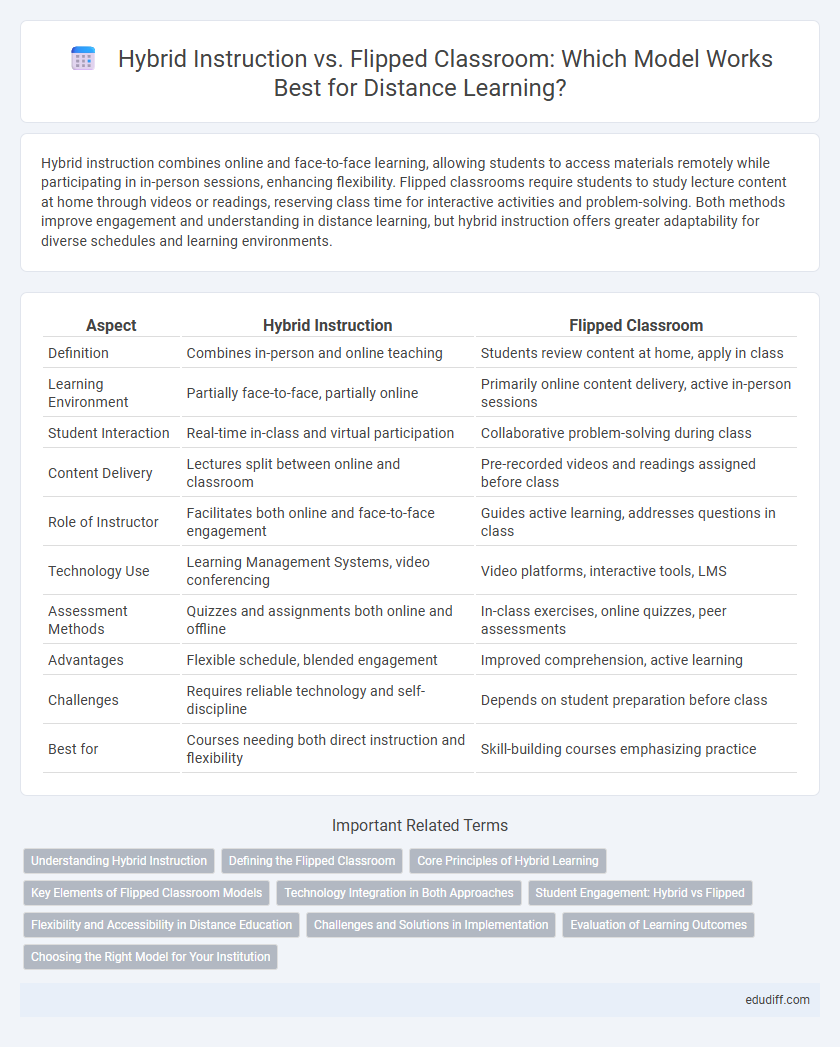
Hybrid instruction combines online and face-to-face learning, allowing students to access materials remotely while participating in in-person sessions, enhancing flexibility. Flipped classrooms require students to study lecture content at home through videos or readings, reserving class time for interactive activities and problem-solving. Both methods improve engagement and understanding in distance learning, but hybrid instruction offers greater adaptability for diverse schedules and learning environments.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Hybrid Instruction | Flipped Classroom |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines in-person and online teaching | Students review content at home, apply in class |
| Learning Environment | Partially face-to-face, partially online | Primarily online content delivery, active in-person sessions |
| Student Interaction | Real-time in-class and virtual participation | Collaborative problem-solving during class |
| Content Delivery | Lectures split between online and classroom | Pre-recorded videos and readings assigned before class |
| Role of Instructor | Facilitates both online and face-to-face engagement | Guides active learning, addresses questions in class |
| Technology Use | Learning Management Systems, video conferencing | Video platforms, interactive tools, LMS |
| Assessment Methods | Quizzes and assignments both online and offline | In-class exercises, online quizzes, peer assessments |
| Advantages | Flexible schedule, blended engagement | Improved comprehension, active learning |
| Challenges | Requires reliable technology and self-discipline | Depends on student preparation before class |
| Best for | Courses needing both direct instruction and flexibility | Skill-building courses emphasizing practice |
Understanding Hybrid Instruction
Hybrid instruction blends in-person and online learning modalities to create a flexible educational environment accommodating diverse student needs. This approach leverages synchronous and asynchronous components to enhance engagement and accessibility while maintaining the structure of traditional classrooms. Understanding hybrid instruction involves recognizing its capacity to facilitate real-time interaction alongside self-paced study, optimizing distance learning effectiveness.
