Flipped classroom models enhance distance learning for pets by allowing owners to access instructional videos and materials at their convenience, fostering a more personalized and consistent training environment. Live lectures offer real-time interaction, enabling immediate feedback and adjustments to training techniques based on the pet's behavior and response. Both approaches improve engagement and effectiveness, with flipped classrooms providing flexibility and live lectures promoting dynamic communication.
Table of Comparison
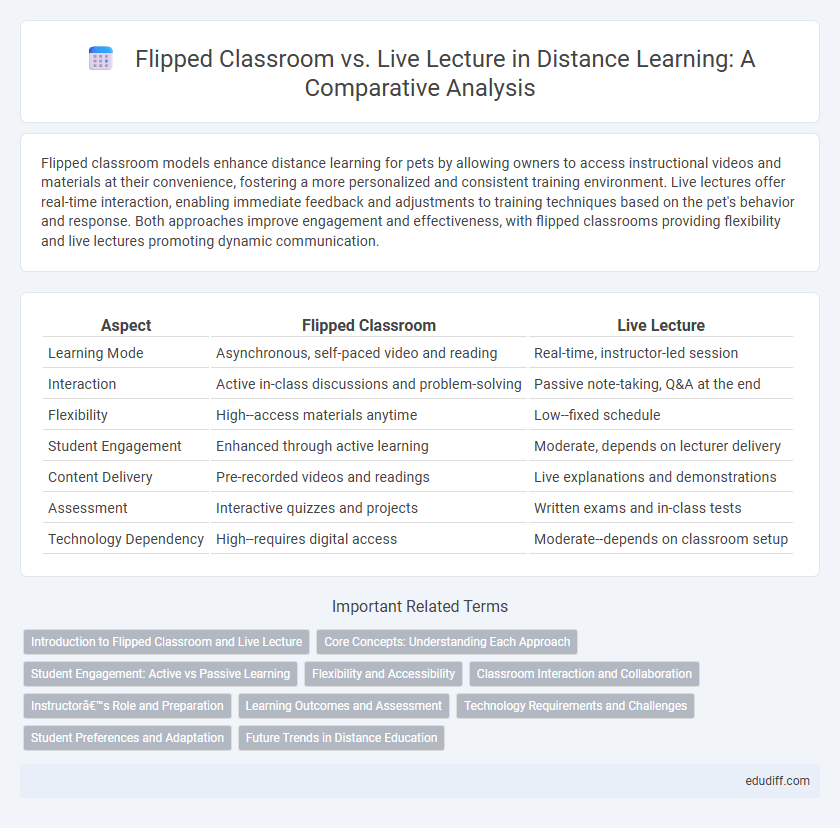
| Aspect | Flipped Classroom | Live Lecture |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Mode | Asynchronous, self-paced video and reading | Real-time, instructor-led session |
| Interaction | Active in-class discussions and problem-solving | Passive note-taking, Q&A at the end |
| Flexibility | High--access materials anytime | Low--fixed schedule |
| Student Engagement | Enhanced through active learning | Moderate, depends on lecturer delivery |
| Content Delivery | Pre-recorded videos and readings | Live explanations and demonstrations |
| Assessment | Interactive quizzes and projects | Written exams and in-class tests |
| Technology Dependency | High--requires digital access | Moderate--depends on classroom setup |
Introduction to Flipped Classroom and Live Lecture
The flipped classroom reverses traditional teaching by delivering instructional content, often online, outside of class, allowing in-person time for interactive activities and personalized support. Live lectures involve real-time, synchronous instruction where the teacher presents material directly to students, facilitating immediate feedback and engagement. Each method leverages different aspects of distance education to enhance learning flexibility and interaction.
Core Concepts: Understanding Each Approach
Flipped classrooms emphasize active learning by having students review core concepts through pre-recorded videos or reading materials before class, allowing interactive problem-solving during sessions. Live lectures focus on real-time delivery of foundational knowledge with immediate instructor feedback, fostering direct engagement and clarification. Both approaches aim to enhance comprehension but differ in pacing and student autonomy, impacting distance education strategies.
Student Engagement: Active vs Passive Learning
Flipped classrooms enhance student engagement by promoting active learning through pre-class video lessons and in-class interactive activities, resulting in higher retention and critical thinking skills. Live lectures often foster passive learning where students primarily listen and take notes, which can limit participation and immediate feedback. Research indicates that students in flipped classrooms demonstrate increased motivation and collaboration compared to traditional live lecture settings.
Flexibility and Accessibility
Flipped classrooms offer enhanced flexibility by allowing students to access lecture materials anytime and review content at their own pace, accommodating diverse schedules and learning speeds. Live lectures provide real-time interaction but require students to adhere to fixed times, which can limit accessibility for those with conflicting commitments or time zone differences. This flexibility in flipped classrooms supports better accessibility for distance learners, fostering inclusive education beyond traditional classroom constraints.
Classroom Interaction and Collaboration
Flipped classrooms enhance classroom interaction by shifting lecture content outside of class, allowing more time for active collaboration and peer-to-peer engagement during in-person sessions. Live lectures often limit interactive opportunities as instructors primarily deliver information, reducing student involvement and real-time discussion. Empirical studies show increased student participation and higher-order thinking skills development in flipped models due to structured collaborative activities.
Instructor’s Role and Preparation
In a flipped classroom, the instructor's role shifts from delivering lectures to facilitating active learning, requiring extensive preparation of digital content and interactive activities. Live lectures demand real-time engagement and adaptability, with instructors focusing on clear delivery and immediate feedback. Effective preparation in both formats enhances student understanding by aligning teaching strategies with the learning environment.
Learning Outcomes and Assessment
Flipped classrooms enhance learning outcomes by promoting active engagement and allowing students to review lectures at their own pace, leading to deeper conceptual understanding and improved retention. Assessment in flipped models often emphasizes application-based tasks and formative feedback, enabling personalized progress tracking and skill development. Live lectures, while facilitating real-time interaction, may result in passive learning, with assessments typically focused on summative evaluations that may not fully capture individual comprehension or practical skills.
Technology Requirements and Challenges
Flipped classrooms require reliable internet access, video recording equipment, and interactive platforms to enable students to engage with content asynchronously, posing challenges in ensuring all learners have equal technological resources. Live lectures depend on stable streaming technology and real-time communication tools, often facing difficulties with bandwidth limitations and audio-visual synchronization. Both models demand robust technical support and digital literacy from students and educators to overcome access disparities and maintain effective learning environments.
Student Preferences and Adaptation
Student preferences in distance education lean increasingly toward flipped classrooms due to their flexibility and active learning opportunities, which foster deeper engagement with the material. Adaptation to flipped classrooms involves developing self-regulation skills, time management, and digital literacy, essential for maximizing learning outcomes. Live lectures remain favored by students who benefit from real-time interaction and immediate clarification, although they may struggle with fixed schedules and reduced personalization.
Future Trends in Distance Education
Flipped classrooms and live lectures represent evolving paradigms in distance education, with future trends emphasizing increased interactivity, personalized learning, and advanced technology integration such as AI-driven analytics and virtual reality. The flipped classroom model improves learner engagement by allowing students to absorb content asynchronously before applying knowledge during synchronous sessions, while live lectures continue to provide real-time interaction and immediate feedback. Emerging trends point toward hybrid solutions that leverage the strengths of both approaches to enhance accessibility and learning outcomes in global distance education environments.
Flipped classroom vs Live lecture Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com