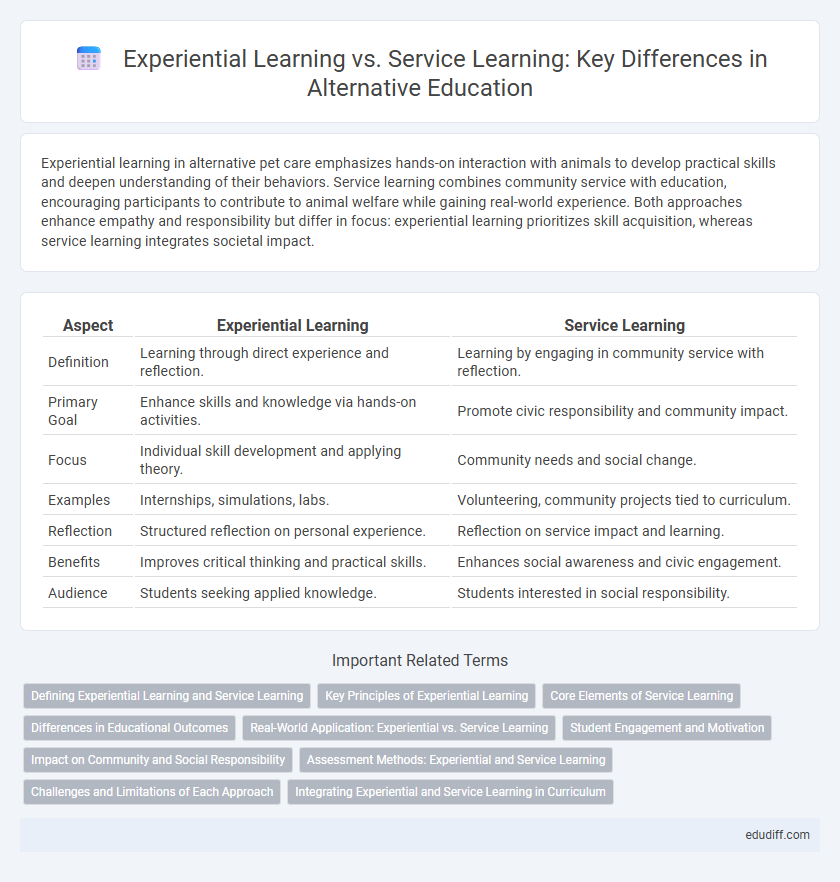
Experiential learning in alternative pet care emphasizes hands-on interaction with animals to develop practical skills and deepen understanding of their behaviors. Service learning combines community service with education, encouraging participants to contribute to animal welfare while gaining real-world experience. Both approaches enhance empathy and responsibility but differ in focus: experiential learning prioritizes skill acquisition, whereas service learning integrates societal impact.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Experiential Learning | Service Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through direct experience and reflection. | Learning by engaging in community service with reflection. |
| Primary Goal | Enhance skills and knowledge via hands-on activities. | Promote civic responsibility and community impact. |
| Focus | Individual skill development and applying theory. | Community needs and social change. |
| Examples | Internships, simulations, labs. | Volunteering, community projects tied to curriculum. |
| Reflection | Structured reflection on personal experience. | Reflection on service impact and learning. |
| Benefits | Improves critical thinking and practical skills. | Enhances social awareness and civic engagement. |
| Audience | Students seeking applied knowledge. | Students interested in social responsibility. |
Defining Experiential Learning and Service Learning
Experiential learning involves acquiring knowledge through direct experience and reflection, emphasizing active participation in real-world tasks. Service learning integrates meaningful community service with instruction and reflection, aiming to enhance both academic learning and civic responsibility. Both approaches prioritize hands-on engagement but differ in their focus: experiential learning centers on personal skill development, while service learning focuses on social impact and community involvement.
Key Principles of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning emphasizes active participation, reflection, and real-world application to deepen understanding and develop critical skills. Key principles include learning through direct experience, fostering learner autonomy, and promoting continuous feedback to enhance personal and professional growth. This approach contrasts with service learning by prioritizing individual cognitive engagement over community service objectives.
Core Elements of Service Learning
Service learning integrates community service with structured reflection, emphasizing collaboration, reciprocity, and civic responsibility as core elements. It differs from experiential learning by intentionally linking academic content to meaningful community engagement, fostering both personal growth and social impact. These foundational components ensure that service learning promotes active citizenship and deepens students' understanding of societal needs.
Differences in Educational Outcomes
Experiential learning emphasizes hands-on activities that develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and self-reflection skills, fostering deeper understanding and retention of knowledge. Service learning integrates community service with academic curriculum, promoting civic responsibility, social awareness, and ethical development alongside educational proficiency. These distinct approaches yield unique educational outcomes, with experiential learning enhancing personal and cognitive growth, while service learning strengthens social engagement and community impact.
Real-World Application: Experiential vs. Service Learning
Experiential learning emphasizes hands-on activities that simulate real-world challenges, enhancing problem-solving and critical thinking skills through direct engagement. Service learning integrates community service with academic curriculum, fostering social responsibility while applying knowledge to tangible societal issues. Both methods deepen understanding by connecting academic concepts with practical, real-life experiences.
Student Engagement and Motivation
Experiential learning significantly enhances student engagement by immersing learners in real-world scenarios that foster active participation and critical thinking. Service learning integrates community service with academic objectives, increasing motivation through meaningful connections between coursework and societal impact. Both approaches cultivate deeper commitment and intrinsic motivation by linking theory with practical application and social responsibility.
Impact on Community and Social Responsibility
Experiential learning immerses students in real-world challenges, fostering critical thinking and practical skills while promoting individual growth. Service learning integrates community service with academic objectives, directly addressing local needs and enhancing social responsibility among participants. Both methodologies cultivate a deeper commitment to community impact, with service learning emphasizing reciprocal benefits and sustained engagement in social issues.
Assessment Methods: Experiential and Service Learning
Experiential learning assessment methods emphasize reflective journals, portfolio reviews, and real-time skill demonstrations to capture hands-on engagement and personal growth. Service learning assessment incorporates community feedback, impact evaluations, and collaborative project reports to measure social responsibility and civic engagement outcomes. Both approaches utilize qualitative and quantitative data to ensure comprehensive evaluation of learning objectives and practical application.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Experiential learning faces challenges such as limited scalability and potential lack of structure, which can hinder consistent skill development across diverse learners. Service learning encounters limitations including the risk of short-term community impact and power imbalances between students and service recipients. Both approaches require careful planning to address resource constraints and ensure meaningful, ethical engagement.
Integrating Experiential and Service Learning in Curriculum
Integrating experiential learning and service learning in the curriculum enhances student engagement by combining hands-on activities with community-based projects that promote real-world problem solving and civic responsibility. Curricula that incorporate both methods support the development of critical thinking, collaboration, and reflective skills through structured experiences aligned with academic objectives. Educational programs prioritizing this integration report improved student outcomes, including increased motivation, social awareness, and deeper understanding of subject matter.
Experiential Learning vs Service Learning Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com