Adult pets benefit from non-formal learning by engaging in playful activities that enhance their obedience and social skills without the rigidity of formal training sessions. This approach fosters natural curiosity and adaptability, allowing pets to absorb commands and behaviors through everyday interactions. Formal learning, while structured and consistent, may not always accommodate the spontaneous and individualized needs of adult pets.
Table of Comparison
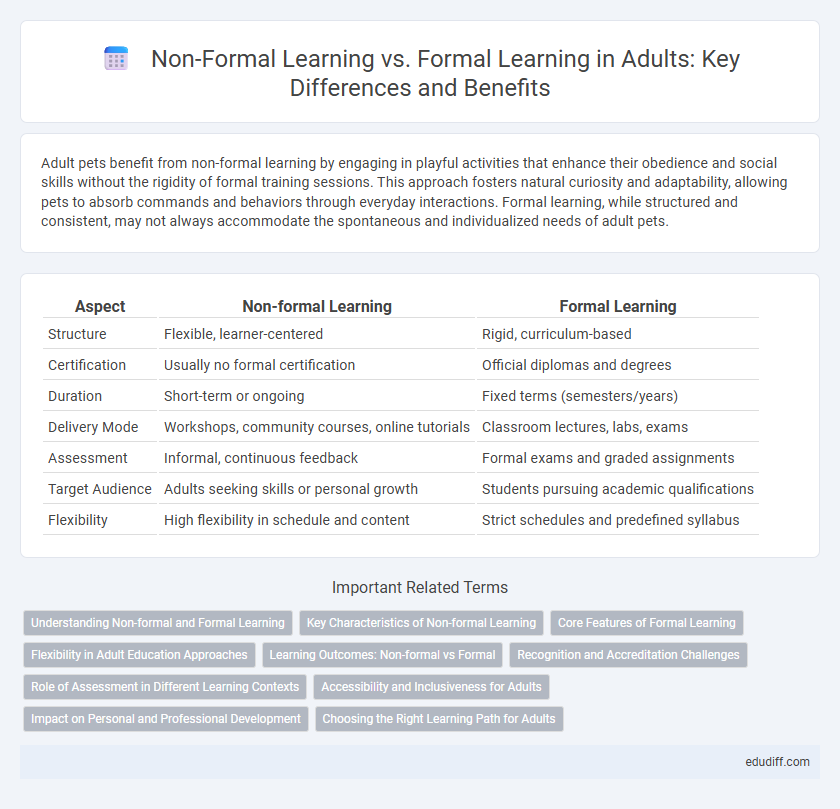
| Aspect | Non-formal Learning | Formal Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Flexible, learner-centered | Rigid, curriculum-based |
| Certification | Usually no formal certification | Official diplomas and degrees |
| Duration | Short-term or ongoing | Fixed terms (semesters/years) |
| Delivery Mode | Workshops, community courses, online tutorials | Classroom lectures, labs, exams |
| Assessment | Informal, continuous feedback | Formal exams and graded assignments |
| Target Audience | Adults seeking skills or personal growth | Students pursuing academic qualifications |
| Flexibility | High flexibility in schedule and content | Strict schedules and predefined syllabus |
Understanding Non-formal and Formal Learning
Non-formal learning refers to structured educational activities occurring outside formal institutions, emphasizing flexibility and learner-centered approaches. Formal learning takes place within accredited institutions, following a standardized curriculum leading to recognized qualifications. Both forms contribute to adult education, with non-formal learning enhancing skills and knowledge in practical contexts, while formal learning provides foundational theory and certification.
Key Characteristics of Non-formal Learning
Non-formal learning is characterized by its flexible structure, learner-centered approach, and voluntary participation, often taking place outside traditional academic institutions. It emphasizes practical skills and real-world application, accommodating diverse learning paces and styles without rigid assessment or certification requirements. This type of learning fosters autonomy, collaboration, and experiential activities tailored to adult learners seeking personal or professional development.
Core Features of Formal Learning
Formal learning is characterized by a structured curriculum, standardized assessments, and official certification that validates knowledge acquisition. It typically occurs within educational institutions such as universities, colleges, or training centers, following a clearly defined syllabus designed by academic authorities. The systematic nature ensures measurable progress, adherence to learning outcomes, and formal recognition essential for career advancement and professional development.
Flexibility in Adult Education Approaches
Non-formal learning in adult education offers unparalleled flexibility, allowing learners to engage with content at their own pace and according to their personal schedules, unlike rigid formal learning structures that often require fixed timetables and standardized curricula. This adaptability supports diverse learning needs, accommodating adults who balance education with work and family responsibilities. Tailored, learner-centered methods in non-formal settings promote continuous skill development and practical knowledge acquisition critical for professional and personal growth.
Learning Outcomes: Non-formal vs Formal
Non-formal learning often yields practical skills and immediate applicability, fostering adaptability and self-directed growth, while formal learning emphasizes structured knowledge acquisition and standardized assessment, leading to recognized qualifications. Outcomes in non-formal settings may be less quantifiable but align closely with personal and professional development goals. Formal learning outcomes are typically validated through certifications, enhancing career advancement and academic progression.
Recognition and Accreditation Challenges
Recognition and accreditation challenges in non-formal learning often stem from the absence of standardized certification, making it difficult for learners to prove their skills to employers and institutions. Formal learning systems typically rely on accredited qualifications, which are universally accepted and facilitate career progression. Bridging the gap requires establishing robust frameworks for assessing and validating non-formal learning outcomes to enhance credibility and recognition in the adult education sector.
Role of Assessment in Different Learning Contexts
Assessment in formal learning environments typically involves standardized tests and graded evaluations that measure learner outcomes against predefined criteria, ensuring accountability and credentialing. In contrast, non-formal learning emphasizes formative assessment methods such as self-reflection, peer feedback, and practical demonstrations, which support personalized growth and skill development without rigid grading structures. The distinct roles of assessment reflect the different goals of each context: formal settings prioritize certification and benchmark achievement, while non-formal settings foster adaptability and lifelong learning through flexible, learner-centered evaluation.
Accessibility and Inclusiveness for Adults
Non-formal learning offers greater accessibility for adults by providing flexible schedules, diverse formats, and minimal entry barriers compared to formal learning's structured curriculum and admission requirements. Inclusiveness in non-formal education is enhanced through community-based programs and culturally relevant content that accommodate varied learning needs and backgrounds. Formal learning institutions often struggle with inclusivity due to rigid policies and standardized assessments that may not address the diverse experiences of adult learners.
Impact on Personal and Professional Development
Non-formal learning significantly enhances personal and professional development by fostering practical skills and adaptability that formal education often overlooks. Unlike formal learning, which provides structured knowledge and recognized qualifications, non-formal learning encourages experiential learning and continuous self-improvement, directly influencing job performance and career progression. Incorporating non-formal learning opportunities results in a more versatile skill set, increased confidence, and greater capacity for innovation in professional environments.
Choosing the Right Learning Path for Adults
Selecting the right learning path for adults involves weighing the flexibility and personalized pace of non-formal learning against the structured curriculum and recognized certification of formal learning. Non-formal learning offers practical skills through workshops, online courses, and community programs, ideal for immediate application and career shifts. Formal learning provides comprehensive knowledge and accredited qualifications essential for professions requiring certification or advanced expertise.
Non-formal Learning vs Formal Learning Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com