Experiential learning in adult pet care emphasizes hands-on interaction, allowing caregivers to understand animal behavior and needs through direct experience. Theoretical learning provides foundational knowledge about pet health, nutrition, and psychology, which supports informed decision-making. Combining both approaches enhances the overall effectiveness of adult pet care by bridging practical skills with scientific understanding.
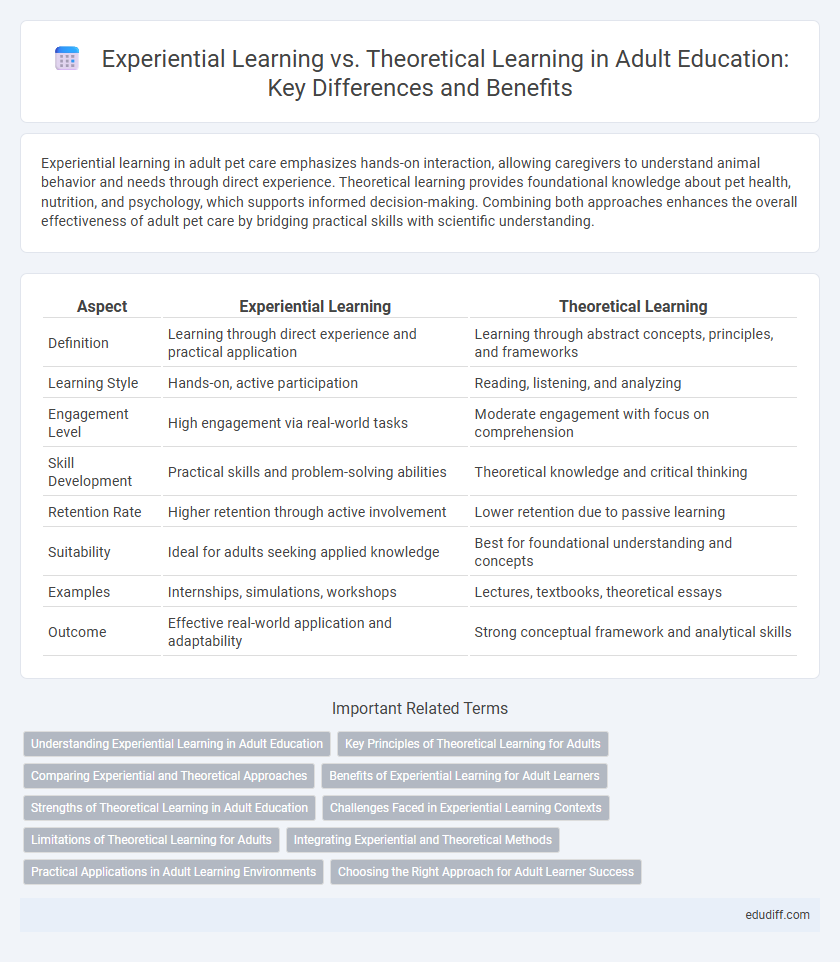
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Experiential Learning | Theoretical Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through direct experience and practical application | Learning through abstract concepts, principles, and frameworks |
| Learning Style | Hands-on, active participation | Reading, listening, and analyzing |
| Engagement Level | High engagement via real-world tasks | Moderate engagement with focus on comprehension |
| Skill Development | Practical skills and problem-solving abilities | Theoretical knowledge and critical thinking |
| Retention Rate | Higher retention through active involvement | Lower retention due to passive learning |
| Suitability | Ideal for adults seeking applied knowledge | Best for foundational understanding and concepts |
| Examples | Internships, simulations, workshops | Lectures, textbooks, theoretical essays |
| Outcome | Effective real-world application and adaptability | Strong conceptual framework and analytical skills |
Understanding Experiential Learning in Adult Education
Experiential learning in adult education emphasizes hands-on experiences and real-world application, enabling learners to develop practical skills and deepen their understanding through active participation. This approach aligns with Kolb's Experiential Learning Theory, which highlights the cyclical process of concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation. Adults benefit from experiential learning as it leverages prior knowledge, promotes critical thinking, and fosters intrinsic motivation crucial for adult development and lifelong learning.