Defining the Flipped Classroom
The flipped classroom is an instructional strategy that reverses traditional learning by delivering instructional content, often online, outside of the classroom while moving activities, including homework, into the classroom. This approach enhances student engagement and allows for personalized instruction during class time. Hybrid instruction combines online and face-to-face learning but does not necessarily require content to be pre-learned, making the flipped classroom a distinct subset focused on pre-class content absorption.
Core Principles of Hybrid Learning
Hybrid instruction combines in-person and online teaching to enhance flexibility and student engagement, emphasizing personalized learning paths and real-time feedback. Central to hybrid learning are core principles such as integrating synchronous and asynchronous activities, fostering collaboration, and leveraging technology for seamless content delivery. This model prioritizes accessibility while maintaining structured interactions to support diverse learner needs.
Key Elements of Flipped Classroom Models
Flipped classroom models prioritize active learning by delivering instructional content outside of traditional class time, often through video lectures and online resources, allowing in-class sessions to focus on interactive exercises and personalized support. Key elements include pre-class preparation, student-centered activities, and formative assessments that promote engagement and deeper understanding. This contrasts with hybrid instruction, which blends online and face-to-face teaching but may not inherently emphasize the student-driven, preparatory nature central to flipped classrooms.
Technology Integration in Both Approaches
Hybrid instruction combines synchronous online sessions with face-to-face learning, leveraging platforms like Zoom and Moodle to facilitate seamless interaction and resource sharing. Flipped classroom emphasizes pre-class video lectures and interactive activities during class time, utilizing tools such as Edpuzzle and Kahoot to enhance student engagement and comprehension. Both approaches integrate digital technology to support flexible, personalized learning experiences that optimize student participation and content mastery.
Student Engagement: Hybrid vs Flipped
Hybrid instruction combines online and face-to-face learning, offering diverse interaction modes that enhance student engagement through flexibility and real-time feedback. Flipped classroom models prioritize active learning by having students review materials independently before class, fostering deeper participation during in-person sessions. Research indicates that the flipped approach increases cognitive engagement and collaboration, while hybrid instruction supports sustained motivation by accommodating varied learning preferences.
Flexibility and Accessibility in Distance Education
Hybrid instruction enhances flexibility by combining online and face-to-face learning, allowing students to access course materials anytime, anywhere. Flipped classrooms increase accessibility by providing pre-recorded lectures that students can review at their own pace, supporting diverse learning styles. Both models improve engagement and accommodate varying schedules, making distance education more adaptable and inclusive.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementation
Hybrid instruction faces challenges such as technology access disparities and scheduling conflicts, which can be mitigated by investing in reliable digital infrastructure and flexible course designs. Flipped classrooms encounter difficulties in ensuring student motivation and managing asynchronous content, addressed through interactive engagement tools and continuous formative assessment. Both models require comprehensive training for educators to effectively blend in-person and online elements while maintaining quality learning outcomes.
Evaluation of Learning Outcomes
Hybrid instruction combines online and face-to-face learning environments, allowing for diverse evaluation methods such as digital quizzes and in-person assessments to measure student performance effectively. Flipped classrooms emphasize pre-class content engagement with in-depth active learning during class, enhancing comprehension and critical thinking, which can be evaluated through project-based assessments and real-time feedback. Studies indicate that both models improve learning outcomes, but flipped classrooms often yield higher retention rates due to their interactive and student-centered evaluation approaches.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Institution
Choosing the right model between hybrid instruction and a flipped classroom depends on your institution's technological infrastructure, faculty readiness, and student engagement levels. Hybrid instruction offers flexibility by combining in-person and online learning, ideal for institutions with diverse student needs and resources. Flipped classrooms emphasize active learning by delivering content online before class, requiring strong digital access and self-motivated students for effective implementation.
Hybrid instruction vs Flipped classroom Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com