including workshops, community courses, and online modules, emphasizing skill development and personal growth without formal accreditation. Understanding the distinctions between these two educational approaches enables adults to select pathways that best suit their learning objectives and career advancement needs.
Key Characteristics: Formal vs Non-Formal Education
Formal education typically involves structured curriculums, standardized assessments, and recognized certifications within institutions like schools and universities. Non-formal education emphasizes flexible learning environments, learner-centered approaches, and practical skills often acquired through community programs, workshops, or online courses. Key characteristics distinguishing the two include the rigidity of schedules in formal education versus the adaptability and contextual relevance found in non-formal education settings.
Structure and Flexibility in Educational Formats
Formal education follows a structured curriculum with fixed schedules, standardized assessments, and clearly defined learning outcomes, ensuring consistent and measurable progress across learners. Non-formal education offers flexible formats, allowing learners to adapt content, pace, and assessment methods to individual needs, promoting personalized skill development outside traditional settings. This flexibility supports adult learners balancing education with work or personal commitments, enhancing accessibility and practical application.
Accessibility: Who Benefits Most?
Formal education offers structured curricula and recognized certifications that benefit individuals seeking clear career paths and academic advancement. Non-formal education provides flexible, targeted learning opportunities accessible to marginalized groups, working adults, and those unable to attend traditional schools. Accessibility in non-formal education often leads to immediate skill acquisition and empowerment for communities with limited access to formal schooling systems.
Curricula and Certification: What’s the Difference?
Formal education follows a structured curriculum set by educational authorities, leading to recognized certifications such as diplomas and degrees. Non-formal education offers flexible, learner-centered programs without standardized curricula, often providing certificates of completion rather than formal qualifications. The key difference lies in the official accreditation and the standardized assessment processes associated with formal education curricula.
Learning Outcomes and Skills Development
Formal education provides structured curricula and standardized assessments that enhance cognitive abilities and theoretical knowledge, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Non-formal education offers flexible, practical learning experiences tailored to individual needs, significantly improving soft skills, adaptability, and real-world application. Both pathways contribute uniquely to skill development and learning outcomes, with formal education emphasizing foundational competencies and non-formal learning enhancing experiential and vocational capabilities.
Role of Technology in Adult Education
Technology transforms adult education by expanding access through online platforms and digital resources, enabling learners to engage in both formal and non-formal education flexibly. Interactive tools like video tutorials, virtual classrooms, and mobile apps enhance personalized learning experiences and skill acquisition. Data analytics and AI-driven programs further tailor educational content to adult learners' needs, improving outcomes and lifelong learning opportunities.
Social Interaction and Learning Environments
Formal education provides structured social interactions within classrooms, fostering peer collaboration and guided teacher-student engagement, which enhances cognitive and social skills development. Non-formal education offers flexible learning environments often centered on community participation and real-world experiences, promoting social interaction through group activities and practical problem-solving. Both settings contribute uniquely to adult learning by balancing institutional support and experiential social engagement.
Lifelong Learning: Integration of Formal and Non-Formal Paths
Lifelong learning emphasizes the seamless integration of formal education, such as accredited degree programs, with non-formal education that includes workshops, online courses, and community training. This approach enhances adult learners' skills adaptability and personal growth by combining structured academic credentials with flexible, interest-driven learning experiences. Recognition of prior learning (RPL) and competency-based assessments play crucial roles in validating knowledge gained through diverse educational pathways.
Future Trends in Adult Education Choices
Emerging technologies and digital platforms are reshaping adult education, increasing the appeal of non-formal education due to its flexibility and personalized learning paths. Formal education institutions are integrating hybrid models and micro-credentials to meet the growing demand for skill-specific, career-oriented programs. Data from the World Economic Forum indicates a significant rise in lifelong learning participation, driven by adults seeking continuous upskilling in rapidly evolving industries.
Formal education vs Non-formal education Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com