Key Principles of Theoretical Learning for Adults
Theoretical learning for adults emphasizes the acquisition of abstract knowledge through structured methods like lectures, reading, and discussion, enabling learners to understand concepts deeply before applying them. Key principles include the importance of cognitive engagement, the use of prior knowledge as a foundation, and the need for clear explanations to facilitate critical thinking and comprehension. Effective theoretical learning also relies on reflective practice that encourages adults to analyze and synthesize new information within their existing mental frameworks.
Comparing Experiential and Theoretical Approaches
Experiential learning emphasizes hands-on engagement and real-world application, fostering deeper understanding through direct experience, while theoretical learning relies on abstract concepts and structured knowledge acquisition. Experiential methods enhance critical thinking and problem-solving skills by immersing learners in practical scenarios, contrasting with the often passive absorption characteristic of theoretical approaches. This comparison highlights how blending both strategies can optimize adult education by balancing conceptual frameworks with actionable insights.
Benefits of Experiential Learning for Adult Learners
Experiential learning enhances adult learners' retention and application of knowledge by engaging them in real-world tasks that develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills. This approach leverages adults' prior experiences, making new information more relevant and easily internalized. Hands-on activities and reflection promote deeper understanding and motivation, leading to improved professional and personal growth outcomes.
Strengths of Theoretical Learning in Adult Education
Theoretical learning in adult education provides a strong foundation of conceptual knowledge essential for critical thinking and problem-solving skills. It facilitates understanding of underlying principles and frameworks, enabling adults to apply knowledge across diverse real-world contexts effectively. This form of learning supports lifelong education by encouraging reflective analysis and deeper comprehension of complex subjects.
Challenges Faced in Experiential Learning Contexts
Experiential learning presents unique challenges such as adapting to unpredictable real-world scenarios and managing emotional responses that theoretical learning often shields from. Participants must develop critical problem-solving skills and resilience while facing immediate consequences of their actions, which can create stress and hinder processing of lessons. Limited access to diverse experiential opportunities and varying facilitator expertise further complicate consistent skill acquisition and assessment accuracy.
Limitations of Theoretical Learning for Adults
Theoretical learning for adults often lacks practical application, limiting the ability to retain and transfer knowledge effectively in real-world settings. Adults benefit more from experiential learning methods that engage problem-solving skills and reflect workplace scenarios, enhancing comprehension and skill acquisition. Reliance solely on abstract concepts can reduce motivation and hinder the development of critical thinking and adaptive expertise needed in adult education.
Integrating Experiential and Theoretical Methods
Integrating experiential learning with theoretical methods enhances adult education by bridging practical application and conceptual understanding, fostering deeper cognitive retention and skill mastery. Experiential activities, such as simulations and real-world projects, complement theoretical frameworks by providing context and immediate feedback, which accelerates critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. This blended approach supports transformative learning experiences that align with adult learners' needs for relevance, autonomy, and competence development in professional settings.
Practical Applications in Adult Learning Environments
Experiential learning in adult education emphasizes hands-on involvement, allowing learners to apply concepts directly in real-world situations, enhancing retention and skill acquisition. Theoretical learning provides foundational knowledge but often lacks immediate practical relevance, making it less effective for adults needing tangible outcomes. Integrating practical applications within adult learning environments bridges the gap between theory and practice, fostering deeper understanding and professional competency.
Choosing the Right Approach for Adult Learner Success
Experiential learning empowers adult learners by engaging them in real-world problem-solving, fostering practical skills and deeper retention compared to traditional theoretical learning, which emphasizes abstract concepts and passive information absorption. Adult learners benefit from customized approaches that align with their professional goals, learning preferences, and prior experiences, enhancing motivation and knowledge application. Selecting the right learning method involves assessing individual needs and contexts to maximize competency development and long-term success in adult education programs.
Experiential Learning vs Theoretical Learning Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com