Telepresence classrooms allow students to interact with teachers and classmates in real time through video and audio technology, creating a more natural and engaging learning environment. Virtual reality classrooms immerse students in a fully digital space, offering interactive simulations and 3D experiences that enhance understanding and retention. Both methods support distance learning but prioritize different levels of engagement and technological complexity.
Table of Comparison
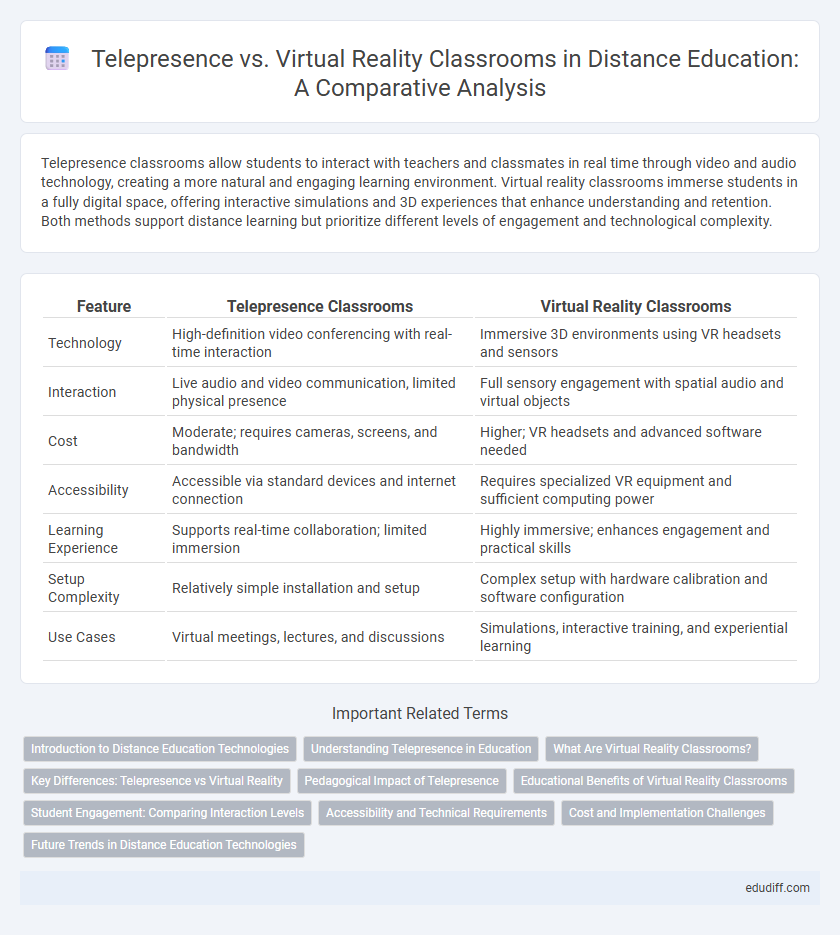
| Feature | Telepresence Classrooms | Virtual Reality Classrooms |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | High-definition video conferencing with real-time interaction | Immersive 3D environments using VR headsets and sensors |
| Interaction | Live audio and video communication, limited physical presence | Full sensory engagement with spatial audio and virtual objects |
| Cost | Moderate; requires cameras, screens, and bandwidth | Higher; VR headsets and advanced software needed |
| Accessibility | Accessible via standard devices and internet connection | Requires specialized VR equipment and sufficient computing power |
| Learning Experience | Supports real-time collaboration; limited immersion | Highly immersive; enhances engagement and practical skills |
| Setup Complexity | Relatively simple installation and setup | Complex setup with hardware calibration and software configuration |
| Use Cases | Virtual meetings, lectures, and discussions | Simulations, interactive training, and experiential learning |
Introduction to Distance Education Technologies
Telepresence technology enables real-time, immersive communication by projecting lifelike representations of remote participants, enhancing engagement in distance education classrooms. Virtual reality classrooms create fully simulated environments where students interact with digital objects and peers, offering experiential learning beyond traditional video conferencing. Both tools leverage advanced distance education technologies to bridge geographical gaps and foster interactive, collaborative learning experiences.
