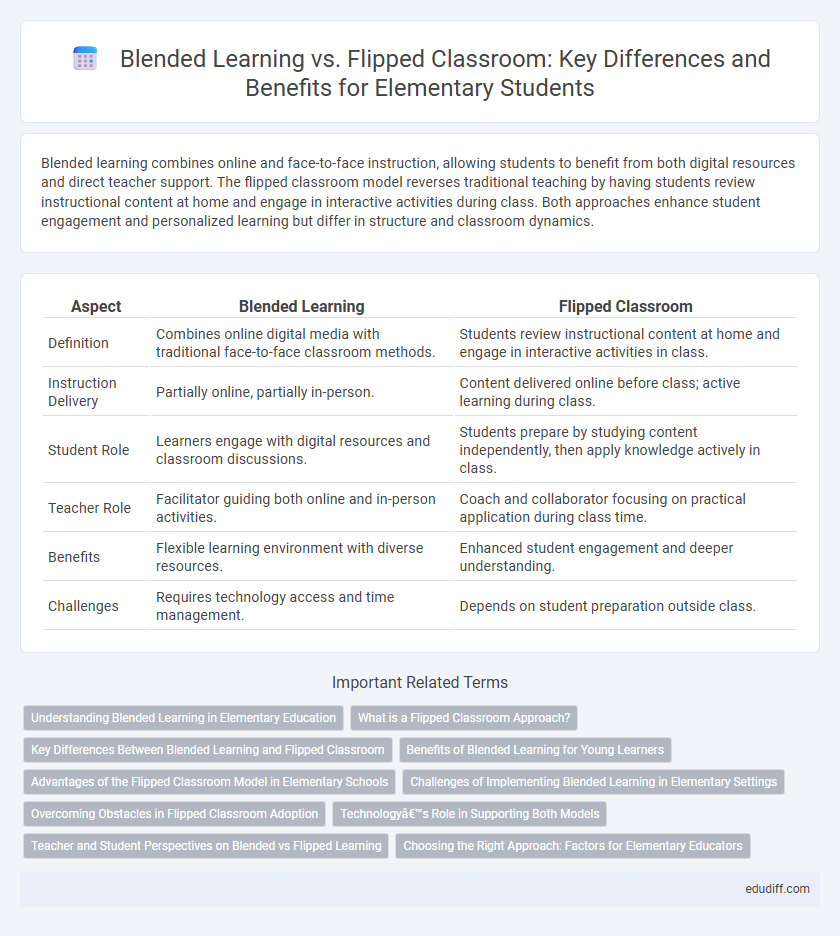
Blended learning combines online and face-to-face instruction, allowing students to benefit from both digital resources and direct teacher support. The flipped classroom model reverses traditional teaching by having students review instructional content at home and engage in interactive activities during class. Both approaches enhance student engagement and personalized learning but differ in structure and classroom dynamics.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Blended Learning | Flipped Classroom |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines online digital media with traditional face-to-face classroom methods. | Students review instructional content at home and engage in interactive activities in class. |
| Instruction Delivery | Partially online, partially in-person. | Content delivered online before class; active learning during class. |
| Student Role | Learners engage with digital resources and classroom discussions. | Students prepare by studying content independently, then apply knowledge actively in class. |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator guiding both online and in-person activities. | Coach and collaborator focusing on practical application during class time. |
| Benefits | Flexible learning environment with diverse resources. | Enhanced student engagement and deeper understanding. |
| Challenges | Requires technology access and time management. | Depends on student preparation outside class. |
Understanding Blended Learning in Elementary Education
Blended learning in elementary education integrates face-to-face instruction with digital tools, allowing students to engage with interactive content at their own pace. This approach enhances personalized learning by combining traditional classroom methods with online resources, promoting improved student engagement and comprehension. Teachers can tailor lessons to meet diverse learning needs, fostering a more flexible and effective educational environment for young learners.
What is a Flipped Classroom Approach?
The flipped classroom approach reverses traditional teaching by delivering instructional content outside of class, often through videos or online modules, allowing in-class time for interactive activities and personalized support. This model fosters active learning, critical thinking, and student engagement by shifting homework to the classroom and lectures to home study. Research shows flipped classrooms can improve student understanding and retention, especially in elementary education.
Key Differences Between Blended Learning and Flipped Classroom
Blended learning combines traditional face-to-face instruction with online activities, allowing for varied learning environments and flexible pacing. Flipped classroom reverses conventional teaching by delivering instructional content online before class, reserving in-person time for interactive, hands-on exercises. The key difference lies in the structure: blended learning integrates online and offline methods throughout the course, while flipped classroom specifically flips the timing of content delivery and practice.
Benefits of Blended Learning for Young Learners
Blended learning enhances young learners' engagement by combining face-to-face instruction with digital tools, fostering personalized learning experiences tailored to individual needs. It supports skill development in technology use while maintaining direct interaction with teachers, promoting a balanced educational environment. This approach also allows flexible pacing, helping students grasp concepts thoroughly and boosting retention through varied learning modalities.
Advantages of the Flipped Classroom Model in Elementary Schools
The flipped classroom model enhances student engagement in elementary schools by allowing learners to access instructional content at their own pace outside of class, fostering better comprehension. It promotes active, hands-on learning during classroom time, enabling teachers to provide personalized support and address individual student needs more effectively. This approach also encourages the development of critical thinking and collaboration skills among young students, boosting overall academic performance.
Challenges of Implementing Blended Learning in Elementary Settings
Implementing blended learning in elementary settings faces challenges such as limited access to technology, varying levels of digital literacy among young students, and the need for teacher training to effectively manage both online and face-to-face instruction. Maintaining student engagement during online segments can be difficult, especially for younger children who require more interactive and hands-on activities. Ensuring equity and consistent internet access at home also poses significant obstacles for successful blended learning implementation in elementary schools.
Overcoming Obstacles in Flipped Classroom Adoption
Teachers implementing flipped classrooms often face challenges such as limited student access to technology and varying levels of digital literacy among elementary students. Overcoming these obstacles requires providing offline resources and offering training sessions for both students and parents to build digital skills. Schools can support this transition by ensuring equitable technology access and fostering collaboration between educators and families to reinforce learning at home.
Technology’s Role in Supporting Both Models
Technology enables seamless integration of digital tools in both blended learning and flipped classroom models, enhancing interactive experiences and personalized instruction. Educational platforms, multimedia content, and real-time assessment tools foster student engagement and support differentiated learning pathways. Access to online resources and collaboration technologies empowers teachers to effectively manage instruction and track progress in elementary classrooms.
Teacher and Student Perspectives on Blended vs Flipped Learning
Blended learning combines online digital media with traditional classroom methods, allowing teachers to customize instruction and provide students with flexible, self-paced learning opportunities. From the teacher's perspective, blended learning facilitates differentiated instruction and ongoing assessment, while students benefit from direct teacher support alongside independent study. In contrast, flipped classrooms require students to engage with instructional content at home, freeing up class time for interactive, hands-on activities, which teachers find enhances student engagement and allows for targeted intervention during class.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors for Elementary Educators
Elementary educators should consider student engagement levels and technology access when choosing between blended learning and flipped classrooms. Blended learning allows a mix of in-person and online activities, supporting diverse learning styles and providing flexibility. Flipped classrooms require students to review instructional content at home, promoting active in-class collaboration, but depend heavily on reliable home internet and parental support.
Blended Learning vs Flipped Classroom Infographic
 edudiff.com
edudiff.com