Understanding Telepresence in Education
Telepresence in education enables real-time, high-definition interaction between students and instructors across distant locations, creating a sense of physical presence through advanced audio-visual technology. Unlike virtual reality classrooms that immerse users in entirely simulated environments, telepresence relies on live video feeds and spatial audio to foster authentic communication and collaborative learning. This technology supports remote learning by reducing the barriers of distance, allowing for synchronous participation and enhancing engagement through realistic, immediate interaction.
What Are Virtual Reality Classrooms?
Virtual Reality Classrooms utilize immersive 3D environments to simulate real-life learning spaces, allowing students to interact with digital objects and peers as if physically present. These classrooms leverage VR headsets and haptic feedback to enhance engagement and improve knowledge retention in remote education settings. By combining spatial audio and interactive avatars, VR classrooms create realistic, collaborative experiences surpassing traditional video-based distance learning methods.
Key Differences: Telepresence vs Virtual Reality
Telepresence classrooms leverage real-time video and audio technology to create an immersive environment where participants can interact as if physically present, emphasizing synchronous communication and enhanced spatial presence. Virtual reality classrooms utilize fully immersive 3D environments powered by VR headsets, enabling users to explore virtual spaces, manipulate objects, and experience simulated scenarios beyond physical constraints. Key differences include telepresence's reliance on live video feeds for realism versus virtual reality's capability for interactive, computer-generated environments that offer greater freedom and engagement in educational content.
Pedagogical Impact of Telepresence
Telepresence classrooms enhance pedagogical outcomes by creating immersive real-time interactions that replicate physical presence, fostering higher student engagement and collaboration. Studies show telepresence technology reduces communication latency and non-verbal cue loss compared to traditional video conferencing, improving comprehension and participation. This approach supports diverse learning styles by integrating synchronous audio-visual cues, which virtual reality classrooms often lack due to hardware and software constraints.
Educational Benefits of Virtual Reality Classrooms
Virtual Reality classrooms enhance educational experiences by immersing students in interactive 3D environments, which improve engagement and retention through experiential learning. These immersive settings enable realistic simulations and visualizations that support complex subject matter comprehension, such as anatomy or engineering. VR classrooms also facilitate personalized learning paths and instant feedback, making education more adaptive and accessible for diverse student needs.
Student Engagement: Comparing Interaction Levels
Telepresence classrooms utilize real-time video and audio to create immersive, face-to-face interaction, enhancing student engagement through direct communication and natural social cues. Virtual reality classrooms employ 3D avatars and simulated environments, fostering interactive experiences that can boost motivation and participation by providing a sense of presence. Studies indicate telepresence often leads to higher sustained attention, while VR environments may increase engagement through gamification and sensory immersion.
Accessibility and Technical Requirements
Telepresence classrooms offer higher accessibility by utilizing standard video conferencing tools compatible with most devices and internet connections, reducing entry barriers for students. Virtual reality classrooms require specialized VR headsets and advanced hardware, posing technical challenges and limiting accessibility for users without sufficient resources. Bandwidth demands for telepresence are typically lower, making them more feasible in regions with limited internet infrastructure compared to VR environments.
Cost and Implementation Challenges
Telepresence classrooms often require high-cost specialized equipment and stable high-bandwidth internet, leading to substantial initial investment and ongoing maintenance expenses. Virtual reality classrooms, while also demanding significant upfront costs for VR headsets and compatible hardware, face added challenges related to software development, user accessibility, and motion sickness issues. Both technologies face implementation hurdles such as ensuring seamless user experience and addressing technical support needs, but telepresence systems may incur higher costs due to physical infrastructure requirements.
Future Trends in Distance Education Technologies
Telepresence technology offers immersive real-time interaction by replicating physical presence, enhancing collaboration in distance education. Virtual reality classrooms provide fully immersive environments that simulate real-world or imaginative settings, fostering experiential learning and engagement. Future trends indicate increasing integration of AI-driven personalization and mixed reality, combining telepresence and VR to create adaptable, interactive distance education experiences.
Telepresence vs Virtual Reality Classrooms Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com